Hemodynamic Disorders (Thrombosis/Emboli/Shock) 3 Flashcards
thrombosis vs embolic?

Thrombosis
what are the risk factors?
what is this called?
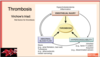
Triad part 1: endothelial activation
if damaged switches from what to what?

endothelial activation
prothrombotic: how?

Triad part 2: Alterations in blood flow
good type of flow?
bad?
how does this cause increased risk?

abnormal blood flow potentiates the triad how?

Triad part 2 alterations in blood flow
when/where would this occur? (5)
for the normal one what happens?

triad part 2: alterations in blood flow
dilated vessels. examples?
how do they affect?

alteration in blood flow
internal obstruction. example?
external interference/compression?
inadequate heart chamber function?

triad part 3: hypercoagulability
what 5 primary causes (deficiency or increases) lead to this?

hypercoagulability
secondary causes?

DVT
what is it? typical location?
risk factors? think about it
signs and symptoms? (3)
how would you check for one?

if a thrombus dislodges what do we get?
where will this go?

pulmonary embolus
what is it? usually comes from?
lodges where?

clinical outcomes of pulmonary embolism
depends on what factors?
3 types?
location of getting lodged?
symptoms?

Hypercoagulability
genetic? (3)
acquired? 7 for sure know what 2?

most common heritable hypercoagulopathy?
mechanism of action?
tested for how?

how to suspect primary hypercoagulable states
events? that happen under what conditions?
tests?

heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
genetic or acquired?
caused by?
in what state? caused by formation of? in reaction to?
steps that lead to this? (4)

Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
also called?
antibodies against what?
present with what complications? (where/with who)
another disease it can be present with?

fate of thrombi? (3)
how does the last step happen?
this can treat stroke under what conditions?

another fate of thrombi?


pathologic features of thromboembolic disease?
what is present? what does it look like? what does each represent?
what does this tell us?























