L10.3 Role of the placenta Flashcards
1
Q
Role of the placenta
A
- Central regulator of pregnancy outcomes
- Interface b/w mother and fetus
- Exchange nutrients and gases
- Barrier
- Immune function
- Hormone production
- Important in separating maternal and fetal circulations
2
Q
4 methods of placental transport
A
- Passive diffusion
- O2, steroid hormones
- Fetal waste - urea, creatinine
- Facilitated diffusion
- Glucose through GLUT transporters
- Active transport
- AA, folate, micronutrients
- Vesicular transport
- For very large molecules - i.e. immunoglobulins
- Captured by microvilli
3
Q
Placenta as a GC barrier
A
- Glucocorticoid barrierPlacenta actively metabolise GC → acts as a barrier
- Express 11β-HSD2 which converts GC into inactive metabolites
- Cortisone → coritsol
4
Q
Immune regulation of the placenta
A
- Modulate immune system to prevent rejection
- Secretes neurokinin B → binds phosphocholoines → assists in dampening immune system
- Inhibit maternal T-cells → lymphocytic suppressors
- IgG AB crosses placenta and provide immunity
5
Q
Endocrine regulation of the placenta
A
- Produces GF, lactogens, FG
- Regulates maternal insulin levels, ↑blood glucose/FA
- Progesterone secretion → maintain endometrial lining and prevents preterm labour
- Leptin → regulating maternal appetite
- Vasodilators/angiogenic factors
6
Q
Placental development
A
- Starts dev early in pregnancy and important for implantation
- Day 7/8 = implantation
- Free floating blastocyst comes into contact and invades uterine lining
- Allows placentation to occur
- Free floating blastocyst comes into contact and invades uterine lining
7
Q
3 ways of placental development going wrong
A
- Placenta previa
- When placenta implants → covers cervix → fetus have no pathway to pass out through
- Need C-section
- Placenta Accreta
- Placenta invades beyond uterus and obstruct other structures
- Causes severe blood loss during delivery
- IUGR
8
Q
Conditions affecting placental development
A
- Pre-eclampsia
- Diabetes
- Malnutrition
- *Essentially maternal stress
9
Q
Placenta classification according to maternal layers
A
- Epitheliochorial (lower primates)
- Mother and fetus have complete capillary network
- Endotheliochorial (carnivores - dogs/cat)
- Fetus capillaries sitting in bath of blood
- Hemochorial (higher primates - i.e. humans)
- Maternal blood directly with fetal chorion

10
Q
Placenta classified according to shape
A
- Discoid (humans, mouse)
- Multicotyledonary (sheep)
- Many implantation sites around the uterus
- Diffuse (horse)
- Encapsulates the whole fetus
- Zonary (cat/dog)
- Ring of placenta

11
Q
Placenta classified according to fetal layers
A
- Hemomonochorial (human)
- One type of fetal cell layer
- The syncitiotrophoblast → what transports nutrients from mother to fetus
- Hemodichorial
- Syncitiotrophoblast + cytotrophoblast
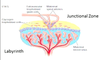
- Hemotrichorial (rodent)
- 2 syncitiotrophoblast + syncitial giant layer → creates a labyrinth for exchange
- Junctional zone above allows for hormone production
12
Q
Zones in rats and humans comparatively
A
- Villous region both in human and rat (Called labyrinth zone in rats)
- Extravillous = maternal uterus which interacts with placenta
- 3 zones in rats and 2 in humans

13
Q
Effect of famine on placental size
A
- Placenta ↓SA (more affected in boys than girls)
- Babies were lighter
- Glucose intolerance → CV/obesity risk ↑
14
Q
What is the Placental ratio and it’s significance
A
- Given fetal body weight → there is an optimal placental weight
- Large = inefficient
- Small = poor development
15
Q
Altered placenta development results in:
A
- Impaired placental structure → altered SA for transport
- Dysregulated nutrient transport
- Impaired endocrine functions (IGF, leptin)
- Dysregulated placental barrier → fetal GC exposure ↑ risk of disease
16
Q
Difference b/w males and females
A
- Overdose of GC/ethanol given:
- Females → good response → upregulate HSD11B2
- Males → bad response → dysregulated
- Hypoxia → impaired GC barrier in females but not males


