Intraoperative Fluid Management and Endocrine Pharmacology Flashcards
Effective vs Innefective Osmoles

Total body osmolality

Plasma vs Water

Colloids in common use

Albumin

Hydroxyethyl Starches (HES)

Adverse effects of Hydroxyethyl Starches (HES)

Dextrans

Biguanides - metformin

Sulfonylurea – glyburide, glipizide, glimepride
meglitinides - nateglinide, repaglinide
Glyburide belongs to the sulfonylurea class of oral hypoglycemic drugs. These medications work by closing potassium channels in the β-cell membranes, leading to depolarization of the cell, and eventual insulin release via calcium reflux.

Thiazolidinediones - PPAR-γ ligand
These drugs are synthetic ligands for the transcription factor PPARγ, a member of a superfamily of nuclear receptors including thyroid and steroid receptors. PPARγ is expressed in multiple tissue types (e.g. skeletal muscle, fat & liver). PPARγ stimulation upregulates the expression of genes involved in lipid & glucose metabolism, insulin signal transduction, and adipocyte differentiation. As illustrated, one mechanism contributing to the glucose lowering effect of thiazolidinediones is an increased expression of the glucose transporter GLUT4.

Alpha glucosidase inhibitor
Competitively and reversibly inhibits enzymes in the small brush border responsible for the breakdown of oligosaccharides and disaccharides

Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitor
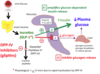
Sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitor (SGLT-2)
Mechanism of Action:
Inhibits the Na-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT-2) in the kidney to reduce glucose reabsorption, resulting in increased urinary glucose excretion, and lower plasma glucose.
SGLT-2 is expressed in the proximal tubule and mediates reabsorption of ~90% of filtered glucose (Kuriyama et al, 2014).
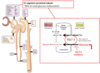
GLP-1 (glucagon like polypeptide-1) analogs
A synthetic analog of glucagon-like-polypeptide 1 (GLP-1) that is resistant to breakdown by DPP-IV.
























