L20- Midgut Flashcards
What is the major artery the supplies the blood to the midgut
superior mesenteric artery

What viscera are included in the midgut?
- distal duodenum
- jejunum
- ileum
- cecum/appendix
- ascending colon
- transverse colon

What two parts of the duodenum are in the foregut? What two parts are in the midgut?
Foregut: Superior part, descending part Midgut: Inferior part, ascending part

What ligament (part of the lesser omentum) anchors the duodenum?
The hepatoduodenal ligament

The descending part of the duodenum wraps around what viscera?
The head of the pancreas

What are secondarily retroperitoneal organs? Name some examples
Viscera that originally had a mesentery but then becomes pressed again the body wall and leaves the peritoneal sac
- Ascending and descending colon
- pancreas (except tail)
- parts of duodenum (2nd and 4th parts)
What two openings can you find in the descending part of the duodenum?
- Major duodenal papilla (opening for main pancreatic duct/bile duct)
- minor duodenal papilla (opening for minor pancreatic duct)

What is the junction between the duodenum and jejunum called?
Duodenojejunal flexure
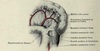
What suspensory muscle of the duodenum inserts on the duodenojejunal flexure (#2) ?

The ligament of Treitz
What are the lesions of the mucosa of the proximal duodenum called?
Duodenal ulcers
What are the grooves on the inside of the jejunum called?
plicae circulares (circular folds)

What are the arches of arterial blood supply to the jejunum called?
Arterial arcades

What are the straight arteries to the jejunum called?
Long vasa recta

Does the ileum have more or less arterial arcades than the jejunum?
More, multiple arterial arcades

Does the ileum or the jejunum have more plicae circulares?
The jejunum has more, ileum has minimal

Describe the physiological herniation of the midgut?
- Grows faster than the abdominal cavity
- herniates out into the umbilical cord in week 6
- intestines rotate 90 during herniation
- rotate another 180 during return of the intestinal loops to the abdominal cavity
- return to the abdominal cavity at week 10-12

What is an omphalocele?
A physiological herniation of the midgut that fails to retract
Viscera covered with amnion in the umbilical cord

What is gastroschisis?
The viscera retract and then later herniate lateral to the umbilicus
- this viscera is not covered in amnion
- usually to the right of the umbilical cord due to a weakness of the anterior abdominal wall

What is the recanalization of the GI tube?
- the lumen of the tube solidifies in month 2 by epithelial tissue
- hollows out again by week 9

What are atresia and stenosis of the GI tube?
Atresia- completely closed stenosis- lumen isn’t wide enough can be caused by failure of GI tube to hallow out also caused by malformation of adjacent structures

What is the ileal (meckel’s) diverticulum?
a remnant of the vitelline duct
- can appear like appendicitis
- 2x2x2 rule: 2% of people, 2 inches long, 2 ft from ileocecal junction

What are the fatty projections off of the colon called?

omental appendices
What are the three smooth bands on the colon called?
teniae coli

What are the small pouches caused by sacculations on the colon called?
haustra















