Larynx Flashcards
(59 cards)
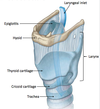
Larynx:
Hollow musculoligamentous structure with a cartilaginous framework
- continuous inferiorly w…?
- opens superiorly into …?
- Continuous inferiorly w **trachea **
- opens superiorly into pharynx
* (postero-inferior to tongue + oral cavity)*
name the following in the larynx:
- 3 unpaired cartilages
- 3 paired cartilages
3 unpaired cartilages:
- thyroid
- cricoid
- epiglottis
3 paired cartilages:
- arytenoid
- corniculate
- cuneiform
what is the function of membranes and ligaments in relation to the larynx?
suspend larynx from hyoid above + trachea below
what is the function of extrinsic muscles in relation to the larynx?
move larynx
facilitate **closing laryngeal inlet **during swallowing
facilitate opening esophagus during swallowing
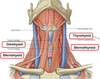
Thyroid Cartilage
what is the usual thyroid angle?
Is it larger in males or females?

90-129 degrees
usually smaller in males –>acute angle –> more pronounced bump
(“adam’s apple” laryngeal prominence - just inferior to superior thyroid notch)
Name 3 extrinsic mm. that attach to the oblique line on the lateral surface of the thyroid cartilage laminae?
sternothyroid
thyrohyoid
inferior constrictor
Cricoid Cartilage
(facts - 3)

- Inferiormost laryngeal cartilage
- Broad lamina posterior, and narrow arch anterior to airway
- Shallow depressions on posterior surface for posterior crico-arytenoid m. attachment
Epiglottis:
- attached to thyroid angle by what ligament?
- projects in which direction?

thyro-epiglottic ligament
Projects postero-superiorly; upper margin projects superiorly behind the pharyngeal part of tongue
Arytenoid Cartilage:
- Name the muscle and ligament that attach to the antero-lateral surface.
- where does the vocal ligament attach?
- Which 2 muscles attach to the muscular process (lateral angle of base)?

1. Vocalis m. and vestibular ligament
2. vocal process (anterior angle of base)
3. Posterior + lateral crico-arytenoid mm.
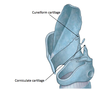
Corniculate and Cuneiform Cartilages:
- what dose the corniculate cartilage attach to?
- What does the cuneiform cartilage attach to?
- corniculate = apex of arytenoid cartilage
- cuneiform = Suspended in quadrangular membrane (anterior to corniculate)
Thyrohyoid Membrane
- what are the attachment points?
- what passes through the opening? (3)
- The thick posterior border is the ______________ ligament?
- The thick anterior midline is the _______________ligament?
- Superior edge of thyroid cartilage <—> Superior edge of hyoid
- internal laryngeal n. + superior laryngeal a. + lymphatics
- = lateral thyrohyoid ligament
- = median thyrohyoid ligament
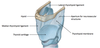
What ligament goes from:
1. anterior surface of epiglottis <–> posterior surface of hyoid
2. Lower border of cricoid <–> Upper border of 1st tracheal ring

- Hyo-epiglottic ligament
- Crico-tracheal ligament
Quadrangular Membrane:
- what are the points of attachment?
- Free lower margin is _________ ligament
- Free upper margin is ____________ fold
- What overlies the vestibular ligament?
- What separates the vestibular ligament/fold from the vocal ligament/fold?
- Epiglottis (lateral margin) <–> Arytenoid cartilage (A-L surface)
- vestibular ligament (Arytenoid cartilage <–> Thyroid cartilage)
- Aryepiglottic fold
- Vestibular fold (false vocal cords)
- Ventricle
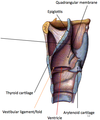
- *Cricothyroid Membrane:**
1. Where is it located/attached?
2. what is the lateral part called?
- Upper free margin of conus elasticus forms _____ ligament?
- what ligamant is b/t the thyroid cartilage (angle) <–> Arytenoid cartilage (vocal process)
- What covers the vocal ligament and vocalis m?
- Between arch of cricoid cartilage + space enclosed by thyroid cartilage
- Conus elasticus
- vocal ligament
- Vocal ligament
- Vocal fold (= true vocal cord)

- Vestibular ligament is ________ to vocal ligament (superior view)?
- They are sepatated by __________?
- lateral
-
ventricle
* *NOTE: true and false FOLDS are mucouse membranes covering their respective LIGAMENTS)*
* true = vocal*
* false = vestibular*

- What synovial joint is b/t inferior horn of thyroid cartilage + cricoid cartilage?
- What actions does it allow?
- Crico-thyroid Joint
-
forward movement + downward rotation of thyroid cartilage on cricoid cartilage
* (increases length + tension of vocal ligaments)*
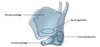
- What synovial joint is b/t cricoid cartilage (supero-lateral surface) + arytenoid cartilage (base)?
- What actions does it allow?
1. Crico-arytenoid Joint
- arytenoid cartilages slide away or towards each other, and to rotate
* (Abduction/adduction of vocal ligaments)*

which joint increases length + tension of vocal ligaments?
crico-thyroid joint
Which joint sbducts/adducts of vocal ligaments?
Crico-arytenoid Joint
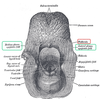
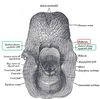
- What is the superior aperture of the laryngeal cavity?
- What are it’s borders?
(anterior, posterior, lateral)
1. laryngeal inlet
2. inlet borders:
anterior = superior epiglottic mucosa
posterior = interarytenoid notch b/t corniculate tubercles
lateral = aryepiglottic fold + cuniform + corniculate cartilages/tubercles

The inferior aperture of the laryngeal cavity is continuous with the___________ + encircled by _________?
trachea
cricoid cartilage

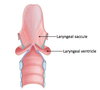
Name + locate the 3 major divisions of the laryngeal cavity:
1. Vestibule: between laryngeal inlet + vestibular fold
2. Ventricle: between vestibular folds (superior) + vocal folds (inferior)
3. Infraglottic space: between vocal folds + inferior aperture of larynx
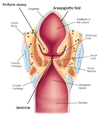
THIS STRUCTURE IS….
- not part of the laryngeal cavity
- b/t aryepiglottic fold (medial) + thyroid cartilage + thyrohyoid membrane (lateral)
- a channel to direct solids/liquids from oral cavity into esophagus
PIRIFORM RECESS
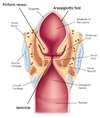
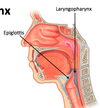
Laryngopharynx
- Where is it located?
- what opens into it’s anterior wall?
- from superior edge of epiglottis <–> top of esophagus
- Opening of laryngeal inlet