L3: Introduction to Modern Physics (Physics Module Lecture 1) Flashcards
(13 cards)
What is temperature?
something that you measure
What is heat for solids?
potential+kinetic energy stored as microscopic vibrations of atoms in their lattices

What is heat for liquids?
energy of moving atoms/molecules

What is heat for gases?
mostly kinetic energy of moving atoms/molecules (eg. see Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution Franklin

What is the equation for heat transferred?
Q=((kA∆T)/l)t?

What does all the variables stand for in Q=((kA∆T)/l)t?
Variables:
Q heat transferred in amount of t time.
Variables: A contact area, ∆ T temp difference
1 Constant: k Thermal conductivity (of material)
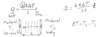
What does it tell you if you double l (thickness)?
Double thickness (l) (in the same amount of time) = half the amount of heat transferred
Slows down heat transfer

What is the SI units of thermal conductivity?
Wm−1K−1

heat change ∆Q gives change in _____∆T. Give the equations.
temperature

constant of proportionality between the left-hand-side and the right-hand-side is _________ (___)
specific heat capacity (c)
What is the typical Typical (bad) unit of Heat capacity?
Jg−1K−1

Which way does the heat flow?
EXAM QUESTION
From body to the ice

Structurally - same mass of water and fat Heat capacity Fat 2300 Water 4180 Will fat or water have the largest temperature increase, if same amount of heat is applied? Why?
EXAM QUESTION
Fat –> because C is smallest


