Heart Failure COPY Flashcards
(26 cards)
Label the parts of the heart on the diagram
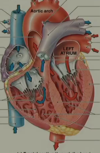

Why does tricuspid valve regurgitation cause venous congestion?
The tricuspid valve normally allows the unidirectional flow of venous blood from the right atrium into the right ventricle.
If it is damaged, when the right ventricle contracts, blood will be regurgitated back into the right atrium and back into the SVC and IVC and into the venous system. These veins are valveless, so allow the back flow of venous blood.
Name the main functions of the heart
Delivery of deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation
Delivery of oxygenated blood to the body
Delivery of nutrients
Removal of waste
Describe the main layers of the heart wall
- Endocardium: squamous cell epithelium
- Myocardium: involuntary striated muscle cells and collagen
- Epicardium
- Pericardium: double membraned sac that fixes the heart in place, lubricates and prevents infection.
What are the 2 main ways in which heart valves usually fail?
- Stenosis: calcification of the valves, causing them to allow less blood through so the ventricles must contract harder to push the blood through → ventricular hypertrophy→ HF.
-
Regurgitation: unidirectional flow of blood is lost. When the ventricles contract, blood is pushed back into the atria as well as the arteries causing congestion. (Left: pulmonary congestion; Right: venous congestion)
- → Dilation of blood vessels and ventricles (loss of muscle tone) → HF.
What is the effect of atrial fibrillation on the cardiac cycle?
Passive filling of the ventricles continues, however there is a loss of atrial ‘kick’ which is needed to fill the ventricles against the rising pressure from passive filling. (30% lost)
This causes under-filling of the ventricles and a loss of cardiac output.
What is systolic heart failure?
Loss of power of contraction of the ventricles
What is diastolic heart failure?
Relaxation of the ventricles in diastole is impaired, therefore the ventricles do not passively fill as effectively → less blood to be pumped out during systole.
What is the ejection fraction?
The percentage of blood ejected from the ventricles during ventricular systole from the total blood that was in there at the beginning of systole.
How do you calculate cardiac output?
SV x HR = CO
(70ml x 70bpm = 4900ml)
Name the 3 most common causes of heart failure
Coronary Artery Disease:
- Post MI
- Chronic ischaemia
Hypertension:
- Struggling against high afterload
Valvular disease:
- Regurgitation of a valve: volume overload (congestion)
- Stenosis of a valve: extra force needed to overcome
Name other causes of heart failure
- Cardiomyopathies
- Arrhythmias
- Drugs (anti-arrhythmics, cytotoxics)
- Toxins (alcohol, cocaine, mercury)
- Endocrine (diabetes, thyroid disease, adrenal disease)
- Nutritional (thiamine deficiency, obesity)
- Infiltrative (sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, haematochromatosis)
- Infective (HIV)
What is high output cardiac failure?
Name 3 causes
- Pregnancy
- Hyperthyroidism
- Anaemia
More common in younger people.
Caused by higher demand on the heart (e.g. anaemia- lack of oxygen means the heart has to work harder to deliver oxygen to tissues)
Name some symptoms of left-sided heart failure
- Dyspnoea
- Fatigue
- Orthopnoea
- Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea
- Nocturnal cough (+/- pink, frothy sputum)
Most symptoms are due to backlog of blood into the lungs (higher preload)
Name some symptoms of right-sided heart failure
- Nausea
- Anorexia
- Reduced mobility
Symptoms caused by venous congestion in the body
What is cor pulmonale?
Right-sided HF secondary to pulmonary disease.
Can present with right-sided signs only
Name some signs of left-sided heart failure
- Bilateral basal inspiratory crackles
- Cardiac wheeze (irritation in small airways of wheeze, monophonic)
- Pulmonary oedema
- Pleural effusion
- Right ventricular heave (caused by pulmonary hypertension)
Name some signs of right-sided heart failure
- Peripheral oedema
- Tender hepatomegaly (+/- pulsatile)
- Raised JVP
- Displaced apex beat
- Facial engorgement
- Abdominal distention (ascites- fluid backing up into liver; congestion in the portal venous system → liver failure, clotting disorders, may present with easy bruising)
Name some signs of reduced cardiac output
- Low systolic BP (cold peripheries, high capillary re-fill time, peripheral/central cyanosis)
- Narrow pulse pressure
- Pulses alterans (heart contracts differently with each beat)
Name some bedside investigations for heart failure
Name some possible findings
ECG:
- Left ventricular hypertrophy: Largest R wave + largest S wave = >45mm (in chest leads)
- Left axis deviation: Lead I positive and lead III negative (limb leads)
- Normal axis: Lead I and lead III both positive
- Right axis deviation: Lead I negative and lead III positive
- Strain: ischaemia (ST depression, T wave inversion)
Name some blood tests for heart failure
What do the various findings mean?
-
BNP (B-type natriuretic peptide/ Brain natriuretic peptide)
- Protein released by the ventricular myocardium when stressed
- Normal <100 pcg/ml
- Raised 100-400 pcg/ml
- High >400 pcg/ml
- U&Es: Cardiac medications can impair renal function
- FBC:?anaemia
- LFTs: HF can cause liver failure
What types of imaging can be used to detect HF?
What signs are indicative of heart failure in this type of imaging?
- Chest X-ray
- Alveolar oedema
- Kerley B lines
- Cardiomegaly
- Upper love Diversion (majority gas exchange occurs in the upper part of the lungs away from the fluid, therefore blood is re-directed here)
- Pleural Effusion
Name 2 special imaging tests that can be used to detect HF
What specifically do these tests detect?
-
Echocardiogram
- Ejection fraction
- Wall size and motion
- Valvular disease
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
- Ventricular function
- Wall size and motion
What are the management strategies for acute heart failure?
- A-E assessment
- Oxygen
- IV access and monitoring
- IV furosemide
- Diamorphine
- Nitrates (GTN infusion)
- NIV (CPAP)


