L3 Spinal cord to the diencephalon Flashcards
•Central nervous system is formed from _____derm
•Central nervous system is formed from ectoderm
List the 3 steps in neuro
- Neuroectoderm cells receive inductive signals from notochord
- Cells thicken to form neural plate
- Lateral neural plate margins fold inwards to form neural tube
What is neurulation?
Development of the nervous system
At embryonic day 20, the cells at edges of neural plate are called _________ cells
Neural crest cells
Label the diagram of neurulation


At embryonic day 24, ________ cells migrate into _______ and differentiate
At embryonic day 24, neural crest cells migrate into periphery and differentiate
Neural crest cells migrate into periphery and differentiate into…
(1) Autonomic and sensory neurons and glia
(2) Cells of the adrenal gland
(3) Melanocytes
(4) Skeletal/connective tissue of the head
What does the mantle layer become?

- Becomes brain parenchyma
What does the Ependymal layer become?
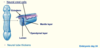
Lines the ventricles
What happens at embryonic day 24 after neural crest cells migrate into periphery and differentiate?
•Neural tube thickens
What does the lumen become?
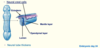
- Becomes ventricles + central canal
Complete the diagram on embryonic day 24 of neurulation

•Neural tube defects occur in ~1/______ established pregnancies
1000
What is anencephaly?
Failure of anterior neuropore to close
= Anencephaly (fatal)
What is spina bifada?
Failure of posterior neural tube to close
= Spina bifida (divided by a cleft)
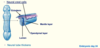
Name the types of neural tube defect circled on the diagram

What type of spina bifida does this show?

Spina bifida occulta (hidden, vertebral arch defect only)
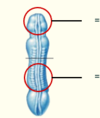
What type of spina bifida does this show?

Spina bifida cystica (e.g.; meningocele = meninges projects out)
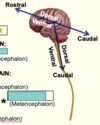
How are primary brain vesicles formed?
•Expansion of cranial end to form main brain regions (primary vesicles)
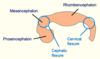
In what direction does the development of the cervical and cephalic flexures occur?
Sagittal
Complete the diagram of the primary brain vesicles


Label where the cervical and cephalic flexures are on the diagram
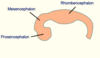
What does the telencephalon form?
(Cerebral hemispheres)
What do the optic vesicles form?
Eyes
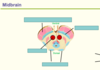
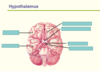
What does the diencephalon form?
Diencephalon (Thalamus/hypothalamus)
What does the metencephalon form?
(Pons/Cerebellum)
What does the myelencephalon form?
Myelencephalon (Medulla)
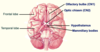
Label the brain directions

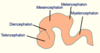
Complete the diagram of the development of secondary brain vesicles


What direction does the pontine flexure develop in?
sagittal
Label where the pontine flexure is on the diagram
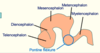
Complete the diagram


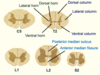
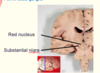
What is grey matter made up of?
Grey matter - mainly neuronal cell bodies (e.g. cerebral cortex, brain nuclei)
What is white matter made up of?
White matter- mainly myelinated axons
Label the areas of the brain
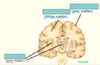

What are the 5 functions of the spinal cord?
- Receives primary afferent fibres from somatic and visceral structures
- Sends motor axons to skeletal muscles
- Autonomic function
- Regulation of bodily functions at unconscious level (reflexes)
- Conveys ascending and descending tracts
•Spinal cord extends from ______ to _______
•Spinal cord extends from atlas to L1
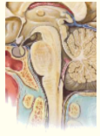
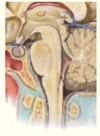
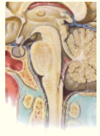
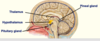
What is the cauda equina?
Cauda equina (Lumbar and sacral dorsal and ventral roots)
In lumbar cistern
Complete the diagram on the anatomy of the spinal cord

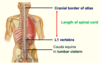
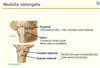
- Spinal cord narrows at L1 to form ___________
- Spinal cord narrows at L1 to form conus medullaris
- ____________ (pia extension) attaches to coccyx
- Terminal filum (pia extension) attaches to coccyx
The spinal cord sits protected within the _________ (in the __________)
•Sits protected within vertebral column (in vertebral canal)
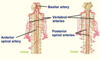
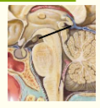
Where does the spinal cord recieve its blood supply from?
Anterior and posterior spinal arteries (from the vertebral arteries)
Segmental spinal arteries (at each level)
Complete the diagram on the anatomy of the spinal cord