Forebrain and Brainstem Disease Flashcards
What is the proper name for the cerebral cortex?
telencephalon
What is the proper name for the region of the brain that the Thalamus is a part of?
Diencephalon
What is the forebrain?
The cerebrum and thalamus
What are the five lobes of the cerebrum?
Olfactory lobes
Frontal lobes
Parietal lobes
Temporal lobes
Occipital lobes

What does the olfactory lobe do?
perception of smell
Limbic system

What does the temporal lobe do?
Auditory area
Vestibular conscious perception
Pyriform lobe forms part of the olfactor and limbic systems

What does the frontal lobe do?
Mainly motor
Corticospinal and Corticonuclear tracts

What does the parietal lobe do?
Mostly sensory, some motor areas

What does the occipital lobe do?
Visual conscious perception

What is the path travelled in sight?
Optic nerve
Optic chiasm
Optic tract
Lateral geniculate nucleus
Occipital lobe

What is the route of the menace response? (after the occipital lobe)
association fibres to Motor cortex, projection fibres to cerebellar cortex via transverse fibers of the pons, efferent cerebellar fibres to facial nuclei, facial nerve

When might you not see the menace reponse (other than defect in the pathway)
Young animals less than 12 weeks
Stressed patients
Lethargic patients
Disorientated patients
Is it normal to have behavioural changes in an animal with forebrain disease?
Can be yes,
Altered behaviour=thalamus
May be depressed, confused, stupor, coma
Can you get seizures assoicated with forebrain disease?
yes
What is hemi neglect syndrome?
When the animal doesn’t perceive some areas of space e.g. may only go for half of their food bowl
What gait changes might be observed with forebrain disease?
May be normal,.
May head press, circle, pace
Proprioceptive ataxia and tetraparesis
Do forebrain lesion animals head turn/circle towards or away from the lesion?
towards the lesion
What does pleurothotanous mean?
Head turn with associated body turn
Decreased postural reactions are associated with forebrain disease on the ****lateral side
contralateral

Decreased facial sensitisation is associated with forebrain disease on the ****lateral side
contra
Which nerve mainly provides sensation to the face?
Trigeminal, all 3 branches (opthalmic, maxillary and mandibular)

Spinal reflexes in an animal with forrebrain disease should be *****
normal
What is the proper name for
a) Midbrain
b) pons
c) medulla oblongata
a) mesencephalon
b) metencephalon
c) myelencephalon
S, T, Y like the order in the alphabet
What are the metencephalon and myelencephalon in combination sometimes called?
Rhombencephalon
If a cranial nerve has autonomic actiom will it be sympathetic or parasympathetic?
ALWAYS parasympathetic
Which part of the brain is the reticular formation found in?
Meshwork of cells throughout the midbrain
What is the ARAS?
Ascending Reticular Activating System
It activates the cerebral cortex and keeps us awake
Hence you will have a comatose state if you have a severe diffuse brain stem problem
What is the red nucleus?
Where the fibres cross over in the mesencephalon
Paw placement deficits with rostral midbrain lesions will be
contralateral or ipsilateral?
Contralateral. Cross over at the red nucleus
What is this posture?
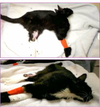
Decerebrate
Extension of all the limbs and stuporous mental status
What is this posture called?
Decerebellate
Problem is in the cerebellum, will be conscious
Hind limbs may be flexed

What is the role of the Oculomotor nerve?
Motor to the extraocular muscles
Parasymapthetic to the sphincter pupillary muscles (cause pupil constriction)
Levator palpebrae superioris
Which extraocular muscles are innervated by the occulomotor?
dorsal, ventral, medial rectus, ventral oblique
What is the pathway of the PLR?
Optic nerve
Optic chiasm
Optic tract
Pretectal nucleus (in thalamus)
Occulomotor nucleus (in midbrain)
Oculomotor nerve
Ciliary ganglion
Short ciliary nerve
What percentage decussation is there at the optic chiasmin dogs and cats?
cats 66%
dogs 75%

What are the names of the two constrictor fibres of the pupil in the cat’s eye?
nasal and malar
What happens to the pupil if the oculomotor doesn’t work?
Dilation of pupil (in cats will look like a D or reverse D depending if nasal or malar is affected
What should you always check for in a cat if you see a D or reverse D shaped pupil?
FeLV associated lymphosarcoma
(it really likes the short ciliary nerves)
What part of their pathways do vision and PLR share?
Optic nerve, optic chiasm and a little bit of the optic tract
If an animal has blindness and an absent PLR the lesion must be..
In the optic nerve, chiasm or first bit of the optic tract
What nerves are found in the pons?
trigeminal
What does the trochlear nerve do?
Just innervates the dorsal oblique!
It is the only nerve that arises dorsally on the brainstem, AND the only one that innervates something on the opposite side of the brain to itself; hence remember dorsal and oblique parts
What will the eyes look like if the trochlear nerve doesn’t work?
Eye rotate, can only see in cat

How might you be able to notice eye rotation due to trochlear nerve dysfunction in a dog?
The optic disc and three prong blood vessels might be rotated
What is the tectotegmental spinal tract?
Originates in the midbrain, responsible for sympathetic innervation to the eye i.e. pupil response to emotional factors.. fear = pupils dilate
What syndrome would damage to the tectotegmentalspinal tract give you?
HORNERS
What is the first neuron of the three neurons in the sympathetic route to the eye?
tectotegmental spinal tract
Where to the sympathetic fibres to the eye exit the CNS?
T1-T3
All sympathetic fibres exit in thoracolumbar region
What is the second neuron of the three neurons in the sympathetic route to the eye?
Cranial cervical ganglion (v close to middle ear)
If an animal has first order Horners syndrome would you expect it to have other signs?
Yes!
If it has a lesion in its midbrain or deep enough in the spine to reach the TTS tract it will not be in a good way..
Which order Horners syndrome might you suspect if the animal also has a forelimb lameness?
2nd order, may be a brachial plexus injury affecting the craniocervical ganglion
Which order of horner’s syndrome might you suspect if you also had any of the following:
Middle ear disease
Facial paralysis
Vestibular dysfunction
A lesion in the pons would give you **** paw position deficits
ipsilateral, the pons is before the cross over point
What are the three branches of the trigeminal?
Occipital
Maxillary
Mandibular
Which branch of V is motor?
Mandibular branch (muscles of mastication)
What nerve might be implicated in an animal with a non sensitive non healing corneal ulcer?
occipital branch of trigeminal. May also see lack of sensation in ipsilateral nostril
What are the four muscles of mastication?
Temporal
Masseter
Digastricus
Pterygoid
What is the (neurological) cause of drop jaw?
Bilateral mandibular branch problem
Why might dogs with dropjaw also have horners?
When the 3rd neuron goes back into the skull it travels very near the mandibular branch of trigeminal, may be secondarily affected
What are the non neurological causes of drop jaw?
Bilateral luxation of TMJ
Mandibular fracture
Oral foreign body - can’t close mouth
What are the neurological causes of drop jaw?
Inflammatory/Infectious
Toxic-Botulism
Trauma (carrying large/heavy objects around)
Idiopathic trigeminal neuropathy
Neoplasia
How do you treat idiopathic dropped jaw?
Physiotherapy, gets better in time
Elastic band around mouth when eating
Feed in ball handfulls
What nerves are in the medulla oblongata?
6-12
If you have a diffuse lesion in the medulla oblongata which side would you expect paw placement abnormalities to be on?
Ipsilateral as is before cross over
What part of the brain might be injured if you had signs of respiratory difficulty?
Medulla oblongata (respiratory centre)
May need to be on a ventilator as can’t use respiratory muscles
Which muscles does the abdcens innervate?
lateral rectus
retractor bulbi
What kind of strabismus will you see if you have a problem with the abducens?
medial
What does the facial nerve do?
Motor to the muscles of facial expression
parasympathetic to lacrimal and salivary glands
Why do you sometimes have vestibular and cochlear signs together?
The vestibulocochlear and facial nerve run very close to each other
Pic shows both together, droopy and head tilt

How is the facial nerve involved in the menace response?
It is the motor part of the menace
What are the possible causes of facial neuropathy?
Infection of the middle ear/inner ear
trauma
Neoplasia
Polyneuropathy (hypothyroidism in dogs)
Idiopathic (lots of them!)
Why might you see KCS in animals with facial nerve damage?
facial nerve parassympathetic to lacrimal glands
Where abouts would you expect to find a lesion in an alert and awake animal with a head tilt AND facial nerve signs - droopiness, KCS, dry nose etc?
Not in the medulla oblongata as would be stuperous, just where the nerves leave the medulla oblongata around the region of the inner ear
Which nerves come from the nucleus ambiguus?
Glossopharyngeal, Vagus and Hypoglossal
Which nerves does the gag reflex test?
IX and X
What is the role of the glossopharyngeal nerve?
Motor to the pharynx and palatine structures
Sensory to caudal 1/3rd of tongue
Parasymp to salivary glands
What does the vagus nerve do?
Motor to the larynx (recurrent laryngeal nerve), pharynx and oesophagus
Sensory to larnx, pharyn, thoracic and abdominal viscera
Parasympathetic to abdominal and thoracic viscera
What is the hypoglossal nerve motor to?
muscles of the tongue
Why do cranial cervical lesions sometimes affect the hypoglossal?
Because the hypoglossal is so caudal in the medulla oblongata


