Lecture 28 In Class Flashcards
Posterior thigh, popliteal fossa. knee joint
What is another name for fibular?
Peroneal.
What are the muscles of hte posterior compartment of the knee?
What are their actions?
-
Hamstring Muscles
- semitendinosus
- Semimembranosus
- Biceps femoris
- Adductor Magnus
extensors of the hip, flexors of the knee
all originate on ischial tuberosity!!!
What are the roots for sciatic nerve?
What does it do?
- L4-S3
- Innervate muscles of poterior thigh
- Tibial part (most of them)
- semitendinosus
- semimenrbanosus
- lg head of biceps femoris
- hamstring part of add magnus

Semitendinosus (has a true tendon)
- ischial tuberosity–> medial tibia (with gracilis and sartoris)
- tibial sciatic (L4-S3)
- extend hip and flex knee
hamstring muscle
Posterior thigh muscle
What is the muscle to the left of the line?

Semimembranosus (looks like a tendon)
- ischial tuberosity –> medial tenondon condyl fibers refelct back up to fossa and become oblique tendon
- tibial part of sciatic (L4-S3)
- extend hip, flex knee
hamstring muscle
Posterior thigh muscle

Biceps Femoris Long Head
- ischial tuberosity–> head of fibula
- tibial part of sciatic nerve (L4-S3)
- extend hip, flex knee
Hamstring muscle
poterior thigh muscle
What muscle is this?
- What is its orgin and insertion?
- What is its innervation
- What is its actions?

Biceps Short head
- lateral lip of linea aspera–> ******head of fibula********
- common fibular part of scatitc (L4-S2)
- flex knee
- only one that does not extend the hip
Hamstring muscle
posterior thigh muscle
What muscle is this?
- What is is Orgin/ insertion?
- What is its innervation
- What is its actions?

Adductor magnus (hamstring head)
- ischial tuberosity–>adductor tuberical of femor
- tibial part of sciatic nerve (L4-S3)
- extend the hip
Most of the floor of the posterior thigh
Hamstring muscle
posterior compartment of the thigh
What is pes anserinus?
What is another name for it?
- conjointed tendon of:
- sartorius m
- Gracilis
- semitendinosus
- anteromedial tibial

what are the attachments for these places

- addcutor tubericle: adductor magnus hamstring part
on medial side from top to bottom,
gracilis
semitendenosis
sartouris
What is the blood supply of the posterior thigh?
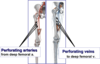
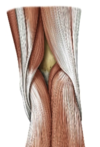
What are the boundreis of the popliteal fossa?
Where is it located?
-
Sup-med:
- semimembranosus
- semitendiosus
- Sup-lat
3.biceps femoris
-
Inf-med
4. medial head of gastrocnemius -
Inf-lat
5. lat head of gastrocnemius
6. plantaris
POSTERIOR FEMUR
-
Roof
-
popliteal fascia
- poterior femoral cutaneus
- medial and lateral sural nn.
- (f/ tibial {medial}
- common fibular nerve {lateral nerve}
- small saphenosus v –> popliteal v
-
popliteal fascia
-
Floor
- femur
- oblique popliteal lig f/ semitenenosis
- stabalize the knee
- popliteus
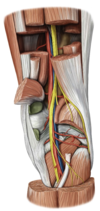
What are the contents of the popliteal fossa?
- tibial nerve (L4-S3)
- medial sural nerve
- popliteal vein
- small saphenous vein
- popliteal artery
- genicular anastomosis
- Common fibular nerve (L4-S2)
- lateral sural nerve
- What type of joint is the tibiofemoral joint?
- Articulations
- What does stibility depend on?
- modified hinge joint
- lateral/medial femoral condyly–> lateral/medial tibial plateau
- ligaments and surround muscles and tendons
Genu varum vrs. Genu Valgum
Genu Varum
- small Q angle bowleg
Genu Valgum
- Large Q angle Knock-Knee
- can increase potential for patellofemoral syndrome
Q angle: perpindicular line of gravity and asis line







