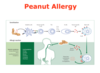
IMM 1 gut immunity .... Flashcards
Homeostasis in gut preserved by?
oral tolerance? depends on?
what promotes oral tolerance?
food allergy considered consequence of?
may underlie food allergen sensitization? where?

gut immunity
why is gut vulnerable?
what does this mean for the intestinal immune system?

exposures in early life, infant gut microbiota and future health?
early-life exposures?
symbiosis?
dysbiosis?
gut microbiota contrib to development of?
disruption causes?

microflora and GALT?

Microflora role in development GALT
GALT consists of?
What are ILFs what do they do?
Microbes and peyer’s patches
MAMPS stim what? also release of what?

immune response againse commensal microflora
how common commensal?
reside where?
can be killed by?
penetrate where? killed by?
survivors?
induce?
live bacteria and LNs
so how would B and T cells interact?

microflora health and disease
which cells associated with inflammation/Crohn’s?
Homeostasis?
allergy/food?
what do they release?

what comprise the mucosal firewall?
what does it do?
steps of microbes at the gut on?

relationship between microbiota, immune system, and diet
malnutrition affects?
microbiota acts as what barrier?
undernutrition?
recurrent infections predispose to?

SCFAs
come from?
these do what?

Immune tolerance?
oral tolerance?
failure results in?

central vs peripheral tolerance?
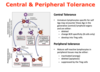
need for peripheral tolerance to antigens in intestine
why not central?

of critical importance in oral tolerance?
4 steps?
critical importance molecules do what?

tow main adverse food reactions?
non-toxic pathogenic mechanisms both?
Non-immune-mediated?
immune-mediated?

whats a food allergy?
two groups reactions?
IgE vs non-IgE?
delayed?