Lab Practical #1 Wheater Flashcards

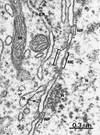







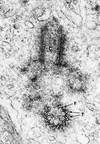




What is this cell?

Neutrophil
What is this cell?

Neutrophil
What is this cell?

Lymphocyte
What is this cell?

Monocyte
What is this cell?

Red Blood Cell and Unactivated Platelet
What is this cell?

Activated Platelet
What is this cell?

plasma cell
What is this cell?

Lymphocyte and endothelium

Thymus, cortex, medulla

Name the structures

- afferent lymphatic vessels
- efferent lymphatic vessels
- capsule
- trabeculae (singular: trabeculum)
- cortex
- medulla
- lymphoid follicles (B-Cells)
- paracortical area (T-Cells)
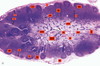
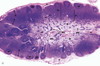
Spleen
White Pulp
Red Pulp


MALT
mucosa associated lymphoid tissue
lumen
hollow interior of organ
simple
refers to an epithelium of one layer of cells
stratified
refers to an epithelium comprised of two or more layers of cells
squamous
extremely flat, shaped like pancake
apical membrane
membrane of an epithelium bordering the lumen
basolateral membrane
the membrane of an epithelium opposite to the apical membrane
epidermis tissue type
stratified squamous keratinized epithelium

Basement membrane

Dermis
- Tissue
- Cell
- Fiber
- dense irregular connective tissue
- fibroblasts
- type I collagen fibers
Capillaries
- Tissue type
- Structure
- Simple squamous epithelium
- Endothelium
Hypodermis
- Type of tissue
- Type of fiber
- cell
- special tissue
- loose connective tissue
- type I collagen fiber
- adipocyte
- adipose tissue

- hair follicle
- arrector pili
- sebaceous gland

Skin of the Eyelid
- Epidermis
- stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
- Conjunctiva
- Tarsal gland
- holocrine secretion
- Sebaceous sweat gland
- Lacrimal Gland
- acinus
- duct
- simple cuboidal epithelium

Small intestine
- Mucosa
- Simple columnar epithelium
- goblet cells
- apical membrane
- basolateral membrane

- Microvilli
- brush border
- Apical Membrane
- Basolateral Membrane
Submucosa
- Loose connective tissue
- (blue)
- type I collagen
Smooth Muscle
- longtitudinal
- (purple)

- articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage)
- type II collagen
- anterior cruciate ligament
- posterior cruciate ligament
- fibular collateral ligament (lateral)
- tibial collateral ligament (medial)
- patellar ligament
- lateral meniscus
- medial meniscus
- fibrocartilage
- type I collagen fibers and type II
- synovial cavity

- Bursa (flat green sac)
- tendon sheath (green wrapped around tendon)
- fibrous capsule (#7) innermost white
Bone
- Fiber
- Cell
- Layer
- System
- Space
- Structure
- Middle Canal
- type I collagen
- osteocyte
- lamellae (singular: lamella)
- Haversian systems
- lacunae
- canaliculi (singular: canaliculus)
- Haversian canal
- Ligaments and Tendons
- Tissue
- Cell
- Fiber
- Light Brown/Pink
- dense regularly arranged connective tissue
- fibroblasts
- type I collagen
Articular Cartilage
- Stain color
- tissue
- cells
- space
- fibers
- structure
- Dark Green
- hyaline cartilage (tissue that makes up articular cartilage)
- chondrocytes
- lacuna
- type II collagen fibers
- perichondrium
Neuroglia
- Neuroglia: surround and support neurons, make myelin
Neuron Histology
- Cell Body (grey-green)
- Nucleus (clear)
- Nucleolus (dark)
Axons
- Bundle of axons is a nerve
- nodes of Ranvier

- High magnification of myelin

- Myelin
- Axon

- Slide is all red
- Endoneurium
- single axon
- Perineurium
- fascicle
- Epineurium
kilocalorie
amount of heat that will raise one liter of water 1 degree celsius
dietary manual calories
is the equivalent of one kilocalories
kilojoule
preferred energy unit in the international system (=0.24 kilocalories)
1 joule/sec
1 watt (rate of energy expenditure)
1 kjoule/min
16.7 watts
1 kcal/min
69.7 watt
VO2 to kilocalories
4.8 kcal/L O2
Direct Method of Measuring Energy Expenditure
- Determined by measuring the rate at which heat is released by the body.
- Based on first law of thermondynamics
Indirect Method of Measuring Energy Expenditure
- Energy expended calculated from teh rate at which oxygen is consumed
- Typical diet, 4.8 kcal of energy are released for each liter of oxygen consumed
MET
- metebolic equivalent
- 1 MET=amount of energy when sitting quietly
- 70 kg person burns 70 kcal/hr
spirometer
gas is squeezed into this machiene to be measured
Gas Volume to Volume at STP (conversion factor)
0.89
Ve
- Volume of gas per minute at STP
- (Change in volume of Gas)*(spirometer calibration 0.133)=volume of gas in liters
- Volume/min=Liters/min
- Ve=(Liters/min)*(factor to convert to STP)
VCO2
VCO2=VeFECO2
- FECO2=fraction of carbon dioxide
- from computer
kilocalories/min
- (liters O2/min)*(4.8 kcal/liter O2)
METS
- Kcal per hour/weight in kg
Vo2 max
the maximum rate of energy expenditure
lactate threshold (anaerobic threshold)
lactic acid begins to increase in the blood because the amount of oxygen delivered to the mitochondria is no longer sufficient o generate enough ATP for the level of exercise
R.Q.
- VCO2/VO2
RQ if only carbohydrate being used
RQ=1
RQ in this experiment
- RQ change due to the release of lactic acid into the blood.
- increased acidity sitmulated peripheral chemoreceptor and increased rate/depth of breathing
- increased ventilation
*
- increased ventilation
Fraction of oxygen in the room
0.2090
Carbonic anhydrase
CO2+H20>H2CO3>H+HCO3
RQ quotient at lactate threshold
- But above the lactate threshold we expect the R.Q. to steadily increase as H+ stimulates the peripheral chemoreceptor and as H+ reacts with bicarbonate in the blood to liberate CO2. This is what we see above about 160 watts.


