Histology Lab Flashcards
thymus
capsule, cortex, and medulla, T cells migrate to the thymus and develop in the cortex and migrate to the medulla
blood thymus barrier
found in the cortex 1. capillary endothelium and basal lamina 2. perivascular connective tissue 3. thymic epithelial reticular cells and basal lamina protects against pathogens
medulla
hassalls corpuscles and mature T cells
diffuse lymphoid tissue
MALT, GLAT etc. mostly B cells
GALT
so large that it pushes out into the submucosa; peyers patch- large aggregates germinal center
lymphoid nodule
located in tonsils
lymph node function
filters lymph and maintains and produces T and B cells
hilum
arteriole blood enters and leaves the lymph node
lymph node regions
cortex- lymph nodules- B cells paracortex- T cells no nodules just lymphocytes, thymus dependent region becuase thymus T cells migrate here medulla
high endothelial venule
- located in the capillaries within the paracortex of the lymph node, simple cuboidal epithelium - 90% of lymphocytes leave bloodstream and enter lymph node here by diapedesis
medulla
central region of the lymph node efferent lymphatic vessel
spleen
left upper quadrant 1. filter blood 2. stores and phagoctoses RBC 3. site of proliferation of B cells and T cells 4. Site of production of antibodies by plasma cells
spleen
red pulp white pulp
white pulp
lymphatic nodules mainly B cells
central arteriole in spleen
through the center of the white pulp
red pulp
no lymphatic centers
thymus contains what percentage of t cells and b cells
100% T cells
Developing T cells move form the cortex/medulla to the cortex/medulla
cortex to the medulla

- capsule
- cortex
- medulla

- mature T cells
- hassalls corpuscle

peyers patch - large lymphoid nodule that has extended fromt he mucosa into the submucosa

GALT
mostly B cells
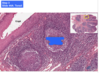
lymphoid noduel - B cells
top to the bottom

coretx
paracortex
medulla

- cortex
- capsule
- afferent lymphatic vessel
- subcapsular sinus
- lymphoid nodule - increased B cells
top left
right
bottom left

T cells
high endotherlial venule
paracortex
light center in the middle of the peyers patch are the ___________ centers
germinal

The cortex (outer region) of the thymus is the region in which T cells mature and become immunocompetent.

This is the medulla of the thymus. T cells originate in the bone marrow, migrate to the thymus (hence the T) for maturation, and then migrate to a secondary lymphoid organ like the paracortex of a lymph node.

These are lymphoid nodules in MALT (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue) of the small intestine. These cells are B cells which both originated and matured in the bone marrow before migrating to other parts of the body.

Tonsils are aggregates of lymphoid tissue (mainly B cells), which sometimes lack a capsule. All tonsils are in the upper section of the digestive tract, lying beneath but in contact with the epithelium. Tonsils assist in combatting antigens entering via the nasal and oral epithelia.

The paracortex (2) is located between the cortex (1) and the medulla (3). It is composed of a nonnodular arrangement of mostly T cells (the thymus-dependent area of the lymph node). The paracortex is the region where circulating lymphocytes gain access to lymph nodes via high-endothelial (post-capillary) venules.

The cortex (A) lies deep to the capsule, from which it is separated by a subcapsular sinus. It is incompletely subdivided into compartments by connective tissue septa derived from the capsule. The cortex contains lymphoid nodules and sinusoids. Lymphoid nodules are composed mainly of B cells but also of some T cells, follicular dendritic cells, macrophages, and reticular cells. They may possess a germinal center. Sinusoids are endothelium-lined lymphatic spaces that extend along the capsule and trabeculae and are known as subcapsular and cortical sinusoids, respectively.
The paracortex (B) is located between the cortex and the medulla. It is composed of a nonnodular arrangement of mostly T cells (the thymus-dependent area of the lymph node). The paracortex is the region where circulating lymphocytes gain access to lymph nodes via high-endothelial (post-capillary) venules.















