Histology Flashcards


What is each color?

Red= PCT
Orange= DCT
Describe the ultrastructure seen here

Juxtaglomerular apparatus at the vascular pole of the glomerulus. Distal tubule (with microvilli brush border) has the macula densa. The afferent arteriole has the juxtaglomerular cells (with renin granules). Extra-glomerular mesangial cells are somewhere.
What is this? What are the layers

Ureters!!!

What is this? What are the layers?

Adventitia
longitudinal muscle
circular muscle
longitudinal muscle
lamina propria
transistional epithelium
What are these?

Urethra and urinary bladder
What is this?

Prostate gland

Trichrome stain. Blue= collagen, pink=smooth muscle.
Glands secrete: prostaglandins, citric acid….other things
What kind of epithelium is this?

Not pseudostratified. 2 layers: basal and columnar
C;est quoi? Normal or abnormal?

Prostatic concretions
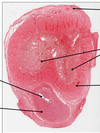

What organ is this from? What do the letters indicate?

S= vascular sinuses
HA= helicine arteries (so named because they follow a helical course when the penis is flaccid)
What is the epithelium in the penile urethra? What is it in the fossa navicularis?

Stratified columnar…. it changes south of the prostate. In the fossa navicularis the epithelium becomes stratified squamous.


What are the zones of the prostate? Which part is encapsulated?
Central zone (surrounds ejaculatory duct, not denoted on picture)
Peripheral zone (major site of prostate cancer and prostatitis)
Transition zone (surrounds the urethra, where BPH happens)
The capsule surrounds the posterior and lateral bits. The anterior (where there are no glands) has it’s own fibromuscular stuff.
What does the corpus cavernosa contain?
Vascular sinuses, smooth muscle, arteries, connective tissue
What are the glands that lubricate the penile urethra?

Glands of Littré
What is this?

EM of podocytes, their primary processes and secondary processes
What is this? What are the layers?

Fenestrated capillary epithelium, basement membrane, podocyte foot processes (filtration slits and slit diaphragms), bowman’s space


