Lect 12 Flashcards
lobar pneumonia
involvement of the entire lobe
what is PNA
inflammation of the lung parenchyma

causes of PNA in people with no known predisposing factors
- mycoplasma pneumoniae
- streptococcus pneumoniae
- chlamydophila pneumoniae
causes of PNA in alcoholics/vagrants
- streptococcus pneumonia
- klebsiella pneumoniae
causes of PNA in people with underlying disease
- streptococcus pneumoniae
- H. influenzae
- pseudomonas aeruginosa
- staph. aureus
causes of PNA in people with persons requiring ventilation
- klebsiella pneumoniae
- pseudomonas aeruginosa
causes of PNA in people with travel/occupational exposure
Legionella pneumophila
what is 6th leading cause of death and most common infectious cause of death
PNA
- mortality rate is 25% in infections requiring hospital admission
PNA can be divided into what two groups
- hospital acquired (Nosocomial)
- develops 72 hours or more following admission
- community acquired (CAP)
- develops in people with limited or no contact with medical settings
community acquired PNA can be divded into what two groups
- typical vs atypical
typical CAP involves infection from which organisms
- S. Pneumoniae
- H. influenzae
- K. pneumoniae
- S. aureus
atypical CAP involves infection from which organisms
- zoonotic
- nonzoonotic
- chlamydia pneumoniae
- mycoplasma pneumoniae
- legionalle pneumoniae
- usually have extrapulmonary involvement and cause systemic infections
what types of ABx will not work against atypical PNA
- PCN because atypical PNA are unresponsive to B-lactams
clinical presentation
- sudeen onset
- sick appearance
- high temperature (>103)
- productive cough
- pleurisy
- consoldiation on CXR
- CP, SOB
typical bacterial PNA
clinical presentation
- gradual onset
- well appearance
- lower temperature <103
- non productive cough
- patchy infiltrates on CXR
- diarrhea, abd pain
atypical bacterial PNA
streptococcus pneumoniae
- gram status
- shape
- gram positive
- lancet shaped diplococcus
streptococcus pneumoniae: typical presentation on blood agar plate
-
alpha hemolytic colonies
- green colored colonies
when does streptococcus pneumoniae occur (season)
occurs more colder, wetter months
streptococcus pneumoniae incidence is in what patient populations
- young children
- adults > 65 yo
reervoir for streptococcus pneumoniae
asymptomatic carriers
streptococcus pneumoniae virulence factor (capsule)
- capsule
- inhibits phagocytosis
- interferes with complement activity
- prevents C3b opsonization of the bacteria

streptococcus pneumoniae virulence factors (seen in gram positive bacteria)
- peptidoglycan-teichoic acid complex
- illicits a significant immune response
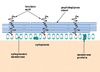
virulence factor specific to streptococcus pneumoniae
- Pneumolysin
- interacts with target cell membrane
- forms transmembrane pores
- results in cell lysis
- activates complement
streptococcus pneumoniae virulence factor: autolysin
- causes lysis of pneumococcus and results in release of pneymolysin and release of other virulence factors
- in response to antibiotic therapy and stationary phase
- attempt by organism to dampen host immune response by overwhelming it
how does consolidation form
- pneumococcus enters respiratory tract and multiples in tissue, stimulating immune response
- fibrinous edema fluid into alveoli followed by red cells and leukocytes
clinical presentation
- sudden onset of fever
- CP
- productive cough with rust colored purulent sputum
strep pneumoniae = pneumococcus
Pneumococcus is sensitive to
optochin sensitivity
what is the bile solubility test
- bile will lyse S. pneumoniae
- no effect on other a-hemolytic strep
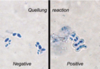
What is the Quellung reaction
- function: to observe capsules
- If the reaction is positive, the capsule becomes opaque and appears to enlarge
how is pneumococcus diagnosed
- agglutination test for capsular polysaccharides
- genetic probe test
- looks for S. pneumoniae specific rRNA
DOC treatment of pneumococcus
Penicillin G
prevention against pneumococcus
- vaccines
-
23-valent capsular polysaccharide vaccine
- recommended persons > 65 yo
-
13-valent capsular polysaccharide vaccine
- >80% infections in childnre < 6 yo
- accountable for 75% of strains of pcn-resistent pneumococcus
-
23-valent capsular polysaccharide vaccine
klebsiella pneumoniae can cause both
- typical CAP and nosocomial (hospital)
Klebsiella pneumoniae
- gram status
- shape
- motility
- gram negative
- bacillus
- non-motile
where is Klebsiella pneumoniae normally found
- normal flora of mouth, skin, intestines
Klebsiella pneumoniae causes pna is what patient populations
- alcoholics
- persons with DM
virulence factors of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Primary: coated by a thick slimy polysaccharide capsule
- antiphagocytic
- prevents MAC-mediated lysis
- adhesins
which organism causes an aggressive necrotizing CAP with predilection for the upper lobes; leads to abscess formation and cavitation; often fatal even with Abx treatment
Klebsiella pneumoniae
- causes necrotic destruction of alveolar spaces, inflammation, and hemorrhage in lung
clinical presentation
- acute onset of high fever
- productive cough with thick, blood tinged currant jelly sputum
Klebsiella pneumoniae
how is Klebsiella pneumoniae diagnosed
- gram stain
- currant jelly sputum
- cxr - cavitation
Klebsiella pneumoniae is resistant to what type of abx
Klebsiella pneumoniae produces beta lactamase
DOC treatment of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- combination
- aminoglycosides
- 3rd generation cephalosporin
- fluoroquinolones
mycoplasma pneumoniae causes what type of PNA
atypical CAP
which organism that causes PNA lacks a cell wall and has a “fried egg” appearance in culture
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Mycoplasma pneumoniae have plasma membranes that contain what compound
sterols
clinical presentation
- non-productive cough that lasts 1-2 months
- fevers, crackles, HA, CP
- relapses are common
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
virulence factors of Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- hydrogen peroxide
- damages epithelium
- prevents clearance of airway and results in colonization of airways
- evades immune system by fusing to host cell membrane through sterols
Mycoplasma pneumoniae can also cause what other conditions
- otitis
- rhinitis
- pharyngitis
- tracheobronchitis
Mycoplasma pneumoniae usually affects what age range
5-20 yo
reservoir of Mycoplasma pneumoniae
humans
- transmitted person to person via respiratory droplets
Mycoplasma pneumoniae diagnosis
- CXR: patchy infiltrates
- sputum culture
- cold agglutinin assay
DOC treatment of Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- azithromycin/tetracycline
chlamydophila pneumoniae causes what type of PNA
atypical PNA
chlamydophila pneumoniae
- gram
- motility
- shape
- gram negative
- non motile
- coccoid
chlamydophila pneumoniae exists in what two forms
- ** obligate intracellular parasites
- 2 forms
- elementary body: infectious form
- reticulate bodies: intracellular form
chlamydophila pneumoniae causes PNA via what process
- result of direct tissue destruction during bacterial replication, in addition to inflammatory response
primary immune response to chlamydophila pneumoniae is done via what cell
PMNs (immunity is not long lasting)
reservoir for chlamydophila pneumoniae
- humans
- transmitted person to person via respiratory droplets
chlamydophila pneumoniae mainly affects what patient population
adults >60 yo
chlamydophila pneumoniae diagnosis
cell culture and microscopy
DOC chlamydophila pneumoniae
- tetracycline/erythromycin


