NECK - vasculature & lymphatics Flashcards
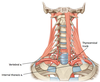
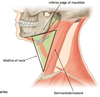
What are the borders of the ANTERIOR triangle?
(medial, lateral, superior)
Medial = Midline of neck
Lateral = Anterior border of sternocleidomastoid
Superior = Inferior border of mandible

What are the 4 blood vessels found in the ANTERIOR trinagle?
(4)
Common carotid a.
External carotid a.
Internal carotid a.
Internal jugular v. + tributaries
What blood vessels are found in the CAROTID triangel (sub-region of anterior)?
(4)
common carotid a.
external carotid a.
internal carotid a.
Internal jugular v.

Trace the ascent of the R. common carotid a.:
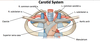
brachiocephalic trunk (posterior to R. sternoclavicular joint) –> R. common carotid a.
- Ascent through neck w/i carotid sheath (lateral to trachea + esophagus)
- Carotid bifurcation near upper edge of thyroid cartilage (C3-C4 iv disc)
Trace the ascent of the L. common carotid a.:

aortic arch –> L. common carotid a.
- ascent through neck w/i carotid sheath (lateral to trachea + esophagus)
- Carotid bifurcation near upper edge of thyroid cartilage (C3-C4 iv disc)
What is the Carotid sinus?
What is its innervation?
Dilation @ common carotid bifurcation
- Baroreceptor (monitors changes in blood pressure)
- Innervation = Glossopharyngeal n. (CN IX)

What is the Carotid body?
What is its innervation?
Collection of receptors @ common carotid bifurcation
- Chemoreceptor (monitors changes in O2/CO2 levels in blood)
- Innervation = Glossopharyngeal n. (CN IX) + Vagus n. (CN X)
Identify the branches of the External Carotid Artery (ECA):
“Some Anatomists Like Fucking Over Poor Med Students”
(from the bottom up)

*NOTE: There are NO branches of the ICA in the neck!!

What are the target areas for the Superior thyroid a. (branch of ECA) ?
(5)
Thyroid gland
Thyrohyoid m.
Sternocleidomastoid m.
Cricothyroid m.
Internal structures of larynx
What are the target areas for the Ascending pharyngeal a. (branch of ECA) ?
(6)
Palate
Tonsil
Auditory tube
Pharyngeal constrictor mm.
Stylopharyngeus mm.
Meninges in posterior cranial fossa
What are the target areas for the Lingual a. (branch of ECA) ?
(6)
Muscles of tongue
Palatine tonsil
Soft palate
Epiglottis
Floor of mouth
Sublingual gland
What are the target areas for the Facial a. (branch of ECA) ?
(5)
Soft palate
Palatine tonsil
Auditory tube
Submandibular gland
Facial structures from inferior border of mandible anterior to masseter m. to medial corner of eye
What are the target areas for the **Occipital a. **(branch of ECA) ?
(5)
Sternocleidomastoid m.
cervical parts of intrinsic back muscles
Posterior scalp
Meninges in posterior cranial fossa
Mastoid cells
What are the target areas for the **Posterior auricular a. **(branch of ECA) ?
(~3)
Parotid gland and nearby muscles
External ear and scalp posterior to ear
Middle and inner ear structures
What are the target areas for the **Maxillary a. ** (branch of ECA) ?
(13)
External auditory meatus
Tympanic membrane (lateral and medial surfaces)
TMJ (temporomandibular joint)
Cranial bones and dura mater
Trigeminal ganglion
(Mylohyoid + Temporalis mm.)
Upper and lower teeth and gum
maxillary sinus
Nasal cavity
Palate
Roof of pharynx
Infra-orbital skin and skin on chin
Structures in infratemporal fossa
What are the target areas for the **Superficial temporal a. **(branch of ECA) ?
(5)
(Temporalis + Masseter mm.)
Parotid gland and duct
Parietal and temporal fossae
External ear (anterior part)
Lateral face (via Transverse facial a.)
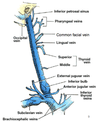
Internal Jugular Vein (IJV)
4 fun facts!
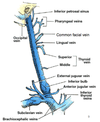
- Dilated continuation of sigmoid sinus
- Exits skull through jugular foramen
- Enclosed by the carotid sheath in neck
- Joins subclavian v.; Subclavian v.+ IJV = Brachiocephalic v.
Name the 6 tributaries of the IJV:
– inferior petrosal sinus
– pharyngeal vv.
– occipital v.
– common facial v.
– lingual v.
– superior + middle thyroid vv.
Blood Vessels in the Posterior Triangle?
(3)
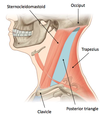
- Subclavian a. and branches
- Subvlacian v.
- EJV and tributaries
Subclavian Artery in the Posterior Triangle:
- Where does the 3rd part of subclavian a. emerges from?
- What does it becomes after crossing lateral border of rib 1?
- between anterior and middle scalene mm.
- axillary a.

Subclavian Artery in the Posterior Triangle:
- Where does the Transverse cervical a. branch from?
- What 3 muscles does it supply?
- branch of thyrocervical trunk (subclavian a.)
* (passes laterally/posteriorly across base of posterior triangle, in front of anterior scalene m.)* - supplies trapezius + rhomboids

Subclavian Artery in the Posterior Triangle:
- Where does the Suprascapular a. branch from?
- What muscles does it supply?
- branch of thyrocervical trunk
* (passes laterally across posterior triangle)* - muscles on dorsal surface of scapula

Subclavian Vein in the Posterior Triangle:
(5 fun facts)
- subclavian v. is a continuation of …?
- runs anterior to what structure in posterior triangle?
- passes anterior to what muscle?
- what major vein drains into the Subclavian v.?
- Subclavian v. + IJV = ???

- axillary v.
- subclavian a.
- anterior scalene m.
- EJV
- Brachiocephalic v.