Lecture 27 (14-7-14) Flashcards
1
Q
What is the demarcation betweent the gluteus and thigh?
A
gluteal fold.
2
Q
Gluteal Dermatomes
A

3
Q
What are the cutanteous nerves of gluteal
A
- Superior L1-3 Dorsal Rami
- Middle S1-3 dorsal rami
- inferior cluneal ventral rami S2,S3

4
Q
What are the superficial gluteal muscles and what do they do?
A
Extensors and aBductors
all the glutes and tensor fasa lata

5
Q
Gluteus maximus
A
- illium, sacrum, coccyx, sacrotuberous lig–> gluteal tuberosity of femor and illiotibial track
- inferior gluteal nerve L5-S2
- actions
- forceful extension of hte hip
- external rotation of extended thigh
- stabilixe the exteneded knee

6
Q
Gluteus Medius
A
- Lateral side of illium–> grater trochanter
- Superior gluteal nerve L4-S1
- actions
- abduction of hte hip
- internal rotate the thigh
- Level pelvis during walking

7
Q
Gluteus Minimis
A
- Inferior part of lateral illium–>greater trochanter
- Superior gluteal nerve.
- actions
- Abduct the hip
- internal rotate the thigh
- level pelvic during walking

8
Q
What is gerdies tubericle
A

9
Q
Tensor Fascia Lata
A
- ASIS, iliac crest–> IT tract, gerdys tubercle
- Superior gluteal n L4-S1
- actions
- abduction of the hip

10
Q
Superior Gluteal nerve injury
A
cannt contract os the the hip will pop up on one side
11
Q
A

12
Q
What are the deep Gluteal Muscles
A
EXXTERNAL HIP ROTATORS

13
Q
Piriformis Muscle
A
- –> greater trochanter
- Sacral plexus S1, S2
- Lateral rotators of the thigh
a deep gluteal muscle

14
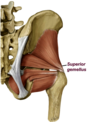
Q
Superior Gemellus Muscle
A
- ischial spine–> medial side greater trochanter
- N. to obturator internus
- Lateral hip rotation
a deep gluteal muscle
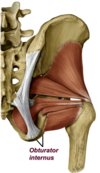
15
Q
Obturator internus
A
- obturator foramne, membrane on medial side–> out through foramen, 90 degree angle–> out lesser sciatic–> greater trochanter
- N. to obturator internus (L5, S1, S2)
- same nerve roots and inferior gluteal nerve
- External thigh rotation
deep gluteal muscle