L8.3 Joints of the Hip & Pelvis Flashcards
1
Q
Lumbosacral
A
- 2o cartilaginous IV joint (L5/S1) - hyaline on either side, fibrous cartilage in between
- Also have synovial zygopophyseal joints (btw articular facets)
- Sup L5 facet: sagittal
- Inf L5 facet: transition to coronal → entire weight of body stopped here
- Curvature of backbone most prominent here
- Disc wide (ANT), narrow (POS)
- Body weight goes ANT to joint → transferred to head of femur
- Head of trabeculae vertically oriented → most dense ∴ weight bearing
- Least dense at the neck → most common fracture

2
Q
Lumbosacral ligaments
A
- Iliolumbar:
- L5 TP → iliac crest
- Also acts as passive accessory lig to sacroiliac joint
- Lumbosacral lig:
- TP → sacrum

3
Q
Sacroiliac
A
- Synovial joint (ANT), fibrous syndesmosis (POS)
- Weight bearing
- Btw auricular surfaces of sacrum & ilium

4
Q
Sacroiliac ligaments
A
- Interosseous lig
- Btw auricle and sacral tuberosity
- Passive support → stops excessive nutation
- ANT/POS sacraliliac lig (interosseous in between the 2)
- Sacrotuberous: ANT surface of sacrum → ischial tuberosity
- Sacrospinous: INF sacrum → ischial spine
- Both sacro ligs stops excessive nutation & forms foramen

5
Q
Nutation of the pelvis while standing?
A
- Pelvis is usually slightly tilted forward while standing → pubic symphysis becomes the floor
- ↓pelvic inlet (SUP), ↑pelvic outlet (INF)
- Promontory of sacrum prone to nutation into cavity due to weight bearing nature
6
Q
What is the reverse keystone concept for the sacroiliac joint?
A
- (sacrum opposite of a normal keystone)
- Arch (iliac bones) holds the keystone (sacrum) in place
- Sacrum is also wide inferiorly, narrow superiorly
- POS ligs, interosseous lig → pulls iliac bones tgt → stops sacrum from excessive nutation
- Ligs lax during pregnancy
7
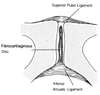
Q
Pubic symphysis
A
- 2o cartilaginous joint
- Fibro disc wider in females
- Works as a ‘tie-beam’ → prevents separation laterally + resisting compressive force via femur

8
Q
Pubic symphysis ligaments
A
- SUP pubic ligament: across pubic tubercle
- INF Arcuate ligament: Supports at sub-pubic levels
- ANT pubic ligament
9
Q
Sacrococcyxgeal
A
Apex of sacrum & base of coccyx
10
Q
Sacrococcyxgeal ligaments
A
ANT/POS sacroccocygeal ligaments

11
Q
Pelvic and lumbosacral fractures
A
- At pubic symphysis & rami
- Fractured at pars interarticularis
- On 1 side: spondylolysis
- On both sides: spondylolisthesis (may slide fwd)
12
Q
Hip joint
A
- Synovial ball & socket
- Btw acetabulum & head of femur
- Margins of capsule:
- ANT intertrochanteric line
- POS above intertrochanteric crest
- INF exposed
- Vascular synovial membrane within capsule
- Avascular hyaline cartilage covers articular parts

13
Q
Hip Joint ligaments
A
- Iliofemoral (‘Y’) ligament of Bigelow:
- Stops hyperextension
- Strongest lig in the body, has 2 branches from bones ∴ a Y shape
- Pubofemoral: Blends with iliofemoral ligament
- Ischiofemoral: Acetabulum (POS) → spirals to ANT surface
- All 3 tighten in hip during internal rotation & extension
- ∴ max stability: slight extension, AB, In rotation
- Bursae sits in the deficiency
- All 3 tighten in hip during internal rotation & extension

14
Q
Other structures of the hip joint?
A
- Acetabular labrum
- Acetabular notch: transverse acetabular ligament spans length of notch
- Fat pads, in the centre of acetabular fossa
- Bursae: Psoas (ANT), trochanteric (POS)
- Ligamentum teres: sits in fovea → attach to labrum
15
Q
Hip joint dislocations & fractures
A
- POS (more common): Hip flexed, add, in rotated (lady cross leg)
- ANT (not common): Extend, ab, ex rotated
- Congenital dislocation: baby bound too tightly, epiphysis not fused yet
- Fractures: Neck of femur → ↓trabeculae, endangers sciatic N
16
Q
Hip movement and muscles involved
A



