Intestine I U6L04 Flashcards
how long is the duodenum?
first 11 inches

what seperates the duodenum from the jejunum?
ligament of Treitz.
The jejunum is ____ feet long, and is defined as the proximal 2/5 of the small intestine.
8
The ileum is ___ feet long, and is defined as the distal 3/5 of the small intestine
12
surface area of jejnum compared to ileium?
jejunum has 3x more surface area than the ileum
greater absoprtion occurs in the jejunum or ileum?>
jejjunum

how is increased surface area achieved in the GI system?
successive folding of the surface
The surface area of the small intestine is amplified at three levels:
(1) macroscopic folds of Kerckring
(2) microscopic villi and crypts of Lieberkuhn
(3) submicroscopic microvilli.
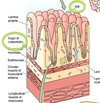
The surface area of the large intestine is amplified at three levels:
(1) macroscopic semilunar folds
(2) crypts (but not villi)
(3) microvilli

average length of the small intestine is
21 FEET
average increase due to mucusal folds?
average increase due to villi?
average increase due to microvilli?
mucosal folds – x 5
villi – x 10
microvilli – x 120
total absorptive surface area of the small intestine is 700 square memters or x ___ in size
x 1000
about ___ of the absorptive surface area is required for absorption.
what is the clinical implication for this?
half the absorptive surface area
half of the absorptive surface area can be surgically removed without compromising absorptive function
celiac disease is associated with a ____ in absorptive surface area
celiac disease is associated with a decrease in absorptive surface area
celiac disease is associated with a decrease in absorptive surface area due to a reduction in the
number and size of microvilli
Sprue is a type of malabsorption syndrome caused by sensitivity to___
gluten
Effect of gluten on small intestine? (2)
Gluten in bread by some means destroys absorptive cells and decreases the number of villi
what is Tropical sprue?
infectious disease associated with diarrhea, malapsprtion, and nutritional deficiencies
where are cells generated in the small intestine? where do they go?
. 1. Cells are constantly being generated at the base of the villi
- then migrate toward the tip, where they are extruded 3-8 days later.

how long are the cells of the intestinal mucosa replaced?
every week
goblet cells secrete protective mucous when stimulated by
acetylcholine
what happens to old extruded cells of the intestinal epithelium
extruded cells are digested in the gut, and their useful contents are recycled
what reduce the rate of cell renewal in the intestinal epithelium? (3)
radiation, malnutrition, or sprue.
The villi are comprised of absorptive cells called ____,
these are columnar epithelial cells in a single layer.
enterocytes
___ secretes the mucuous the lubricates the small intestine during peristalsis
goblet cells
what is common about goblet cells and enterocytes?
they have a common stem cell in the base of the crypts
The undifferentiated cells of the crypt secrete what? What does this cause
secretes NaCl from the blood into the lumen, and water follows osmotically
when do crypt cells stop secreting NaCL? what do they do after
stop secreting when they migrate upwards
get an absorptive function, absorbing with NaHCO3 or NaCl

radiation victims can experience what GI sx?
intestinal bleeding
diarrhea
slow death from malapsroption and dehydration
why are cells of the intestinal mucosa particularly vulnerable to radiation damage?
there is a high turnover of these cells
Intestinal absorptive cell. Transfer of materials occurs via two parallel pathways:
- transcelular pathway
- paracellular pathway
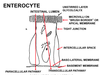
transcellular pathway
across the brush border, then through the cytoplasm, and finally across the basolateral membrane;
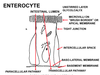
the shunt pathway (also called the paracellular pathway)?
viz. through the tight junction and the extracellular space.

tight junctions have high permeability for what?
low permeability for what?
high affinity – H20 and cations (like Na and K)
low permeability – anions
what is the major mamebrane for absorption of nutrients?
the brush border
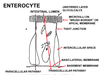
The ___ membrane contains ectoenzymes
apical (brush border)
what are ectoenzymes?
ectoenzymes (enterokinase, disaccharidases, and peptidases) complete the digestive process.
what does the basement membrane (lamina propria) contain?
capillaries and lacteals
how is the tight junction in a intestinal cell?
wraps around the cell like a collar
from leaky to most tight…
ilium? colon? jejunum?
jejenum (most leaky) –> ileum –> colon (most tight)
When you drink a glass of water, the liquid is rapidly absorbed in the ___ by osmosis.
jejunum
difference between dietrary intake and feacal otuflow equals
loss through kidney, lungs, sweat
this maitnains body fluid in a steady state
9.5L of fluid enters the body each day and must be ___

absorbed to prevent diarrhea and dehydration
___ absorption is responsible for more than half of the total fluid absorbed.
jejunal
what takes over it function if the jejunum is removed surgically?
ilum
Water and most nutrient substances are absorbed from the
duodenum and upper jejunum, being completely absorbed by the end of the jejunum.
what are two examples of substances not absorbed completely absorbed by the end of the jejunum.
vitamin b12 and ionized bile salts
what does vitamin b12 require to be absorbed?
combined with intrinsic factor
ionized bile salts undergo
enterohpetic circulation
where are ionized bile salts and vitamin b12 absorbd
in the distal ileum