Lecture 24 (7-7-14) Flashcards
1.Detail all the musculature of the internal pelvis 2. Describe the perineum and the location of the Urogenital Diaphragm 3. Discuss the external genitalia and the descent of the testicles as well as the layers of the spermatic cord 4. Define the fascial layers of the perineum 5. Outline the contents of each layer of the perineum in detail 6. Describe the anal triangle 7. Introduce the branches of the pudendal nerve and vessels 8. Discuss some common clinical conditions of the perineum
What are the walls of the pelvic cavity and what does each one contain?
Lateral wall (1)
- “hip bones”
- Obturator m, n, a, v
Anterior walls (2)
- pubic bones and pubic symphasis
Posterior wall (3)
- sacrum and coccyx
- sacroiliac joints
- sacrial plexus
- periform plexus
Floor (4)
- pelvic diaphragm
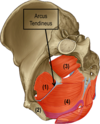
Obturator internus
- Medial surface of obturator membrane–> leave true pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen –> (turn 90 degrees) freater trochanter of femur
- nerve to obturator internus (L5-S2)
- lateral/ external rotation of hip
**in lateral wall of the pelvis**
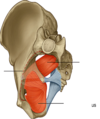
Piriformis
- leaves the pelivs through the greater sciatic formen–> insert on femur
- S1-S2
- external/ lateral rotation of the hip
bed for the nerves of the sacral plexus
posterial pelvic wall

- What does the pelvic floor do?
- What does it include on the bottom?
- what makes this up?
- sling that supports the abdominopelivic viscera. and it resist in intra-abdomincal pressure
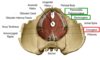
- Pelvic diaphragm
- Levator ani muscles (green)
- puborectalis
- pubococcygeus
- iliococcygeus
- coccygeus aka ischiococcygeus (Red)
- Levator ani muscles (green)
What structers enter/ leave the pelvis at these levels?
- Above the piriformis
- Below the piriformis
- Greater sciatic foramen
- Lesser foramen
- Above: superior gluteal n & a
-
Below:
- inferior gluteal n & a
- sciatic nerve
- Pudendal n
- internal pudendal artery
-
Out Greater sciatic foramen
- obturator muscle tendon
- pudendal veins
-
Back in lesser sciatic foramen
- pudendal n
- interal pudendal a

- What does the urogenital diaphragm contain?
- Where is it?
- What does it do?
- nerves, arterise, and glands for the external genitailia
- below the inferor border on teh pelvic diagphrams muscles
- seperates perineum into superfical and deep pouches.
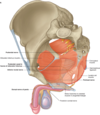
What is the the fascia around the testie?
Tunica albuginea
What seperates the urogential triangle into the superfical and deep pouches?
Perineal membrane

What are the contents of the superficial perineal space
- Bulbospongious muscles
- ischiocavernous muscles
- Perineal membrane
- Pelvic diapgragh (levator ani muscles)
- inferior surface of the pelvic diaphragm
- Superficial transverse pernieal muscle
- Colle’s fascia (superficial perineal fascia)
- suspensory ligament of clitoris/ penis
- external anal sphincter
Finish this after more studying!

What are the contents of the Deep perineal pouch?
- sphincter urethra m
- sphincter urethrovaginalis
- deep transverse perineal muscles
- compressor urethrae
- opening for vagin
- opening for urethra
bold= only in females

What is in the superficial perineal pouch in males?
- 2 corpora cavernosm
- corpus spongiosum
- ischiocavermosus muscles
- Bulbospongiosus m.
- perineal membrane
- crus of penis
- bulb
What are the contents of the deep male perineal pouch?
- perineal membrane
- cowpers glands
- external urethral spincter
- deep transverse perineal m.


