L13: Anatomy, Physiology of the Vestibular System Flashcards
What is the role of the vestibular system?

What happens to the vestibular system and the cerebellum when you are drunk?
- Vestibular system stops working
- Cerebellum is not listening to vestibular system
What are 4 features that are included in the vestibular system?
- Peripheral vestibular apparatus
- Vestibular components of the 8th cranial nerve
- Vestibular nucleii in the brain stem
- Central nervous system projections
Where is the peripheral vestibular system?

What are the 2 types of labyrinths in the ear?
- Bony (outer)
- Membranous (inner)

What is the purpose of the inner, soft membranous labyrinth?
- Hair follicles/cells
- Deflect the fluid the other way
What is the inside fluid called?
endolymph
What is the outside lfluid called (between the hard shell of the boy and inside the membranous)?
perilymph
What are the 5 distinct sensory organs in the peripheral apparatus?
- 3 semicircular canals (SCC)
- Anterior
- Horizontal
- Posterior orientation
- 2 Otolith organs
- Utricle
- Saccule
Sensory end organs
- SCCs = Crista Ampullaris
- Otoliths = Macula

What are the 3 semicircular canals (SCC)?
- Anterior
- Horizontal
- Posterior orientation

What are the 2 otolith organs?
- Utricle
- Saccule

What is the sensory end organs of semicircular canals (SCC)?
Crista Ampullaris
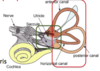
What is the sensory end organs of Otoliths?
Macula

What do the sensory end-organs look like?

What is the function of the cupula?
Used in diagnosis and rate and direction that the hair cells move
What are otoconia made of?
Calcium carbonate crystals stuck on gel-like structure
What is the structure of the crista ampullaris? List 2 features.
- Hair cells of the ampulla (SCC) rest on a tuft of blood vessels, nerve fibres and supporting cells
- A gelatinous membrane called the Cupula overlies each crista

A gelatinous membrane called the _____ overlies each crista
Cupula

What is the function of the cupula?
Holds them (crista) together and allows the hair cells to move

What is a sterocilia?
50-70 small cilia
What is a kinocilium?
1 large cilia
Cilia arranged according to size from _____ (shortest/tallest) to _____ (shortest/tallest)
shortest; tallest
What is the purpose of the cilia?
- Allows activation of the nerves to be more systematic
- Depolarise or hyperpolarise
- Moving one way or the other
Otolithic membrane is similar to ____ of Crista Ampullaris but also has embedded calcium carbonate crystals called ____.
cupula; otoconia
What is the otolithic membrane?
Otolithic membrane is similar to cupula of Crista Ampullaris but also has embedded calcium carbonate crystals called otoconia

What is the 3 purposes of the otolithic membrane?
- Increases the mass of the cupula (gel-like systems)
- Shearing force on gel like system
- Gives constant weight of the hair cells = tells us constantly where we are in space (keeps vestibular system constantly on)

Increased mass of the otolithic membrane means the maculae are sensitive to_____ and _____.
gravity; acceleration

How does the displacement of sensory hairs work?

Each afferent nerve fibre in the peripheral vestibular apparatus has a baseline ____ rate
firing
Deflection of stereocilia toward kinocilium results in a _____ (increase/decrease) in the firing rate of the afferent neuron
increase

Deflection of stereocilia away kinocilium results in a _____ (increase/decrease) in the firing rate of the afferent neuron
decrease

Hair cells will bend in the ____ (same/opposite) direction to head movement – fluid flow is the _____ (same/opposite). Give an example if the head starts to move to the left.
opposite; opposite
- To the way we move (eg. start turning to the left –> the fluid is going to the right )
- If suddenly stop –> fluid will go left

When the head is tilted or the body experiences acceleration, the hair cells are ______ and allow detection of the head’s position in space and linear acceleration.
deflected

The stimulation of the otolithic maculae is designed for _____ sensitivity.
linear
What are 4 characteristics of the vestibular nerve?
- Vestibular component of 8th cranial nerve (vestibulocochlear nerve)
- Afferent nerve only
- Travels through the internal auditory canal with the facial nerve and enters the brainstem at the ponto-medullary junction
- Debate over whether it is a peripheral or central structure in vestibular pathology – * peripheral for us

What are the 2 splits of the 9th cranial nerve (vestibular nerve)?
- Superior vestibular
- Inferior vestibular

What are 3 structures that the superior vestibular nerve supplies?
- anterior canal
- horizontal canal
- utricle

What are 2 structures that the inferior vestibular nerve supplies?
- posterior canal
- saccule

What is the primary processor for central processing?
vestibular nuclear complex in brain stem
The primary processor has connections between incoming afferent input from ______ and motor output _____
vestibular system; neurons
Central processing occurs concurrently with the processing of other sensory info. This is called _____.
Integration
What are the central connections of the vestibular system?

What are 4 major vestibular nuclei in the pons and medulla?
- superior
- lateral
- medial
- inferior

The 4 major vestibular nuclei are located in the ____ and ___
medulla; pons
The 4 major vestibular nuclei are connected to the nuclei of the _____, _____ and _____ nerves (CN (- eye muscles- 3, 4 & 6)
abducens; trochlear; oculomotor
_____ is what calibrates our vestibular system (stabilises)
Vision
You will feel ____ and ____, if vision is fine but vestibular is not
imbalanced; giddy
What do the complex feedback loops between the vestibular nuclei in the brainstem and cerebellum look like?

What do the afferent input from vestibular system also going directly to cerebellum look like?

What is the cerebellum?
An adaptive processor
What are the 3 functions of the cerebellum?
- Monitors vestibular performance and readjusts central vestibular processing Refine the movements –> without it –> very clumsy
- Calibrates vestibular reflexes
- Cerebellar projections have an inhibitory influence Extra signs and symptoms –> neurologists look for these extra symptoms
What does the link from the thalamic nuclei and the cortex look like?

What does the output of vestib nuclei directly to ocular muscles via cranial nerves 3,4 and 6 look like?

What can the problem be in a poor Marden Pull test?
- Possible vestibular system impairment (don’t know where they are in space)
- Motor problems (eg. parkinson’s)
What does the Excitatory output to Csp and Tsp spinal motor neurones look like?

What are 4 structures that the verterbro-basilar circulation provides blood supply for?
- peripheral apparatus
- vestibular nerve
- brainstem nuclei
- cerebellum.

If you have whiplash or neck pain, what is the risk?
Can have vascular problems
If we lose vascular supply to the vestibular system, what are 3 effects?
hair cells in the vestibular system
Eg. migraines –> dizziness
Eg. sudden deafness –> medical emergency (very compromised)
What is the integration of the vascular and nerve supply to the vestibular apparatus?

The Vestibulo cochlear artery (posterior vest A) is the _____ (superior/inferior) division of vestib N
inferior
Vestibulo cochlear artery (anterior vest A) is the ______ (superior/inferior) division of vestib N
superior
What are semicircular canals?
Rate sensors
What are 2 functions of the semicircular canals?
- Provide sensory input about head velocity
- Enables the Vestibular ocular reflex (VOR) to generate an eye movement that matches the velocity of the head movement..
The alignment of the SCC are characterised by three important spatial arrangements. What are they?
- Perpendicular arrangement
- Coplanar pairing of SCCS
- Direction of excitation
Each canal plane is perpendicular to the other ____ canals with allows sensing of movement in _____ planes
two; all
What are the 3 planes that SSC sense movement?
- Yaw (right / left)- Horizontal rotation
- Pitch (front/back)- Flexion /tension (up and down)
- Roll/bank (ear up/down/Bank = side to side )- Lateral flexion

The 6 individual canals form ____ coplanar pairs
three Co-plane together (anterior of one side and posterior of other side are co-planar)
What is the “push-pull” rhythm in the co-planar pairing of SCCS?
the endolymph of the co-planar pair is displaced in opposite direction with respect to to the ampulla
Therefore, within the co-planar pair, increased neural firing on one side will _____ (increase/decrease) neural firing on other side
decrease
The planes of the canals are closely aligned with the optimal pulling direction of the _______ muscles. What does this allow?
extra-ocular
This allows the vestibular ocular reflex (VOR) to be precisely calibrated to direction and velocity of head movement

Medial and lateral rectus are directly aligned with the _____ system
horizontal

What are the 3 advantages co-planar pairing?
- Provides “sensory redundancy” in the event of unilateral loss
- Allows brain to ignore changes in neural firing that occurs on both sides simultaneously (eg. changes due to increase body or environmental temp)
- Assists in compensation of sensory overload
What happens when there is damage to one side of the vestibular system?
(while can get the other side to compensate)
Once turn the other side of = not good enough data
Don’t usually go for the bad side and will turn good side off
What is a simple rule to tell the directions that excite each canal?
“ a canal is excited by head motion towards that canal, in the appropriate plane”
The right horizontal canal is excited by ____ head turns
right

The right posterior canal is excited by ______ left head tilts
right posterior

The left anterior canal is excited by ______ head tilts
left anterior

What direction does the fluid go in ampullopetal?
Displacement “toward” the ampulla
What direction does the fluid go in ampullopetal?
Displacement “away” from the ampulla
Head turns will cause excitation of one vestibular nerve and ____ of its paired canal
inhibition
The vestibular nerve which is being inhibited will drop to a firing rate of 0 (spikes per second) for head velocities at _____ deg/sec (normal daily activities average 120 deg/sec). Therefore, head velocities > 180deg may be unquantifiable by _____ the vestibular system
180; half
Response to rotations that excite a canal are _____ (greater/less) than response to rotations that inhibit a canal
greater
Clinically – people with a UVL (unilateral vestibular lesion) often avoid ____ head motion ____ (toward/away) the side of the lesion (inhibitory signal on intact side is not adequate enough at high speeds)
rapid; toward
What are utricle and saccule?
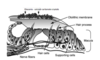
Utricle and Saccule are arranged to enable them to respond to motion in all three dimensions in an ____ individual
- saccule = ____ (vertical/horizontal)
- utricle = ____ (vertical/horizontal)
Sense orientation of the head with respect to gravity (tilt)
upright; vertical; horizontal

What are 3 sense linear acceleration of the head?
- occipito-caudal
- antero-post
- lateral

Sense orientation of the head is with respect to _____ (tilt)

What are the otolith organs: utricle and saccule?

What is the vestibular ocular reflex?
important mechanism to maintain stable vision during rapid or non-constant head movements
What are 3 characteristics of VOR?
- Head must be moving at variable velocity
- Visual target is stationary or in motion
- Maintain image of interest steady on the fovea of the retina during head movements
What are 2 components of VOR?
- Angular VOR - compensates for rotation (SCCs)
- Linear VOR - compensates for translation (otoliths)
What are 4 characteristics for angular VOR?
- Rotation of the head stimulates SCCs
- Triggers an inhibitory signal to the extraocular muscles on one side and an excitatory signal to the muscles on the other side.
- The result is a compensatory movement of the eyes.
- Eyes opposite to head rotation

What are 3 characteristics of VOR?
- Eyes opposite to linear head movement
- Mediated by the otolith organs (Eg. problems with not knowing that they are in a lift)
- Most important when near targets are being viewed and the head is being moved
What is Ewalds 1st law?
Eye and head movement always occur in the same plane of the canal being stimulated and in the direction of the flow of the endolymph
Eye movement being referenced is named by the fast component of nystagmus (the compensatory eye movement to acceleration – the VOR)
What is Ewalds 2nd law?
Horizontal canal stimulation towards the utricle (cupula towards) produces a greater response than inhibition (cupula moving away from the utricle)
What is Ewalds 3rd law?
In vertical canals (PSCC & ASCC) reversal of the cupular movement causes stimulation and inhibition within the functional pair of canals.
In Ewalds 2nd and 3rd law, asymmetric neural function is accommodated if both _____ of the functional pair are working
canals
In Ewalds 2nd and 3rd law, asymmetric neural function builds a bias (velocity storage centre) if canals of the functional pair are ______ in their function.
asymmetric
What are 4 consequences of asymmetry?
- Dizziness – vertigo, Spinning, giddiness – Nausea / vomiting / Oscillopsia (Unable to see )
- Imbalance / falling / ataxic gait
- Tilting
- Nystagmus (jumping eyes)
What is nystagmus?
“Jumpy” eyes
Involuntary rhythmic movement of the eye consisting of a slow drift of the eye in one direction, with a corrective quick “jerk” in the opposite direction – Slow drift is the pathological feature

What is the result of nystagmus?
an imbalance of neural signals arriving at the occulomotor neurons

What is nystagmus described as?
in reference to the patient and by the direction of the fast component

A nystagmus, if there is a torsional component, it is named by what the ____ pole of the eye is doing
superior

An nystagmus can be ____, _____ or _____ (torsional)
horizontal; vertical; rotary

What is the gain of VOR?
Gain = output /input – i.e. eye movement head movement
What does a gain of 1 mean (in VOR)?
Eye movement velocity = head movement velocity
Normal Eg. 200/200
What does a gain of 0.5 mean (in VOR)?
eye movement velocity < than head movement velocity
What is classified as abnormal in VOR gain?
Anything lower than 1 = abnormal (vestibular loss)
Gain is _____ (increased/decreased) with vestibular loss
decreased
What is the difference between nystagmus and gain or VOR?
Nystagmus = there is a loss (don’t know if its from the brain, vestibular system)
Gain of VOR = there is a loss (know that its from the vestibular)
What are 3 other oculomotor systems?
- Smooth pursuit tracking
- Saccadic eye movements
- Optokinetic system
What are 4 characteristics of smooth pursuit tracking?
- Maintains an object of interest on the fovea with and without head movements
- Trajectory of object must be predictable
- Pursuit mechanism not sustainable with velocities > 70/s; frequencies >1Hz; accelerations >240/sec
- Used instead of the VOR to maintain clear visual viewing from no movement to head movements up to 5 Hz
What is a characteristic of saccadic eye movements?
Mechanism to replace a target of interest onto the fovea if has moved off
What are 3 situations where saccadic eye movements are used?
- smooth pursuit cannot be used secondary to pathology
- outside the normal velocity for pursuit
- trajectory is unpredictable
What are 4 characteristics of optokinetic system?
- Maintains visual objects on the fovea when in constant motion – no acceleration so the VOR is not active
- Is a combination of both pursuit tracking and saccades – so tracks the object and then resets to the next object or the same one with the head in a new position
- With just visual motion can create strong sensation of motion
- This system backs up the VOR when the head is not accelerating or decelerating
What does the summary of the VOR reflexes

What is the purpose of the Vestibulospinal reflex (VSR)?
stabilise head on the body and maintain upright posture
What does the VSR result from?
from motor output from vestibular nuclei to spinal motor neurones
What is the VSR used for?
Uses otolith input to a greater extent than the SCCs - ie related to tilt / gravity rather than rotation
What is an example of the VSR?
– e.g. standing on a boat rocking side to side, VSR stabilises head by counteracting trunk sway
What are the 3 major connects of the VSR?
- Lateral vestibulospinal tract – antigravity postural motor activity
- Medial vestibulospinal tract – ongoing postural changes or head righting in response to SCC
- Reticulospinal tract – unclear / probably involved in most balance reflexes
What is the function of the vestibulocollic reflex (VCR)?
Acts on the neck musculature in order to stabilise the head
The VCR has head movement that counter the movement sensed by the ____ or ____ organs
otolithic or SCC
What are the 3 roles of the vestibular system in postural control?
Depends on the nature of the task & on the environmental conditions
Most important when:
- stabilisation of the head is critical for good performance
- when somatosensory or visual information is not available
- when there is conflict between the somatosensory and visual systems



