Learning and Memory Flashcards
(34 cards)
What organisms were use to study the principles of learning and memory?
(Hint: There are three)
Aplysia
Dogs
Or
Human patients
For Apylisa learning behaviors, what reflex is used as a model for learning behaviors?
Gill withdrawal reflex
What are the two stimuli that would cause the aplysia to have the withdrawal gill response?
(1) touch on the mantle or siphon
OR
(2) a strong or noxious (harmful) shock to the head or tail
What are examples of simple learning?
(Hint: There are three)
Habituation
Sensitization
Dishabituaution
What is habituation?
The cessation (brought to an end) of a response to a stimulus after repeated presentation of the stimulus
True or False: Habituation is among the simplest of all forms of learning.
After repeated touches to the siphon or mantle, Aplysia “learns” to no longer withdraws gill.
True
Cellular mechanism of habituation
After the repeated firing of A.P. in sensory neuron
____________ channels in the terminal (activates/deactivates)
Transmitter vesicles at the terminal are _____________
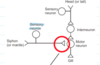
V.G. Ca2+
deactivates
depleted
What is sensitization?
An increase in the strength of any reflex, caused by one or more strong stimuli other than the stimulus that usually evoke the reflex.
What is dishabituation?
The full recovery of the original strength of a habituated response after the presentation of some strong, novel stimulus
Occurs after habituation
Cellular mechanisms of sensitization and dishabituation
___________ is released by the facilitating interneuron onto the terminal of siphon sensory neuron.
A _______ is activated
which activates ___________
increase _______ levels
activates ____
phosphorylates V.G. K+ channels and close them
The A.P. therefore stay longer and result in larger gill response.

Serotonin
G Protein
adenylyl cyclase
cAMP
PKA
What is the most studied type of complex learning?
Associative learning
Or
Conditioning
What model can be used for observation of conditioning?
Invertebrates
and
Vertebrates
Who was the first person to study conditioning with a dog?
Hint: Experiment: He conditioned a dog to salivate to the sound of a bell.
Ivan Pavlov, a Russian psychologist in the early 20th century.
True or False: Aplysia can learn to associate a non-noxious stimulus (a slight touch to the siphon) with a noxious stimulus (a stong poke or shock to the head)
True
Before conditioning the animal (will/will not) exhibit the gill withdrawal reflex (GWR) in response to the light touch to the siphon.
After conditioning, it (will/will not) exhibit GWR to a light touch.
Will not
Will
In the example of Aplysia, what is an unconditional stimulus?
Poke in the head
response does not require training
In the example of Aplysia, what is a conditional stimulus?
A light touch to the siphon
response requires training
True or False: Aplysia is repeatedly touched lightly (CS) on the siphon, later bonked on the head (US). (Bonked a minute later)
This is associative learning.
False
CS and US need to be paired for associative learning
US alone cause sensitization

Associate learning is similar to _____________.
Hint: Think back to Synaptic Transmission, Lec. 10
Associate LTP
Cellular mechanism of Associative learning
Light touch (CS) alone (does/doesn’t) cause conditioning
Cause a (few/large) A.P in siphon sensory nerve
causing a relatively (small/large) Ca2+ influx into terminal
which will cause a (small/large) amount of transmitter releases which (does/doesn’t) cause a response in the motor neuron
Also, Ca2+ slightly elevates ______lvels in the siphon sensory neuron terminal by activating ___________ which turns on _____________.
However, the effect on _______ is too small to cause significant phosphorylation of ____ channels

doesn’t
few
small
small
doesn’t
cAMP
calmodulin
adenylyl cyclase
cAMP
K+
Noxious stimulation alone (does/does not) condition, but sensitize
Two things happen
__________ of the direct pathways cause gill withdrawal
___________ of facilitating interneuron’s _______ pathways cause sensitization

does not
Activation
Activation
G protein
True or False: Mantle sensory neuron pathway is also sensitized
True

Combining siphon light touch (CS) with noxious head stimulation (US) results in ____________________.
Associative learning
Associate learning happens in aplysia due to
____________is activated by __________ from siphon touch and the activated more by the ________pathways from the head bonk.
_______ phosphorylate many ______ channels (thus close them) chasing a big increase in the strength of the GWR in response to the light touch of the siphon
______ also causes permanent changes through _________________________________.

Adenylyl cyclase
calmodulin
G protein
cAMP
V.G. K+
cAMP
cAMP-regulated gene transcription strengthening the synapses