images Flashcards
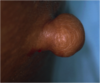
Fibroepithelial polyp
aka skin tag, acrochoordon, fibroma molle, squamous papilloma

FEP

epithelial inclusion cyst
filled with keratinous debris, lined by squamous epi and ganular layer
if ruptures -> foreign body giant cell rxn

epithelial inclusion cyst

Seborreheic keratosis
proliferation of epidermal basal cells

acanthosis nigricans

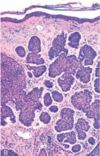
multiple cylindromas (papules)

cylindromas are composed of islands of basaloid cells containing occasional ducts that fit together like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle.

Perinasal papules and small nodules of trichoepithelioma

Perinasal papules and small nodules of trichoepithelioma are composed of buds of basaloid cells that resemble primitive hair follicles

sebaceous adenoma
look like rounded slightly yellow nodule

Pilomatrixoma
ghost cells

apocrine carcinoma

hemangiomas

hemangiomas

hemangiomas

errupitve xanthomas

erruptive xanthomas

Benign Fibrous Histiocytoma (Dermatofibroma)

Solar Lentigo

Melanocytic Nevus, Junctional Type

Melanocytic Nevus, Junctional Type

Melanocytic Nevus, Junctional Type

Melanocytic Nevus, Compound Type