Histology of Skin Flashcards
Three layers of skin/integument and tissue type of each
- Epidermis: keritinaized stratified squamous epithelium
- Dermis: dense irregular connective tissue
- Hypodermis: loose connective tissue (with many adipose cells)
Differences between thick skin and thin skin
Thin skin
- Has thicker dermis (makes it easier to suture)
- Has no lucidumlayer
- Has hairs, sebaceous glands, but fewer eccrine sweat glands
Thick skin
- Thick strarum corneum
- Lacks hairs, sebaceous glands, and apocrine sweat glands
- Thinner dermis
- Has more eccrine sweat glands
4 layers of the epidermis
From top to bottom
- Cornified layer
- Dead cell layer
- Granular layer
- Contains keratohyalin granules
- Spinous layer
- Contains langerhans cells
- Basal layer
- Contains merkel cells and melanocytes
Can Gorillas Sing Base?
Keratinocytes
Produce keratin which is a protective structural fibrous protein of skin
- Mitotically active in nasal layer
- Requires types I & II to form intermediate filament

Langerhans Cells
Monocyte derived dendritic antigen presenting cells
- Mediate T cell immunity
- Role in allergic contact dermatitis
- Found in spinous layer
- “Tennis racket shaped” on slide

Melanocytes
Derived from neural crest cells and produce melain via enzyme tyrosinase
- Melanin gives skin color and protects DNA of mitotic keritinocytes from UV damage
- Found in basal layer

Merkel Cells
Modified keritinocytes that function in touch sensation
- Associated with sensory nerve terminals
- Form desmosomal attachments to keritinocytes
- Found in basal layer of thick skin
Basal cell attachemnt to basement membrane vs each other
Basal cells attach to basement membrane via hemidesmosomes
Basal cells attach to each other via desmosomes
Effects of UV light on melanocytes and skin
- Darken melanin
- Increase number of melanosomes
- Increase melanin production
- Increasekeratinocyte uptake of melanosomes
- Sometimes increase number of melanocytes
Layers of dermis
Papillary layer
- Thin layer of loose connective tissue that fills epidermal ridges
- Contains Meissner touch corpuscles
Reticular layer
- Dense irregular connective tissue
Contents of dermis
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic cessels
- Nerves
- Sweat glands
- Sensory receptors
- Hair fillicles with sebaceous glands and arrector pili smooth muscle
Dermal papillae
Dermis projecting into epidermis
- Helps hold epidermis in tight contact with dermis
- Allows blood circulation to get as close as possible to epidermal keritinocytes
- Allows Meissner’s touch corpuscles to come as close as possible to surface of skin
Circulation of the skin and thermoregulation
Arteries and veins run through hypodermis and branch upward to form plexuses
- Cutaneous plexus at junction of hypodermis and dermis
- Papillary plexus at junction of papillary dermis and reticular dermis
Ateriovenous anastomoses (shunts) can send blood directly from arterioles to venules to reduce head loss
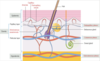
Composition and function of hypodermis
Composition
- Loose connective tissue
- Adipose cells
- Blood vessels
- Epidermal appendages (sweat glands and hair follicles)
Function
- Insulation
- Shock absorbtion
- Energy storage
- Ability of skin to slide over joints
Two types of sweat glands
Apocrine sweat gland
- Axillary and anogenital region
Eccrine sweat gland
- Ubiquitous but most numorous in palms and soles
Piloscebaceous unit
Pilosebaceous unit includes hair, hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and arrector pili muscle

Nerve endings, Meissner corpuscles, and Pacinian corpuscles
Nerve endings are associated with Merkel cells
- Touch
Meissner’s corpuscles
- Mechanoreceptors in hermal papillae
Pacinian corpuscles
- In deep dermis and hypodermis
- Sense pressure and vibration



