Heart, Blood and Blood Vessels Flashcards
Heart Auscultation
The process f listening to heart sounds

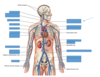
Pulmonic Area
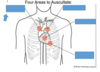
Aortic Area
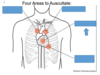
Tricuspid Area

Mitral Area

S1

Tricuspid and Mitral Valves close

S2

Aortic and Pulmonic valves close
Bradycardia
Slow heart rate
Heart murmur
Swooshing sounds between heart sounds, caused by a leaking valve or valve that has lost its pliability
Heart rate
The number of heart beats per minute
Stenosis
A valve that has lost its pliability
Regurgitation
Leaking valve
Pulse Palpation
The process of feeling the pulse with the fingertips
Pulse
Throbbing of arteries as blood is propelled through them
Normal Blood Pressure
120/80mm Hg
What tool is used to measure blood pressure?
Sphygmomanometer
Systolic Pressure
The period of time during which the ventricles contract
Diastolic Pressure
The period of time during which the ventricles relax
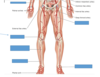
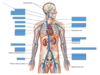
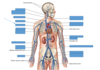
What are common arteries that can be palpated to find a pulse?
Temporal, carotid, brachial, ulnar, femoral, radial, popliteal, posterior tibial, dorsalis pedis
Sounds of Korotkoff
When taking blood pressure, pressure is released to the level of the systolic arterial pressure, blood flow through the brachial artery resumes but becomes rough. This causes sounds of Korotkoff
P Wave
Depolarization of the cells of the left and right atria
QRS Complex
Depolarization of left and right ventricles
T Wave
Repolarization of left and right ventricles
Hematocrit
The proportion of total blood volume composed of red blood cells
What are the two components of whole blood?
Plasma: fluid portion
Formed elements: cellular portion
What are the types of granulocytes?
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
What are the types of agranulocytes?
Monocytes and lymphocytes

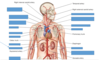
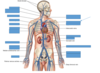
Thoracic Aorta
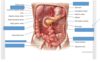
Inferior mesenteric artery
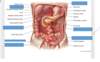
Left common iliac artery

Right external iliac artery