Discrete Population Dynamics Flashcards
(13 cards)
What is a discrete population model? (How is it different to the continous models)
The use of continous modelling is sometimes not appropriate for biological systems.
This is because many systems have no overlap in generations and population growth occurs in discrete steps.
Continous modelling might be a good approximation depending on time scales involved and the time between generations, however in some cases the discreteness is very important.
What type of equation is used to construct discrete models?
- Difference Equations
What is the difference equation for geometric growth & decay?

What is the solution to the difference equation for geometric growth & decay?
The difference equation for geometric growth and decay is given by the following:
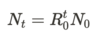
What are the fixed points of the difference equation?
The fixed points of the difference equaton obey the following:
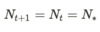
How does cobwebbing work?
Cobwebbing involves the following process:
- Draw parameter R0 .
- Draw fixed point line.
- Move from starting value to the parameter line, move horizontally to the fixed point line and repeat.

What is the stability criteria for difference equations?
The Asymptotic stability criteria is similar to the continuous case for ordinary differential equations. The stability criteria is the following:
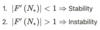
What is the logistic map?
The logistic map is the discrete version of the logistic equation, which is given by:

How is the logistic map derived from the logistic equation?
- Approximate the derivative term with a first principles definition.
- Scale time so that delta t = 1 for one generation.
- Change to dimensionless form.

What is period doubling behaviour?
Period doubling behaviour is when in the long term limit the population reaches a permanent oscillation between two distinct values.
This behaviour is understood by considering the doubly interated map, that has the same fixed point along with additional fixed points that are only real for certain parameter values.

How does Chaos emerge in discrete models?
Chaos emerges from higher order maps. These are more complicated to solve as the polynomials involved to find the fixed point are higher order.
Dynamical Chaos is when for almost all inital conditions we no longer see oscillations of a finite period.
This means that any slight variations in the inital population result in massivley different results overtime.
What are delayed difference equations?
Delayed Difference Equations are the discrete analogue to the delayed differential equations considered in the continous modelling.
What is the discrete version of the Hutchison-Wright model?
The discrete delayed logistic equation is given by:



