Lecture 1: Ante- and Perinatal Pharm Flashcards
Describe the change in collagen fibers that occurs with cervical ripening?
- Phase 1: collagen fibers are well-organized and uniform-size
- Phase 2: fibril size is less uniform with more spacing between disorganized fibers to allow for ↑ in mechanical compliance of the cervix

What are the clinical indication for using the synthetic PGE1 analog, Misoprostol?
- Termination of intrautrine pregnancy if <70 days in combo w/ mifepristone
- NSAID-induced gastric ulcer prevention
List 4 off-label uses for Misoprostol?
- Cervical ripening
- Labor induction in pt without cervical dilation
- Incomplete abortion
- Post-partum hemorrhage

How do the pharmacokinetics of Misoprostol differ from Dinoprostone?
- Misoprostol = stable at room temp; oral w/ onset in 30 mins
- Dinoprostone = needs to be refrigerated and much more expensive
What are some of the maternal AE’s associated with oral administration of Misoprostol?
- N/V
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Chills + shivering
What are some of the maternal AE’s associated with intravaginal administration of Misoprostol?
- Uterine contractions occurring too rapidly
- Prolonged uterine contractions
- Uterine rupture

What is an AE associated with Dinoprostone when used during abortion?
Fever UNRESPONSIVE to NSAIDs

What is the MOA of Carboprost?
Synthetic prostaglandin F2α analog
What are the clinical indications for the prostaglandin F2α analog, Carboprost?
- Induce abortion by stimulating uterine contractions btw 10-30 wks, if failure of another for expulsion of fetus, premature rupture of membranes w/ previable fetus and inefficient activity
- Post-partum hemostasis for refractory bleeding

What is the route of administration for the prostaglandin F2α analog, Carboprost?
Must be given by deep IM injection
What are the contraindications for using the prostaglandin F2α analog, Carboprost?
- Hypersensitivity
- Acute PID
- Active cardiac, pulmonary, renal, or hepatic dysfunction
What are some of the major AE’s assoc. w/ the prostaglandin F2α analog, Carboprost?
- HTN and pulmonary edema since potent vasoconstrictor (unlike vasodilator PGE2)
- Chills/shivering but tends to reduce body temp (unlike PGE2)
- Perforated uterus or cervix + UTI’s + blurred vision + asthma

What are the clinical indications for using oxytocin?
- Induction of labor once cervix is dilated****
- Post-partum hemostasis for refractory bleeding****
How is oxytocin administered?
IV w/ infusion pump, requires careful monitoring
The use of oxytocin is contraindicated for the induction of labor in what 2 scenarios?
- If lungs are not mature
- Cervix is not ripe –> rupture
What is a maternal AE associated w/ oxytocin?
Water intoxication
Ergot alkaloids work by stimulating what 3 types of receptors?
- Adrenergic
- Dopaminergic
- Serotonergic
What are the effects of ergot alkaloids on both the uterus and the vasculature?
- Uterus = prolonged/tonic uterine contractions
- Vasculature = constricts aterioles and veins

What is the post-partum use of ergot alkaloids?
- Used to ↑ uterine tone + ↓ bleeding; given after delivery
- Second choice for limiting post-partum bleeding (oxytocin = 1st)

What are the significant AE’s associated with Ergot Alkaloids?
- IV results in HTN
- N/V and HA followed by convulsions and possibly death

Contraindications for the use of ergot alkaloids include what?
HTN and hypersensitivity
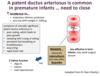
After birth the ductus arteriosus should close spontaneously within a few days due to what 2 factors?
- Construiction caused by ↑ oxygen tension
- ↓ circulating PGE2 due to its metabolism in lungs

What drug class does Alprostadil belong to, route of administration, and what is it used for?
- Synthetic PGE1 similar to misoprostol for parenteral administration
- Maintains PDA
What are the 2 indication for using Alprostadil in an infant?
- Pre-term infants w/ congenital heart defects –> allows them to mature sufficienctly to cope w surgery
- Heart defects –> used to maintain PDA to sustain pulmonary and systemic blood flow