Lecture 12 Part 1 - Strain Gauges Flashcards
(10 cards)
Derive elastic deformation equation (dA/A) for a conductor with the following perameters
Length, l, m
Area, A, m2
specific resistance, p (row)
Resistance R = pl/A
N.B. All terms can vary

What is the equation for the resistance of a conductor?
Variables
Length, l, m
Area, A, m2
Specific Resistance, p
Resistance = pl/A
Using an Equation give a definition of strain sensativity
Explain the terms in the definition equation

What construction iterations have strain gages gone through?
Origionally unbonded wire filament with a bulky attatchment arrangement
- New wire filament gauge, bonded to surface using adhesive (Simmons and Ruge)
Present form
Thin film carrying a small strain-sensing element - includes tabs/terminals for lead connections

What is the procedure for attaching a gauge to a surface?
7 steps
- Rust, paint removed by sanding
- Solvents used to remove all traces of oil and grease
- Surface etched by a suitable acid
- Surface neutralised
- Gauge positioned using a rigid tape
- Adhesive applied, allowed to cure
- Cover to prevent environmental damage

What is the most important part of the strain gauge application process?
Why is it the most important part?
Adhesion is the most crucial step as the gauge needs to transmit the strain from the component and cannot do this without good adhesion?
What is the definition of Strain sensativity?
Use equations to express your answer, include axial and transvers strain
Exclude negligable terms

Wheatstone bridge
What is measured - include a labelled drawing of a wheatstone bridge
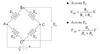
What is the output of a wheatstone bridge and what is it made up of?

Wheatstone Bridge
Show using equations how the change in output PD can be calculated if the resistances are varied




