Large animal neuro exam Flashcards
Should you do a systematic exam or a head to tail exam?
Combination of the two probably best in horses, use a checklist!
Where in the brain is grey matter located?
On the outside

Where in the spinal cord is grey matter found?
On the inside (White matter is on the outside)
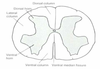
What is white matter made up of?
myelinated nerve axons

What is the grey matter made up of?
The cell bodies of those axons

Why might it be important to establish whether any horses have been showing respiratory signs if you have a neurologically abnormal horse?
Equine herpes (EHV 1)- can cause neuro signs but more commonly respiratory
What is the most common cause of stringhalt?
Toxic peripheral neuropathy
causes hyperflexion hind limb gait
Why is it important to do a general physical exam before neuro exam?
There can be many non neuro things that can cause neuro like signs
e.g. heart failure causing generalised weakness
Jaundice may be making the horse depressed
Could it just be lame? e.g. acute lameness due to foot abscess
What region of the brain is head pressing associated with?
Forebrain disease
What area of the brain is excessive yawning associated with?
Forebrain disease
Which region of the brain might be implicated if you have bizarre behavioural changes e.g. circling, hyperaestesia, head turn, odd poses, etc
Fore brain
What region of the brain is implicated in seizuring horses?
forebrain
May start as focal and then become generalised
Cerebellar disease in horses is rare or common?
Rare, much more so than smallies
What are the common signs associated with cerebellar disease?
Spastic or exaggerated movements
Absence or diminished menace response
Intention tremor
Ataxia WITHOUT weakness
What breed does cerebellar abiotrophy affect?
Arabians
Rare genetic disease
What are the pons reticular formation and medulla collectively called?
the brainstem
What part of the brain is being described:
ascending proprioceptive pathways
descending motor pathways
cranial nerve nuclei
Brainstem
What is the reticular formation?
Part of the brainstem, to do with consciousness
The bit caffeine works on to wake you up!
Why do horses with brainstem disease often blink excessively?
Nystagmus (often associated with vestibular disease) causes the horse to blink
What nerve might be compromised in a horse with a wonky muzzle or droopy ear?
Facial nerve (VII)
What are the twelve cranial nerves
opthalmic
optic
occulomotor
trochlear
trigeminal
abducens
facial
vestibulocochlear
glossopharnygeal
vagus
accessory
hypoglossal
What nerve is the afferent component of the PLR?
OPtic nerve
What nerve is involved in the efferent component of the PLR?
occulomotor (parasympathetic fibres) constrict the pupil
What is the pathway of the menace response?
optic nerve
optic chiasm
thalamus
opposite occipital cortex
facial nerve and nucleus
cerebellum
REQUIRES FOREBRAIN INVOLVEMENT OF THE CONTRALATERAL CEREBRAL CORTEX

