Immunology Flashcards
Bcl-2
Anti-apoptotic protein
Decreased expression of Bcl-2 –> more susceptible to apoptosis
usually happens after inflammation
Where does B cells mature for birds
bursa of Fabricius 華氏囊

Compare small lymphocyte, lymphoblast and effector cell
Where do T and B lymphocyte mature for humans
T: thymus(but will regress with age)
B: bone marrow,bursa,Payer’s Patches
IL-1 / IL-6
IL-1: Promotes inflammatory response and fever
IL-6: promote innate immunity and elimination of pathogens
both secreted by activated macrophages
The 3 most important APC
Which one is the most potent?
Which one(s) need(s) to be activated in advance?
B-cell, Macrophage, Dentritic cell (most potent)
B-cell and Macrophage need activation. Dentritic cell doesn’t
MHC restriction and what cell
receptors on the surface of that cell could only recognize the antigen bound to MHC molecules.
T cells
IL-2
immunoglobin that can activate the T cells by binding to its surface receptor
Histamine
cause inflammation
receptors of it available on T cells
cell adhesion molecules
-確保T cells and APC 可以靠得很近+strengthen the bond between CD3/TCR on T cells and MHC on APC –> effective crosstalk
Increased expression of cell-adhesion molecules allows effective cytokines or cytotoxic substances transfer
- eg CD2 and LFA-1 on T cells
Which cell stimulate B lymphocyte by means of cytokines?
Th1? Th2? function of the other cell?
Th2
Th1: causing inflammation and activate macrophage
Cytoplasmic granules performed by NK cells
Perforin (穿孔素):在細胞膜上穿孔。
Granzyme (顆粒酶—):啟動細胞 apoptosis
ADCC
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
via FcγRIII(CD16)
NK cell上有 Fc receptor (FcγRIII/CD16) –> bind to Fc of antibody
- antibody in circulation detects antigen on a cell –> binding
- NK cell detect and bind to that antibody –> releasing cytokines 或 cytoplasmic granules,
- Cell lysis
ADCC除了NK以外中性球酸性球巨噬細胞也可以透過此機制消滅cell,癌細胞就是這樣消滅的
Macrophage in different Tissue (lung/CT/liver/bone/kidney/brain)
lung: alveolar macrophage
CT: histiocyte
liver: Kupffer cell
bone: osteoblast
kidney: mesangial cell
brain: microglial cell
Stages of Phagocytosis on macrophage
- psedopodia偽足:on the macrophage to 抓住 antigen –> 吞進去變成 phagosome
- fuse with lysosome –> phagolysosome
- Degradation of the antigen into smaller peptides of ~10 units
- if it is suitable –> sent to MHC II to express to T cells
Opsonization
Opsonization調理作用-透過antibody 幫忙
- After antigen coated with appropriate antibodyà the complex binds to antibody receptor on macrophage membrane
- More readily than antigen alone + enhance phagocytosis
- 若抗原被專一性抗體 coating,則其被吞噬的機率將提高 4000 倍。(ADCC)
- 不是所有抗體都有中和作用(僅少部分有中和作用的才叫中和抗體),但是所有抗體都可以進行調理作用。
Complement proteins
promote inflammatory response and elimination of pathogens
secreted by activated macrophages
Tumor necrosis factor(TNF)
secreted by activated macrophages
- to kill tumor cells
What are the granulocytes? Which one attacks parasite? Which one is not phagocytic? Which one causes allergy by histamine secretion?
Neutrophil, Eosinophil, Basophils
Eosinophils destroy the membrane of parasites by releasing eosinophilic substances
Basophil
polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PNL)
Neutrophils
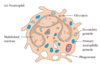
What does cytoplamic granules of Mast cell contains?
肥大細胞
- histamine(組織胺)
- Pharmacologically active substance
- IgE-primed (IgE binding 在mast cell或basophil上能觸發histamine的分泌),造成allergies。




