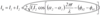2. Classical Interferometry Flashcards
(38 cards)
What are two popular models describing the nature of light?
Electromagnetic wave model (EM wave model) Quantum model
What are the basic principals of the EM wave model for describing the nature of light?
Light consists of energy in the form of EM waves EM disturbance propagates through space A wave is described by two vectors
What are the two vectors describing a wave in the EM wave model for describing the nature of light?
E - electric vector H - magnetic vector
What are some of the shortcomings of the EM wave model for describing the nature of light?
Predicts infinite energy for small wavelengths No clear expression for nature of light Doesn’t provide an explanation for some phenomena (e.g, photoemission)
What are the basic principals of the quantum model for describing the nature of light?
Light consists of ‘bundles’ or photons of energy Behavior of photons is described using statistical mechanics
When is EM wave theory applicable?
For long waves (wavelengths up to around 1m) For light waves (wavelengths between 1mm to 1nm)
When is the Quantum model applicable?
For light waves (wavelengths between 1mm to 1nm) For short waves (down to around 1A (0.1nm))
What is the application of long waves? (around 1m)
Long waves are radio waves
What is the application of light waves (1mm - 1nm)
Light waves range from infrared to UV
What is the application of short waves? (around 1A)
Short waves are x-rays
What are Maxwell’s Equations based upon?
Based on wave theory by Coulomb and Faraday Relies on 4 constitutive equations to lay out a set of rules defining interaction of electromagnetic waves with matter
What are the field parameters for Maxwell’s equations?
E, Electric vector H, Magnetic vector (E and H define EM field) D, Electric displacement vector J, Current density vector B, Magnetic induction vector (D,J and B are field quantities)
For a non conducting medium that is free of electric charge what must electric vector E satisfy?
ε is dielectric constant, µ is magnetic permeability, c is speed of light (or light wave)

For a harmonic plane wave propagating in the z-direction what is the equation for electric vector E?
A = amplitude of wave
v = c /√(ε µ ) = speed of propagation
λ = wavelength of light

Draw out a monochromatic, linarly polarised light wave undergoing simple harmonic vibration

What is Irradiance?
Time averaged square of amplitude, measureable by photo sensors

What is the frequency for any given wave?

What are the lhe wavelenths for the different catagories of light?

What is the generalised equation for a wave propagating along some axis in terms of the electric vector?
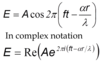
What is the unit position vector?
l, m and n are directional cosines

What is the general position vector?
l, m and n are directional cosines

What is the generalised equation for a wave propagating along the z axis with an added phase shift, in terms of the electric vector?
ϕ is a phase shift
ϕ and A can vary in the spatial domain
terms regarding time can be disgarded as the optical frequencies cannot be detected

What do the electric vecotor, E and Magnetic vector, H define?
The EM field
Draw out a warped wavefront?