Intro to Cardiovacular Flashcards
(16 cards)
what are the 3 tissue leayers of arties and veins? what are they made of?
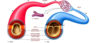
- Tunica externa (outer-most layer)-made of connective tissue-aka adventitia
- Tunica interna (inner most layer)-made of thin layer of endothelial tissue
- Tunica media (middle layer)-made of smooth muscle and elastic tissue
_____experience much higher BP than _____, so they have a stronger wall
- arteries
- veins
How does the tunica media vary b/w different arteries?
- Conducting (elastic) arteries–>(i.e. aorta); high amount of elastic fibers [able to stretch]
- Muscular (distrinuting) arteries–> control the flow of blood to differnt parts of the body; high amount of smooth muscles
- Arterioles–> all smooth muscle (control flow of blood in capillary beds)
Know anatomy of the heart


Flow Chart of the pathway of blood Flow
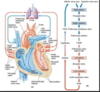
Chart
What is Diastole, what happens to each kind of valve?

Diastole=the heart is relaxed and filling with blood from the SVC, IVC and Pulmonary veins (from the lung carrying Oxygenated blood)
AV valves (Mitral and Tricuspid) are open
SL valves (Aortic and Pulmonary) are closed
What is Systole and what is happening to the major valves?

the ventricles are contracting, pumping blood out of hurt and into lungs and body
use the:
- pulmonary truch and pulmonary arteries (blue=blood deoxygenated
- aorta
AV valves are closed (don’t want blood rushing back to atria)
SL valves are open (access to the above regions)
Compare and contract the pulmonary circulation and the systemic circulation

Pulmonary Circulation: goes into lungs
right heart –>pulmonary trunk –>arteries –>capillaries in the lungs –>pulmonary veins
Systemic Circulation: goes to the rest of the body
left heart -> aorta -> arteries throughout the body ->capillaries throughout the body ->veins -> superior and inferior vena cava
What is a portal vein?
vein that connects a capillary bed to another capillary bed
portal veins connect two capillary beds
hepatic portal veins connect the capillary bed of digestive tract to capillary beds of liver
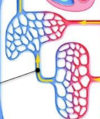
in arteries the average pressure = _____ Hg
in veins, the average pressure = ______Hg
in arteries the average pressure = 100mm Hg
in veins, the average pressure = 5-10 mm Hg
______ come together to form veins
Venules
(A)n_____________ a collection of vessels that allow multiple possible pathways of blood flow to the same tissue. Where could you find one?
Anastomoses
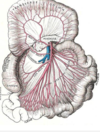
in the digestive tract =superior mesenteric artery. if one of the arterial branches is blocked, no region of the intestine will be deprived of blood; important in the digestive tract because intestines move around often and arteries can get blocked
ALSO FOUND IN THE JOINTS
how does blood flow in lungs differ from blood flow in gut?
- in lungs, pulmonary arteries branch repeated, but don’t reconnect; so occlusion of any part of branch downstreamwill cause loss of blood supply
- in digestive tract, if one of the arterial branches is blocked, no region of the intestine will be deprived of blood because branches reconnect at capillary level
- what is the function of the lymphatic system?
- Are there any downside to this system?
- It is a system of capillaries and ducts that functions to drain excess fluid out of the tissues and back into the blood.
- Lymph capillaries are more porous than blood capillaries, so it’s easier for the excess fluid to move into the lymph than back into the blood.
how much lymph is produced by day? _______
3 L
lymph goes thru lymph nodes and gets put back in circulation near the ________ of the heart
Right atrium



