Lecture 12: Oral and Nasal Cavities, Pharynx & Pterygopalatine Fossa Flashcards
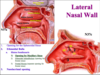
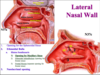
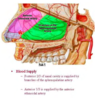
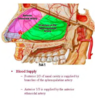
What is the major arterial supply to the posterior 2/3 of the nasal cavity?
-
Sphenopalatine artery, through its 2 major branches:
1) Posterior Lateral Nasal artery
2) Posterior Septal artery
Label this


The parotid duct pierces what muscle and drains into the mouth where?
- Pierces the Buccinator M.
- Drains into mouth opposite the crown of the 2nd upper molar

Which nerve is the Submandibular duct in close relationship to?
- The lingual nerve spirals around the submandibular duct from superior-lateral to inferior-medial
- Looking in floor out mouth the duct sits on top of the nerve

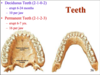
What is the dental formula for adults and how does it work?
In each set, incisors (I) are indicated first, canines (C) second, premolars (P) third, and finally molars (M), giving I:C:P:M.
- Formula 2-1-2-3 for upper teeth indicates 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars, and 3 molars on one side of the upper mouth
What is the dental formula for children’s (decidous) teeth?
- 2-1-0-2
- 2 incisors, 1 canine, 0 pre-molars, 2 molars on each side of the top and bottom
What provides the GSA and SVA fibers to the anterior 2/3 of tongue; and what is each of the nerves responsible for?
- Lingual nerve from Trigeminal (V): supplies the GSA fibers for pain, temp., touch
- Chorda Tympani from Facial (VII) supplies the SVA fibers for taste
*Chorda Tympani from Facial n. travels with the Lingual n. to the tongue

What supplies the GVA and SVA fibers to the posterior 1/3 of tongue?
Glossopharyngeal (IX) is responsible for both the GVA and SVA (taste) fibers.

The tonsillar fossa region of the tongue is innervated by what nerve?
- Glossopharyngeal (IX) nerve
- Arises from endoderm of 2nd pharyngeal arch
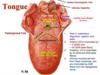
All the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue are innervated by; what is the one exception and its innervation?
- ALL tongue muscles = hypoglossal (CN XII)
- Except! Palatoglossus is innervated by CN X

Unilateral hypoglossal palsy results in what; which way does tongue deviate and why?
- Paralysis, atrophy, and fasciculations of the intrinsic muscles of tongue
- When protruded, the normal genioglossus deviates the tongue toward the affected side!
*BILATERAL paralysis may cause airway obstruction (dyspnea), dysarthria, and dysphagia

The tongue is supplied by which artery and branch?
Lingual artery and its terminal branch, the profunda lingual artery

Which vein drains the tongue and into where?
Lingual vein drans into IJV or facial vein

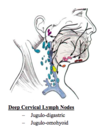
Lymphatics from the tongue primarily drain to where?
-
Deep Cervical LN’s:
1) Jugulodigastric
2) Jugulo-omohyoid
What is the innervation and action of Tensor Veli Palatini muscle?
- Innervated by small branch of Mandibular n. (V3)
- Tense the palate and opens the auditory tube (depressurizes middle ear)

What is the innervation and action of Levator Veli Palatini muscle?
- Innervated by CN X, pharyngeal plexus
- Elevates the soft palate

Paralysis of the Tensor Veli Palatini or Levator Veli Palatini muscles will lead to?
Muscles of the non-paralyzed side will pull or deviate the uvula TOWARD the normal side

What is the blood supply and innervation like to the palate, including hard and soft palate?
- Greater palatine nerve and artery supply hard palate
- Lesser palatine nerve and artery supply soft palate
- Nasopalatine nerve supplies anterior 1/3 of hard palate
*The greater and lesser palatine arteries are branches off the descending palatine artery, which is one of the last branches off the Maxillary artery!