NECK - bones & fascia Flashcards
Anterior & posterior boundaries of the neck?
anterior = lower border of mandible to upper surface of manubrium** **
posterior = superior nuchal line to intervertebral disc between C7 and T1 vertebrae
inferior boundary of neck?
top of sternum to acromion
(encloses base of neck)
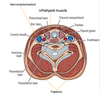
Vertebral compartment contents?
(4)

Vertebral compartment:
Cervical vertebrae
muscles
spinal cord
cranial nerves
visceral compartment contents?
(3)
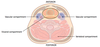
Visceral compartment:
Larynx
pharynx
glands (thyroid, parathyroid, and thymus)
Vascular compartment contents?
(2)
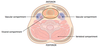
Vascular compartments (2 of them):
Major blood vessels
CN X (vagus n.)
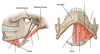
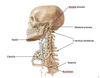
name the bony landmarks:

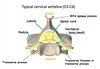
which cervical vertebrae are considered “typical” ?
C3-C6
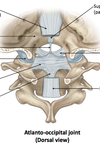
C1 is also called?
it participates in what 2 major joints?
Atlas
atlanto-occipital joint (w. occipital condyles of cranium)
atlanto-axial joint (w. axis [C2])

C2 is also called?
it participates in what major joint?
Axis
atlanto-axian joint (w. atlas [C1])

Name the components:
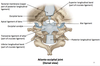
- Name the 3 attachments of the cruciate ligament?
(superior, inferior, transverse)
- What is the purpose of the transverse ligimant?
Superior longitudinal band → basilar part of occipital bone
Inferior longitudinal band → dorsal surface of C2 body
Transverse ligament → small tubercle on the medial aspect of the superior articular facet of C1 (wraps around the dens of C2)
2. Transverse lig. KEEPS DENS FLEXED

- name the attachments of the Anterior atlanto-axial ligament?
- what is it a continuation of?
- Lower edge of ventral arch of C1 ↔ Front of C2 body
- Cranial continuation of anterior longitudinal ligament

- name the attachments of the Posterior atlanto-axial ligament?
- what differentiates it from the posterior longitudinal ligament?
- Lower edge of dorsal arch of C1 ↔ Upper edge of laminae of C2 (arch to arch)
- Distinct from posterior longitudinal ligament (goes fr. Vertebral body to vertebral body)

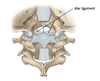
- name the attachments of the Alar ligament?
- what is its main function?
- Medial tubercles of occipital condyle ↔ Dens of C2
- Resists excessive rotation of head on axial dens
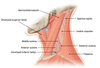
Name the superior, anterior, & posterior attachments of the hyoid bone:
superior = floor of oral cavity
inferior = larynx
posterior = pharynx
(all via ligaments)
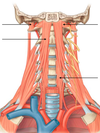
- Name the layers/sublayers of NECK FASCIA.
- name 3 functions of fascia.
Superficial fascia
Deep fascia
- investing
- pre-vertebral
- pre-tracheal
- carotid sheath
2. FUNCTIONS:
- movements of neck (e.g. twisting)
- swallowing
- deep fascia controls spread of infection
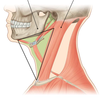
Name the fascia:

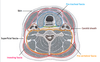
Identify the fascial layers surrounding the 4 facial compartments:
1st compartment: area surrounded by investing layer
2nd compartment: area surrounded by pre-vertebral layer
3rd compartment (visceral compartment): area surrounded by pre-tracheal layer
4th compartment: area surrounded by carotid sheath
the superficial fascia contains what muscle?
what is its action & innervation?
Platysma
muscle of facial expression (pulls the corners of mouth downward)
innervated by facial n. (CN VII)

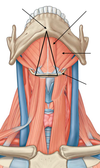
Neck: Investing Layer of Deep Fascia
name the 2 superior attachments:
external occipital protuberance
superior nuchal line
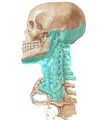
Neck: Investing Layer of Deep Fascia
name the 4 inferior attachments:
scapular spine
acromion
clavicle
manubrium