L15- DNA repair Flashcards
DNA integrity can be looked at in 2 ways
- at the level of nucleotdie- mutations
- at the level of chromsosomes (nondisjunction)
if DNA integrity is lost
pathogenic
types of DNA breaks
Single stranded
double stranded
single stranded damage
One strand will remain intact
Not as bad as DS break
double stranded damage
breaking the double strand is very damage

which compoenents of DNA can be dmaaged
all components e.g. bases and sugar phosphate backbone
what causes DNA damage
exogenous and endogenous sources
endogenous causes of DNA damage
error in DNA replication (replication stress)
exogenous sources of DNA damage
Anti-cancer Drugs
Mutagenic chemical - smoking
Alkylation agents
Radiation
Ionising – most comes from radon gas in the ground
Free radicals
what usually happens when healthy DNA becoems damaged
is damaged DNA can be recognised by DNA repair mechanisms which makes the DNA healthy again.
when does m utation occur
when DNA damage is not recognised or repair mechanisms dont work
endogenous sources of single stranded damage
i. Replication stress
ii. Free radicals
exogenous sources of single stranded damage
i. Deamination due to nitrites
ii. UV radiation
exogenous sources of double stranded dmaage
X-ray/Y-ray
definititon of replciation stress
‘Inefficient replication that leads to replication fork slowing, stalling and/ breakage.’
replication stress is an example of
an endogenous source of damage, which causes replication stress
how many factors causes replication stress
3
outline 3 factors which cause replication stress
1) Replication machinery defects
- Misincorporation by DNA polymerase
- Proofreading error by DNA polymerase
2) Replication fork hindrance
- Forward and backward slippage
- e.g. Trinucleotide repeats
3) Defects in response pathway
replication machinery defects
Misincorporation by DNA polymerase
Proofreading error by DNA polymerase
what leads to replciation fork hindrance
repetitive DNA
types of replication fork hindrance
forward slippage
backward slippage
what sort of mutation is forward slippage
deletion mutation
what type of mutation is backward slippage
insertion mutation
forward slippage mechanism
New strand has an extra nucleotide (A)
Newly synthesised strand loops out

backward slippage mechanism
New strand is missing a nucleotide (A)
Template strand loops out

backward fork slippage leads to
trinuclotide expansion seen in Huntingotns and fragile x syndrome
Huntingtons disease is a
trinucleotide repeat disorder
which gene is affected in huntingtons
HTT gene
which codon affected
CAG repeat- polyglutamine
CAG repeats cause
neurone degenration
- mutant protiein aggregates in neurones affecting basal ganglia
when DNA damage levels are too high or persist the cell can …. (3)
- goes into senescence (G0)
- undergoes apoptosis
- undergoes uncrontrolled cell division- tumour
when do the cell cycle checkpoint occur
G1 When entering the S phase
G2 checkpoint
Checkpoint in. mitosis
G1 checkpoint
is the environment favoruable to enter DNA replication
G2 checkpoint
is all DNA replicated?
is all DNA damage repaired?
checkpoint in mitosis
are all chromosmes properly attache to the mitotic spindle?
repair mechanisms for single stranded breaks in DNA
1) Mismatch repair
2) Base Excision repair
3) Nucleotide excision repair
what is G0 (senecence)
Permanent cell cycle arrest- will never divide again (wont pass bad DNA), but will continue with normal function
mismatches occur due to
endogenous errors during replication
- DNA polyemerase adds wrong nucleotide (happens 1/100,000 nucleotides)
what proofreads DNA and reduces error rate
Exonucleases- attached to DNA polymerases -checks the for mismatches and replaces with correct nucleotide
Reduces error rate
DNA repair mechanism for endogenous causes of ssDNA breaks
mismatch repair mechanism
mismatch repair emchanism
- Mismatch is detected in newly synthesised DNA
- New DNA strand is cut and mispaired nucleotides and neighbour removed
- Missing patch is replaced with correct nucleotides by DNA polymerase
- A DNA ligase seals the gap in DNA backbone

exogneous causes of ssDNA breaks
harmful chemical or physical agents
harmful chemicals
Nitrites and nitrosamines in cured or pickled food
Nitrites and nitrosamines in cured or pickled food cause
deamination
e.g. Removal of amino group from nitrogen bases (change cytosine à uracil)
DNA repair mechanism when deamination occurs
e.g. Removal of amino group from nitrogen bases (change cytosine à uracil)
base-excision repair
base excision repair
1) Converts a cytosine base into a uracil
2) The uracil is detected and removed, leaving a base-less nucleotide
3) The base-less nucleotide is removed, leaving a small hole in the DNA backbone
4) The hole is filled with the right base by a DNA polymerase and the gap is sealed by a ligase
physical agent swhich cause ssDNA damage
UV radiation
UV radiation causes
- UV radiation creates pyrimidine dimers (most often with 2 adjacent thymine)
- Thymines forms bonds with eachother distorting the whole DNA strand
what is used to repair ssDNA dmaage caused by UV radiation
nucleotide exicision repair
nucleotide exicision repair
1) UV radiation produces thymine dimer
2) Once dimer has been detected, the surrounding DNA is opened to form a bubble
3) Enzymes (exonucleases) cut the damaged region out of the bubble
4) A DNA polymerase replaces the excised (cut-out) DNA and ligase seals the backbone
dsDNA breaks cause
most delterious damage
what causes ds breaks
exognous cause: ionising radiation (X-ray and Y-ray)

X-ray and Y-rays
- Can break phosphate backbone of both DNA strands
- Causes double stranded breaks
- Usually not a clean break- often an over hanging region
DNA repair mechanissm for ds breaks
1) Non-homologous end joining
2) Homologous directed repair
ssDNA repair meechanism
- mismatch
- base excision repair
- nucleotide exicision repair
non homologus end joining
- DNA protein kinase(KU70/80) binds to each end of the broken DNA and recruits artemis
- Artemis cuts off jagged ends
- Ligase enzymes binds two ends of DNA
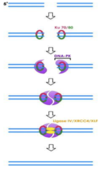
non homologus end joining involves
loss of some geentic information
- error prone repair
how does homolgous recombination occur
We have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes that have similar genetic material and code for the same traits- similar nucleotide sequences… therefore a double stranded break can be repaired using a sister chromatid
- outline homologous recombination
A protein complex called MRN binds to each end of the broken DNA and recruits exonucleases which remove nucleotides from one strand of the DNA
End 1 is placed next to a similar nucleotide sequence called the homologous sequence and starts to base pair with complementary region
This creates a loop in the homologous DNA
DNA polymerase synthesises nucleotides to extend end 1 until it reaches a sequence which is complementary to end 2
End 1 releases the homologous DNA and its last few nucleotides bind to the last few nucleotides of end 1
DNA polymerase fills the gap on both sides of the union and DNA ligase seals the bond

homologus recombination is
more reliable than non-homolopgus end joining
- no loss of genetic info


