Imaging and Anatomy Flashcards
KIDNEYS
What is the round apex of the medullary pyramid known as?
What is the functional unit of a kidney? Which part is located in: a) the cortex? b) the medulla?
At which vertebral levels are the renal hila found: a) left? b) right?
What are the contents of the renal hila?
Renal papilla
Nephron: a) glomerulus, b) tubule
a) L1, b) L1/2
Renal vein, renal artery, ureter, lymphatics, nerves, renal sinus fat
KIDNEYS
Which renal vein is longer? Why?
Give 3 useful imaging modalities of the kidneys?
Left renal vein is longer, it passes anterior across the aorta to reach the right sided IVC
Ultrasound, CT, MRI
What structure is circled?

Transverse colon
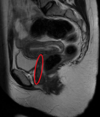
What structure is circled?

Duodenum
What structure is circled?
Liver
What structure is circled?

Spleen
What structure is circled?

Splenic artery
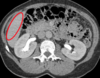
What structure is circled?

Adrenal gland
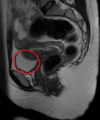
What can be seen at points:
A?
B?
Arrows?
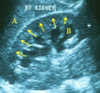
A) Right lobe of liver
B) Dilated calyx
C) Renal cortex
KIDNEYS
What is the main advantage of CT?
What are the disadvantages of CT?
What is the best way to see calculi on CT?
What are the 3 stages of CT imaging, from first to last?
Can see most pathologies
Radiation, and contrast induced nephropathy
No contrast
Corticomedullary, nephrographic, excretory
KIDNEYS
Describe the corticomedullary stage of CT?
Describe the nephrographic stage of CT?
Describe the excretory stage of CT?
25-75s after IV contrast
80-180s after IV contrast
5-15 min after IV contrast
In the retroperitoneum, there are 3 fundamental spaces. Which are shown by the:
Red arrow?
Blue arrow?
Green arrow?

Red = Anterior pararenal
Blue = Perirenal (enclosed by renal fascia)
Green = Posterior pararenal
What is CT contrast induced nephropathy?
There will be an increase in what?
What are some risk factors?
An impairment in renal function within 3 days following IV administration of contrast in the abscence of an alternative cause
Urea and creatinine
Renal impairment, diabetes, heart failure, nephrotoxic drugs, MI in 24 hours
What fluids should you give before a CT contrast scan of the kidneys?
1-1.5ml/kg 0.9% saline 12 or 6 hours before and after contrast administration.
Sodium bicarbonate 1 hour pre-procedure and 6 hours post
What are the main advantages of MRI to image the kidneys?
What are the diadvantages?
Visualise lots of pathologies and can do MR angiogram
Long time and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis