Key Points Flashcards
(26 cards)
What is the general form of a continous population model for a single population?
A continous population model in general is given by:
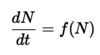
What are the fixed points of a continous population model?
The fixed points of this model satisfy:
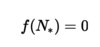
What must a fixed point satisfy to be feasible?
And a feasbile fixed point must be positive to correspond to a physically meaningful biological population:
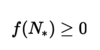
What are the stability criteria for a fixed point of a continous population model?
A fixed point has the following (asymptotic) stability criteria:
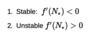
How can the stability of a continous delay model be analysed?
Why are discrete models needed?
Discrete population models are useful as differential equation models imply a continuous overlap of generations. Many species have no overlap between successive generations and so population growth is in discrete steps.
These models are represented mathematically using difference equations.
How can the following difference equation be solved?
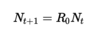
This difference equation can be solved directly to obtain geometric growth / decay based on the value of the net reproductive rate R0:

What is the general form of a difference equation?
In general a difference equation has the following form:

What defines a fixed point of a difference equation?
A fixed point satisifes:
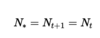
What is the stability criteria for a difference equation?
With stability criteria somewhat analagous to the continous case:
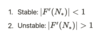
What is the general equation for the ‘moments’ of a probability distribution?
The moments of a population distribution are given by:
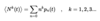
What is the general equation of a probability generating function?
The probability generating function is given by:
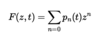
How is the extinction probability found from the probability generating function?
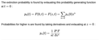
What is the general form of a two population model?
A two population model has the general form:
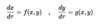
What are the fixed points of the two population model?
Where fixed points are the natural extension of the single population continous case:
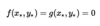
What are Nulcines?
Nulcines are lines where the derivatives are zero:

How can the direction of Nulclines be determined?
The direction of the motion aling the nulclines is given by:
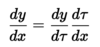
How are fixed points defined from the Nulclines?
What is the Community Matrix?
The Community Matrix is defined as the following:
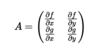
How can the stability of a two population model be analysed?
The eigenvalues of the Community Matrix can be analysed for each fixed point.
What is the standard equation to find the eigenvalues of the Community Matrix?

How else can the eigenvalues of the Community Matrix be determined?

What are the stability relations for the eigenvalues of a two population model?
The stability is based on the following relations:
- Both eigenvalues have negative real components - Stable / Attractor
- Eigenvalues have real parts with mixed sign - Unstable (Saddle Point)
- Both eigenvalues have positive real componennts - Unstable / Repellor
How can stability be indicated using the Trace and Determinant approach?
Stability can also be considered in terms of the trace and determinant without needing to obtain the actual eigenvalues to get an idea of whats going on: