KNEE: Lectures 1 and 2 Flashcards
Pt Scenario
First contact practitioner
if OPEN INJURY
OBSERVE:
Active bleeding? Bone protruding?
First contact practitioner
if Fx:
OBSERVE:
WB w/out an AD?
First contact practitioner
if Knee Dislocation
Tibiofemoral vs.
Patellofemoral vs.
Muscular avulsions vs.
Vascular issues
-
Tib/Fib
- Is varus/valgus alignment similar to uninjured side?
-
Patellofemoral
- is patella centered in knee joint?
-
Muscular avulsions
- is there a loss of contour @ insertion site? Muscle retraction?
-
Vascular issues
- is the foot or lower limb cyanotic?
First contact practitioner
if Knee Jt Infection/Septic Joint
OBSERVE:
is the joint swollen and red?
First contact practitioner
Open Injury
PALPATE:
NOTHING IF OPEN!!
First contact practitioner
Fx:
PALPATE:
Fibular head, Patella
First contact practitioner
Knee Dislocation
Tib/fib vs.
Patellofemoral vs.
Muscular avulsions vs.
Vascular issues
PALPATE:
-
Contour of the limb:
-
Tib/Fib
- are injured knee mm’s more/less active vs. uninjured?
-
Patellofemoral
- Is patella tender on medial side?
-
Muscular avulsions
- Is there a loss of contour near muscular insertion?
-
Vascular issues
- are distal pulses intact?
-
Tib/Fib
First contact practitioner
Knee jt Infection/Septic Joint
PALPATE:
-
Joint swelling
- intra-articular vs. extra-articular
- **Sweep Test**
First Contact Practitioner
Stop the Party, Call ED ….
- OPEN INJURY
-
Neurvascular injury
- diminished or absent pulses
- absent sensation
- Obvious Fx OR
-
(+) Ottawa Knee/Ankle Rules
- HIGH index of suspicion Fx
-
Gross misalignment of limb
- Disloc. w/out reduction
- DO NOT try to reduce UNLESS transit time to ED is prohibitively long
First contact practitioner
Continue Exam; Refer out when finished:
-
Tib/Fib OR Patellofemoral Dislocation
- NO (or min.) neurovascular issues
- Normal alignment
- spont. reduction
- Muscle avulsions
*NOTE: presentation is not emergent, BUT should be assessed by other providers to ensure medical stability
Knee Rules for det. Need for Radiography
Ottawa Knee Rules
- Age 55+
- Isolated tenderness of patella
OR
- Tenderness over fibular head
- Unable to flex knee past 90deg
- Unable to bear wt. immed. OR in ED for 4 steps
***HIGHLY SENSITIVE BUT NOT VERY SPECIFIC***
*REMEMBER SnNout and SPpin
Knee Rules for det. Need for Radiography
Pittsburgh Knee Rules
- Blunt trauma OR a fall as MOI + one of following:
- Age under 12
- Age over 50
- Unable to bear wt. in ED for 4 steps
JAMA and the Ottawa Knee Rules
- DEC in need of radiography w/out missed fx’s
- HIGHLY sensitive, reliable, very acceptable
Rehab after Prolonged Immob. (Fx)
Sx modulation and Impairment Resolution:
what do you want to focus on?
- resolve effusion/edema
- improve mm activation/DEC atrophy
- normalize painful mm contracts.
- Restore limtd motion, DEC jt stiff.
- Restore normal mvmt patterns
Neurovascular Assessment of Knee Joint
Circulatory Issues: 2
- Vascular Injury
- DVT
Neurovascular assessment of Knee
Circulatory Issues:
Vascular Injury
- Arterial injury interrupts blood to distal tissues
- Arteries are susceptible @ jts AND when making sharp turns around bony prominences
POST. KNEE JT DISLOCATION
Impacts what?
- POST knee jt dislocation
- impacts Popliteal Artery
- check Post. Tib pulse
- impacts Popliteal Artery
POSTEROLATERAL KNEE JT INJURY
Impacts what?
- Posterolateral knee jt injury
- impacts supply to Ant. Tibial Artery
- Check Dorsalis Pedis Pulse
DVT
what is it and what can it do ?
- Clotting/blocking of a distal vein
- can dislodge and move thru circulatory system to Central Aspects —– heart & lungs
DVT
More common when and why?
- More common after Sx
-
hip, knee, leg/calf, abd, chest
- Reduces bloodflow to a part of the body
-
hip, knee, leg/calf, abd, chest
DVT
Reasons why Sx can INC DVT risk: 3
- Tissue debris, PRO, fats may move into veins following Sx
- Vein walls damaged—> releases subs. that promote blood clotting
- Prolonged bed rest
Arterial Assessment
Dorsalis Pedis Pulse
Check if POSTEROLATERAL KNEE JOINT INJURY bc Ant. Tib. Artery
Top of foot, lateral to EHL tendon
distal to Navicular

Arterial Assessment
Post. Tib. Pulse
Check if POST. knee jt dislocation bc impacts Popliteal Artery
Post to medial malleolus

Well’s Clinical Prediction Rule for DVT
- Probability of DVT:
- 3pts==HIGH RISK 75%
- 1 to 2pts== MOD. RISK 17%
- <1 pt==LOW risk 3%

Circulatory Status for DVT:
risk INCs w/ AGE, esp. after 60
Lifestyle factors?
- Sitting or inactive for long time
- Long plane or car trips
- Extra wt.
- BC pills or patches
- Smoking
S/S of DVT
NOTE: 1/2 of all DVT cause NO sx’s
Some you will see….
- Swelling in one or both legs
-
Pain or tenderness in one or both legs
- MAY only occur during walking or standing
- Warmth in the skin of affected leg
- Red or discolored skin in affected leg
- Visible surf. veins
- Leg fatigue
Neuro Screening
Common Peroneal Nerve
Motor vs. Sensory Function
- MOTOR:
- Ankle DF
- Great toe EXT
- Toe EXT
- SENSORY
- 1st web space—-DEEP BRANCH
- Dorsal surf. toes 3-4—-SUPERFICIAL BRANCH

NEURO SCREENING
Tibial Nerve
Motor vs. Sensory Function
- MOTOR:
- PF
- Toe FLEX
- little bit of Inversion
- SENSORY:
- Plantar aspect of calcaneous
- Plantar aspect 5th toe

LE Peripheral Nerve Map
see pics

Expected Gait Devs in Acutely Injured Knee
2
- Noticeable limp
- Flexed Knee Gait
Gait Devs in Acutely Injured Knee
Noticeable Limp
Why?
- avoiding WB on injured limb
- Short stance time on injured limb
- Short step length for uninjured limb
Gait Devs. for Acutely Injured Knee
Flexed Knee Gait
Why and theories?
- avoids TKE
- avoids eccentric knee flex.
-
Theories:
- Quad-avoidance gait vs. Optimal length-tension for quads
- Co-contract of quads/HS to LIMIT MOTION
Knee Joint Swelling:
Joint Effusion
- Fluid contained W/IN a body cavity
- Knee jt==Largest Synovial Cavity in body
- intra-art injury==intra-art swelling
- extra-art injury LIKELY WONT CAUSE INTRA-ART. SWELLING
KNEE JOINT SWELLING
Joint Edema
GEN term for swelling
*can likely move edema thru tissue
Effusion Assessment
Stroke Test, Sweep Test
UP medially
DOWN laterally

Interventions/Sx Modulation
Effusion Control
RICE
- Rel. Rest
- avoid excess. WB
- use AD
- Ice
- 20 on 20 off
- Compress
- knee sleeve, ACE
- mm pumps—-QUAD SETS!!!
- knee sleeve, ACE
- Elevate
- Knee ABOVE heart
Assess & Tx of Limtd ROM and Pain Gen. structures
Sx Modulation
Knee EXT Measurements
- Resting knee EXT
- Knee EXT w/ Quad Set
- Knee EXT during SLR

Knee EXT ROM Considerations
Resting Knee EXT
True PROM
- Rest pos or Loose-pack pos.
- 20-30deg of FLEX
- Check and see if indiv. can rest w/ their limb on table and no post. support
- Can indiv. rest their limb w/ heel supported and nothing under knee?
-
Where is discomfort felt???
-
POST
- capsule vs. HS tendons vs. gastroc
- ANT
- “pinching”
-
POST
Knee EXT ROM Considerations
Knee EXT w/ Quad Set
AROM
- does quad visibly contract?
- does contraction produce sup. patellar glide?
- does glute max. co-contract?
- typ see “reduction” in EXT when asked to contract quad
- knee stays same place, greater troch rises bc glute contracts
- does this cause pain?
-
ANT
- patellar tendon vs. quad tendon vs. quad mm
- RETROPATELLAR
- POST.
-
ANT
Quad Lag
Lag Sign
- indic’s mm is not capable of holding end range pos.
- ability of mm to maintain pos. lags behind total ROM
- NO ext. resist—-BW only
Quad Lag
Max EXT-EXT during SLR*****
- quads not able to maint. full knee EXT when there is no support to Tibia
-
Formula:
- MAX EXT - EXT during SLR
Quad Lag
If present, what does this mean?
CONSIDERABLE mm weakness!
MMT >3/5
-
individual likely not strong enough to achieve ACTIVE TKE in gait
- Hyperextension thrust vs. Flexed knee gait
Quad Lag
What do you want to do to address this?
- Restore mm activation towards End Range
- SUP patellar mobs
-
Quad Sets***
- can be combo’d w/ SUP patellar glide to facilitate quad contraction
- SAQ’s
- TKE ex’s
- prone vs. standing vs. DF’d
Quad Lag
Isometrics
Muscle Setting Ex’s
- LOW-MOD intensity iso. ex —– little to no resist.
- practicing mm activation
- No appreciable inc in strenght—-MAY slow atrophy
- INC recruitment of mm
- ADD. uses
- relaxation, circulation, reduce pain/spasm
Active/Passive Knee Flex.
Limitations in Knee FLEX freq. targeted w/ HEEL SLIDES
To INC FLEX
- Active Heel Slide
- use HS to achieve MAX FLEX.
- Active Assited Heel Slide
- hand or belt to apply overpressure @ end range
- Passive Heel Slides
- fully use hand/belt
Interventions in Sx Modulation Phase
Painful MTU’s
LOAD CAREFULLY!!!
- 2-3/10 pain
- soft tissue mobs
- GENTLE stretching of mm’s
- LOW grade Iso’s
- mult. angles
Interventions in Sx Modulation Phase
Limited ROM
- Patellar mobs (as necessary) —– CAN ALWAYS MOBILIZE PATELLA!!!
- AROM (if pain free OR min. pain)
- AAROM (if pain free)
- PROM (if pain free)
- Cyclic ROM (flex/ext)—> helps w/ ROM + Effusion
- stationary cycling w/out resist.
-
Injured ligament….
- restore ROM w/out INC pain or overstressing ligament
Add. Interventions for TKE
when Acute or Symptomatic

Classification of Knee Related Sx’s in Motor Control Phase
Stiff Knee
- Limtd ROM
- Painful or Uncomfortable ROM
- MM Length restrictions
Classification of Knee Related Sx’s in Motor Control Phase
Unstable Knee
- Ligamentous instability
- Meniscal Issues
- Poor Neuromuscular control
- Pain related instability
Classification of Knee Related Sx’s in Motor Control Phase
Weak “Knee”
- Limtd Strength of a Muscle relevant to knee jt function
- Pain-related weakenss
Simplified Tx Approach!!!
If its contributing to Activity Limitations or Participation Restrictions AND…
-
if its Limited
- Mobilize it!
- if its Tight
- Stretch it!
- if its Weak
- Strengthen it!
- if it Moves Funny
- Retrain it!
- if its Involved
- Load it thoroughly
-
If its Injured**
- Do all of this CAREFULLY!
Joint Mobilization to Improve Knee Flexion
Patellofemoral Joint
What happens as knee flexes?
- patella glides INFERIORLY
- lateral facet and odd facet contact femur
- greater compression laterally—-esp w/ effusion
- bc high lat. wall of trochlea
Joint Mobilization to Improve Knee Flexion
Patellofemoral Joint
Intervention:
- Medial and Inf glides IN FLEX
- Medial tilt mobs in Resting****
- when patello moves the most!
Joint Mobilization to Improve Knee Flexion
Tibiofemoral Joint
What happens as Knee Flexes?
- Tibia glides POSTERIORLY
- MIN. tibial rotation
- MAYBE some post. pinching or impinge.
Joint Mobilization to Improve Knee Flexion
Tibiofemoral Joint
Intervention:
- Jt distraction in Sitting
- POST glides IN FLEX
-
If Post. Impinge.
- Ant/Rotational glide
Joint Mobilization to Improve Knee EXT
Patellofemoral Joint
What happens as knee EXTs
- patella glides SUPERIORLY
-
FULL EXT== min. contact w/ walls of trochlea
- GREATER compression LAT.—-bc tilt of patella
Joint Mobilization to improve Knee EXT
Intervention:
- Medial + Superior glides in FLEX
- Medial tilt mobs in RESTING
Joint Mobilization to improve KNEE EXTENSION
Tibiofemoral Joint
What happens here when knee EXTs?
- Tibia glides ANTERIORLY
- Tibia must Externally rotate to engage Screw Home Mechanism
Jt. Mobs to improve KNEE EXT
Tibiofemoral Joint
Intervention:
- Jt. distraction in SUPINE
- ANT glides in EXT
- If missing TKE—–MAY need to bias Tibial ER
Proximal Tib/Fib Jt Mobs
When performed ?
- PAIN in Distal Anterolateral Knee Jt OR specifically @ Fibular head
- mostly ANT/POST glide req’d for norm. ankle motion
- impacted w/ injury to biceps femoris
Assess. and Intervention of Muscle Performanc in Motor Control Phase
GOLD STANDARD for measuring QUADS Strength in clinical studies
Electromechanical Dynamometry
Isokinetic Machine
*HIGHLY reliable
*expensive
Assess. and Intervention of Muscle Performanc in Motor Control Phase
1-RM
Leg Extension
Can use SL leg press if needed
- Procedure:
- alternating limbs
- fully ext. knee
- HOLD 2s
- return under control
- Failure det’d by 3 unsuccessful attempts @ a single weight
- MAX wt. lifted recorded for ea. limb
- alternating limbs
Leg Press 1-RM
Standard Leg Press S/L
- Knee @ 90
- Hip ~90
- Compensation avoided:
- gastroc-soleus min’d
- OPP limb suspended
Leg EXT 1-RM
Standard Leg EXT Machine
- knee @ 90
- hip @ ~90
-
2 ranges tested:
- 90-0
- 90-45
Remember….
W/ BIG mm’s
Functional Tests!!!
L.EXT
L.Press
HHD’s
Functional Strength Testing:
Ex’s
- Sit to Stand/Chair Rise test
- Forward Step Down Test
- Lateral Step Down test
- S/L Squat test
More Functional Tests Ex’s
- 30s Chair Rise
- 5x S2S test
- SL 30s vs 5x ea leg
- Forward step down—-endurance
Assessment and Intervention of Muscle Performance in Motor Control Phase
Also consider…
MM’s that control Femur
- glute max
- glute med
- ER’s
- iliopsoas
- sartorius
Assessment and Intervention of Muscle Performance in Motor Control Phase
Also consider…
MM’s that control Tibia
- Gastroc/Soleus
- Peroneals
- Post. Tib
- Ant. Tib
MOST important aspect in Knee Function
Strengthening Quads!!! during Motor Control Phase
Quads Isometric Matrix
ADD IN PICTURE!!!
SLIDE 32 IN FIRST KNEE LECTURE!!!!
Sit to Stand
Anterior View
trunk moves vertically
pelvis stays lvl
Knees stable in frontal plane (slight hip ABD encouraged)
foot should NOT over-pronate
Sit to Stand
Lateral View
no L/S flexion
pelvis + hips move trunk into Flex.
motion comes from knees
CoP should NOT shift into ball of foot
What should you remember w/ sit to stands as an intervention?
YOU CAN MAKE THE DISTANCE LOWER OR HIGHER!!!
Mini 30deg squats or Full 90deg squats
or anywhere in b/w!!!
Advanced WB ex.
Sit to Stand
Preferential squatting
Key points:
- surgical leg BEHIND good leg
- shift wt. onto sx limb
- load thru heel
- avoid excess. trunk flex
Perturbation Training in Knee Jt Stability
What is it?
- Progressive, purposeful manipulation of support surfs. to promote active stabilization and NMSK control of knee
Perturbation Training in Knee Jt Stability
Studies in ACL deficiency and Post-Op ACL
*good clinical and biomech. results*
- Knee jt. mechs resemble uninjured indiv’s after completing ~10 sessions of perturbations
-
Reduction of wear & tear
- normal knee jt loading
- normal knee jt flex/ext excursion during gait
- reduction in knee Ext/Flex co-contraction
-
Reduction of wear & tear
- Improved confidence/reduced mvmt-related fear
- SOME improves in clinical measures
- ex. hop tests
Perturbation Training in Knee Jt Stability
SOME bennies for OA, not consistent
- Pts w/ OA more heterogenous than pts after ACL injury
Meniscal Tears
Longitudinal
(Buckethandle)
- springy end feel
- IMMEDIATE REPAIR
- easy to screw up
- meniscus flips over into joint

Meniscal Tears
Oblique
- typ. older pts
- does OK w/ repair

Meniscal Tears
Radial or Transverse
see pics

Meniscal Tears
Horizontal
- when you bear wt. w/ this tear—–> pushes edges closer together

Meniscal Tears
Complex Degenerative
- does well w/ OR w/out Sx
- Older pts—degenerative
- you want to DEC mech. sx’s

Meniscal Injuries
MOI
- Cutting/Pivoting
- sudden direction change w/ foot fixed ground
- HYPERFLEXION
- HIGH impact compression
- MCL or ACL Mechs.
Meniscal injuries
MOI
MCl or ACL Mechs…..why?
- MCL
- deeper fibers connect to MCL
- ACL
- connects to Ant. Horn or Med. Meniscus
Meniscal Injuries
S/S
- Twist/tearing sensation @ time of injury
- Severe pain ON injury—-Effusion 6-24 hrs POST-injury
- Giving way on injury
- Later, intermittent pain, effusion
- CATCHING OR LOCKING
- Jt. line tenderness
- Limtd ROM w/ premature end feel
- IF piece of meniscus IN joint
- Repro. of sx’s w/ deep squatting or HYPERFLEX pain
- **Quad inhibition**

Meniscal Special Tests:
5 “Cluster” Dx Tests
REVIEW YOUR LAB NOTES!!!!
YOU GOT THIS SHIT!!!
- Joint line palpation
* be sure to go BEHIND KNEE!!!
- Joint line palpation
- McMurray
* Axial loading- can combine IR, ER, ABD, ADD
- McMurray
- FLEX overpressure
- EXT overpressure
- Hx of Catching or Locking
Clinical Composite Score for Meniscal Patho.
**accurately detects meniscal patho.
- Studied 635 knees w/ 5 Dx (cluster tests) tests eval’d presence of meniscal lesions
- Hx catching/locking
- Jt line tenderness
- Pain w/ forced HYPEREXTENSION
- Pain w/ MAX passive Knee FLEXION
- Pain or Audible click w/ McMurray
Mensical Special Tests
Thessaly Test
see pics

The “Dancing” one
Meniscal Special Tests
Apley’s Compression
Apley’s Distraction
Exactly what it sounds like…..the Med/Lat rotate Tibia

NON-OP Tx of Meniscus Tears
What did MeTEOR Study find?
- Often, acute tears are operatively addressed
-
DMT’s (degen meniscus tears) MAY be amenable to non-op care
- lg, multi-center study of OP vs. NON-OP for DMT vs. OA (MeTEOR Study)
- 6m after randomization, 30% NON-OP groud had sx
- 94% of OP group had Sx
****REMEMBER WE WANT TO TRY AND AVOID GEN. ANASTHESIA ****
Sx vs. PT for Meniscal Tear w/ OA
The New England Journal of Medicine
BIG DEAL TO BE PUBLISHED BY THEM!!!
-
NOTE:
- equivalent outcomes in WOMAC scores AND KOOS Pain Scores b/w the 2 methods!!!

Summary of PT Regimen
Sx vs. PT for Meniscal Tear and OA
New England Journal of Medicine
PHASE I

Summary of PT Regimen
Sx vs. PT for Meniscal Tear and OA
New England Journal of Medicine
PHASE II
&
PHASE III

Knee–Meniscal Injuries
Partial Menisectomy
When?
- IF meniscal tear disrupts mechanics of the knee AND pt is not a good candidate for meniscal repair
-
****DEBRIDEMENT***
-
remove as little as poss.
- down to a stable rim
-
remove as little as poss.
Rehab Following Arthroscopic Debridement (Menisectomy)
*NOTE: these are EASIER to rehab
3 things we focus on:
- Muscle Strengthening and Joint Mobility
- Ambulation
- Return to Activity
Rehab Following Arthroscopic Debridement (Menisectomy)
*NOTE: these are EASIER to rehab
Muscle strengthening and joint mobility
- Isometrics, AROM, PF mobs IMMEDIATELY
- Soft tissue manip. of portal scars when healed
- Progress to PREs when tolerated
- consider NMES
Rehab Following Arthroscopic Debridement (Menisectomy)
*NOTE: these are EASIER to rehab
Ambulation
- WBAT IMMED. w/ least restrictive AD
- progress to FWB when walking w/out limp
-
usually 1-2 wks
- want NEGATIVE quad lag
-
usually 1-2 wks
Rehab Following Arthroscopic Debridement (Menisectomy)
*NOTE: these are EASIER to rehab
Return to Activity
- TM running if…
- quad strength >80%
- NO jt. pain
- trace or less effusion
- Lvl Surf. Running, sprints, agility if…
- normal gait on TM
- no reactive effusions after TM running or any progress. of activity
- Return to full activity (usually about 6 wks) if…
- quad strength >90%
- HOP Tests if returning to lvl I or II sports
Meniscal Repair
When considered?
- considered when lesion is in area of good vascularization
-
IF tear w/in 3mm of periphery
- vascular
- IF 3-5mm from periphery
- gray zone
- IF >5mm from periphery
- avascular
-
IF tear w/in 3mm of periphery

Indications and Contraindications for Meniscus Repair
NOTE: ACL + Meniscus together===> MORE blood supply ===> better healing
see table

Superior Vertical divergent suture
Inferior vertical divergent suture
see pics

Radial Meniscus Tear Repair
see pics

Repair for Flap Tears
see pics

Meniscal Repair of Avascular, Central Region
*Becoming MORE COMMON
*Want to preserve meniscus when possible!!!
- Mods. of Sx tech’s to enhance healing in this area used:
- Fibrin clot
- Rasping of synovial fringe
- Creating vascular access channels

Meniscal Repair of Avascular, Central Region
Older Pts 40+
What did this study show?
30 repairs in pts 40+
26 pts asymptomatic; had NO further Sx after mean of 34 mos
see pics for Rehab program + Conclusions

Meniscal Repair of Avascular, Central Region
Younger pts <20yo
what did this study find?
- 71 knees of indiv’s <19yo
- 75% had NO sx’s and showed no signs of clinical failure @ follow-up (18-51 mos)
see pics for Rehab Program followed:

Meniscus Root Repair
**NOTE: where meniscus is most firmly attached
usually protected 4-6wks
*like trying to carry a bucket w/out other side of handle attached ****
- HOOP STRESS!!!
- disrupting root can cause meniscal extrusion in WB
- AFTER repair—WB can sig. stress repair
- shown in Biomech. studies not clinical studies
-
HS’s attach to medial meniscus****
- contraction causes post. glide
Meniscal Repair and Transplantation
- preserve meniscal tissue at all costs
-
Goal of Rehab:
- prevent excess WB and compression that has pot. to disrupt graft or transplant
- protocols based on type of meniscal lesion, concomitant proc’s, stage of degen.
- Peripheral tears progressed quicker vs. central tears****
-
SPECIFIC ROM & Heckman et al strongly recommend patellar mobs in ALL directions!!!
- can always mobilize patella!!!

Explain Cartilage Cyclic Loading
- Cartilage is like a sponge
-
Load ON==
- push BAD stuff OUT
-
UNLOAD==
- GOOD stuff comes IN
-
Load ON==

Articular Cartilage
Explain…
- SELF-lubricating
- Load Applied=== Fluid RELEASED
- Load Released===Fluid ABSORBED
- Lack of intermittent loading REDUCES lubrication process
Articular Cartilage Respone to Loads
in Knee
when REDUCED LOADING
-
Reduced Nutrition
- == degen changes
-
Reduced Lubrication
- == INCs friction b/w jt surfs
- == degen changes
- LOW coeff. of friction
Articular Cartilage Response to Loads
in Knee
when EXCESSIVE LOADING
- *Actually has ability to bear VERY LG LOADS
- Damage to collagen fiber network
- Proteoglycan wash out
- Loses ability to respond to compressive AND shear forces
Articular Cart. Response to Loads
in Knee
when IMPACT LOADING
- Occurs when loads applied @ FAST RATE
- Cart. becomes stiffer
- now unable to deform and redistribute loads fast enough
The Knee–Art. Cart. Response to Immobilization
see pics for REVIEW

Physical Stress Theory
Tissue Stress= Load/Area of Load Application
- Too MUCH or Too LITTLE stress may be harmful to bio. tissue
- Window of Adequate Stress that maintains health of biologic tissue

Joint Stress/Tissue Stress== Force/Area of Force Application
-
FORCE components
- current or prev. injury
- Magnitude of Load
- body mass
- activity surface
- foot wear
- AD (grad. use)
- Muscle and motor strength
-
Area of Force Application components
- Loading rate
- Joint mobility
- Joint alignment

Osteoarthritis
OA
- Degen of Art. Cart.
- 80% indiv’s 65+
- Females>Males
- 70% vs. 30%
- Risk Factors:
- age, gender
- occup/rec. activity
- obesity***
- LE malalign.
- QUAD WEAKNESS
- Prev. structural damage to knee****
OA Self-Report Symptoms
- ***Typ. stiffness in morning that resolves w/in 30 mins**** CARDINAL SIGN
- Pain w/ prolonged sitting bc no cart. nutrition
- creak/crack/crunch (crepitus)
- Occ. pain @ night
- diff’s on stairs
- bc poor eccentric control
OA S/S
- Pain w/ WB
-
Loss of Jt Mobility====CAPSULAR PATTERN
- Flex > Ext ***************
- poss. effusion
-
Quad weakness and/or inhibition
- remember quad strength super important in obstructive lung diseases too!!!!!!
- Osteophyte formation
Altman’s Criteria for OA
Clinical
6 Criteria
- Age >50yrs
- Stiffness >30mins
- Crepitus
- Bony tenderness
- Bony enlargement
- No palpable warmth

Altman’s Criteria
Clinical and Laboratory
Knee Pain and @ least 5 out of 9 criteria
- Age >50yrs
- Stiffness >30mins
- Crepitus
- Bony tenderness
- Bony enlargement
- No palpable warmth
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate <40
- Rheumatoid Factor <1:40
- Synovial Fluid signs of OA

Altman’s Criteria
Clinical and Radiographic
Knee Pain and @ least 1 of 3 Criteria
- Age >50yrs
- Stiffness >30mins
- Crepitus
- Osteophytes

OA
Look @ picture specifically @:
Osteophyte formation
Sclerotic (hardening) subchondral (below cart.) bone
Narrowing of jt. space (loss of art. cartilage)

OA
Basic Tx Approach
Alter Joint Stress by Minimizing Loads and Maximizing Area of Load Application
Joint/Tissue Stress==Load/Area of Load Application
- mm strength and jt. mobility
- Wt Control: diet+exercise
- AD’s
- proper foot wear+orthotics
- modif. of act. surfs
- minimize impact loading
Osteochondral Lesions

- separation of fragment of art. cart. from the underlying subchondral bone from the epiphysis
-
Cart. pulls off of bone==> delaminates
- *NOTE: different from OCD which is seperation of the ACTUAL BONE FRAGMENT from the subchondral region
-
Cart. pulls off of bone==> delaminates
- Result from:
-
prolonged, repetitive loading OR traumatic, high impact loading
- typ shearing injury to WB area of bone
- seperation of cartilage in the Weakest zone
- *tidemark area*
-
prolonged, repetitive loading OR traumatic, high impact loading
Risk Factors Assoc’d w/ Articular Cart. Lesions
- pt age
- INC age==INC likelihood (bc degen.)
- Presence of meniscal tear
- ACL Injuries (following are presented w/ cum. loading w/ shearing forces:
- 2-5yrs after ACL w/out repair, odds were 2.2x higher of having subsequent art. cart. injury vs. in first year
- after 5 yrs odds inc’d to 5.9x
- Retrospective study showed prevalence of art. cart. lesions w/ ACL injury to be 19%
- Large study of pts undergoing arthroscopy 60% were found to have chondral lesions
- Clinical exam may be inconclusive w/ pts presenting w/ non-specific complaints of jt pain or swelling
Traumatic Osteochondral (OC) lesions
Lateral Patellofemoral Dislocation
- OC lesion occurs on relocation
- Med border of patella compresses against lat. fem. condyle as it is reduced by quads. contraction
- Combo of compression + shear cause OC fx of either the lat. fem. condyle OR med. inf. patellar surf.
Traumatic OC Lesions
ACL Rupture
- During displace. of femur, ant tibial spine may contact med. fem. condylar surf. ==== causes lesion
- Lat. fem. condyle can also be injured by forceful compression + shear that occurs when femur and post-lat. tibia collide during relocation of a “giving way” episode
Osteochondritis Dessicans (OCD)
- Defect in subchondral region w/ partial OR complete separation of bone fragment
- Overlying art. cart. may remain intact
- Prognosis depends on age and WB surf. affected AND the condyle

OCD
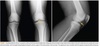
OCD w/
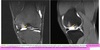
OCD
Presentation, Signs, Symptoms
- COMMON older children/young adult MALES
- no hx traumatic event
- accumulative trauma/stress mech.
- phys. active adolescent OR
- rel. sedentary, overweight
- non-local knee pain WORSE w/ jumping/WB
- intermitt. effusion w/ pain
- catching/locking/giving way IF loose body present
- Laxity test NORMAL
- affected fem. condyle tender
- forcible compression on affected side==Crepitus
OCD
Tx
- Rel good healing pot. IF physeal plates NOT YET CLOSED + lesion stable
- improved if art. cart. over lesion INTACT
- WB restricted 6-8wks
- some evidence for casting <12yo
- PT works on strength + ROM DURING pd of NWB
- sx follows pts for 6mos before return to high impact act.
-
IF UNSTABLE LESION OR CLOSED PHYSEAL PLATES====Sx Repair
- == fragmental separation
- PT Role==Recognize when present and refer out
Art. Cart. Repair Procedures
More for Osteochondral defects:
- Abrasion arthroplasty
- Micro-Fx
- promotes blood supply + bone healing
- Mosaicplasty (OATS)
- Autologous (from self) Chondrocyte (cartilage cells) Transplantation w/ Periosteal Graft
- Re-align. proc’s
Basic Science and Sx Tx Options for Articular Cartilage Injuries of the KNEE
written by physicians for PT’s

Abrasion Arthroplasty

to joint OR jt. surf.
one small portion
- subchondral bone abraded to create bleeding in lesion site
- Fibrin clot forms in lesion
-
Fibrin clot facilitates mesenchymal cells to form fibrocart. in the defect
- Mesenchymal Cells:
- stem cells found in bone marrow that are important for making and repairing skeletal tissues: cartilage, bone, and fat found IN bone marrow
- Mesenchymal Cells:
Micro-Fx Procedure

Abrasion Arthroplasty ON STEROIDS!!!!
- Sm. holes punctured in subchondral bone
- Stem cells from bone marrow migrate into lesion site
- Stem cells become chondrocyte-producing cells that eventually synthesize fibro-cart. in the lesion site
*NOTE: athletes + older adults PRIOR to TKA will use.
Mosaicplasty (OATS) Procedure
Osteochondral Autograph Transplant Sx

- Hyaline cart. grafts w/ underlying subchondral bone harvested from NWB site
- Grafts press-fitted into lesion site
- SMALLER lesions get Autologous (from self) grafts
- LARGER lesions get Allografts (from cadaver)
NOTE: Fibrocartilage vs. Hyaline Cartilage
Fibrocartilage is WEAKER
Hyaline Cartilage is STRONGER
Autologous Chondrocyte Transplantation w/ Periosteal Graft
*graft==something put over top of something else (think skin grafts w/ burns)

- Autologous (self) chondrocytes (cart. cells) from biopsy (taken from YOU) grown in culture
- Cultured chondrocytes injected INTO lesion site
-
Periosteal graft fixed OVER lesion site
- to keep them in there***
- Stims formation of more hyaline-like (STRONGER) cartilage in lesion
Autologous Chondrocyte Transplantation w/ Periosteal Graft
*graft==something put over top of something else (think skin grafts w/ burns)
Another Pic of procedure

KNEE
Re-alignment Procedures
Tibial Osteotomy (tomy==cutting)
- Closing Wedge
- Opening Wedge
- Mechanical Axis shifted AWAY from affected compartment
- totally re-align joint
- arthrokinematics changed

Cartilage Repari Proced’s
Post-OP Rehab
- Pd of NWB/PWB 6wks
- aquatics + de-weighing devices for progressive WB
-
Controlled Jt. Mob. Acts.
- EARLY MOTION GOOD
- Motion combining compression + shear NOT GOOD
- EX. loading jt thru range
- DO use passive, AAROM, NWB AROM
-
Intermittent loading > static loading
- loading should be compressive w/out shear
-
Resistance Ex.
-
brief, intermittent isometrics holding only few secs/rep > sustained iso’s
- iso’s avoids compression combined w/ shear
- IF resistance ex’s w/ motion— use arcs of motion that do NOT engage lesion
- MOST lesions engaged b/w 20-70deg knee flex.
- NMES to INC quad strength
-
brief, intermittent isometrics holding only few secs/rep > sustained iso’s
Current Concepts for Rehab and Return to Sport after Knee Art. Cart. Repair in Athlete
Tables 1 & 2

Current Concepts for Rehab and Return to Sport after Knee Art. Cart. Repair in Athlete
Table 3



