Head and Neck 7 Flashcards
How many fossa is the floor of the skull divided into?
3
What do grooves and depressions in the skull indicate?
Where, in life, blood vessels and other structures ran
Which bone forms the posterior boundary of the anterior cranial fossas?
Sphenoid
What is A?

Frontal bone
What is B?

Olfactory foramina
What is C?

Optic canal
What is D?

Foramen rotundum
What is E?

Foramen ovale
What is F?

Foramen spinosum
What is G?

Foramen lacerum
What is H?

Internal acoustic meatus
What is I?

Jugular foramen
What is J?

Hypoglossal canal
What is K?

Foramen magnum
What is L?

Occipital bone
What is M?

Parietal bone
What is N?
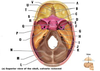
Posterior cranial fossa
What is O?

Temporal bone (petrous part)
What is P?

Middle cranial fossa
What is Q?

Hypophyseal fossa of sella turcica
What is R?

Greater wing of sphenoid
What is S?

Lesser wing of sphenoid
What is T?

Anterior cranial fossa
What is U?

Crista galli of ethmoid bone
What is V?

Cribiform plate of ethmoid bone
What bone forms the anterior boundary of the middle cranial fossa?
Sphenoid
Which bones form the floor of the middle cranial fossa?
Sphenoid and temporal bone (squamous and petrous parts)
Which bone forms the posterior border of the middle cranial fossa?
Occipital bone
What four bones come together to form the H-shaped pterion?
Frontal
Parietal
Temportal
Sphenoid

What bones form the anterior and posterior borders of the posterior cranial fossa?
Anterior - sphenoid
Posterior - occipital
What structures pass through small foramina of the skull?
Nerves
What structures pass through large foramina of the skull?
Nerves and blood vessels
What foramina is present in the anterior cranial fossa?
Foramina of the cribiform plate
What passes through the foramina of the cribiform plate?
Olfactory nerve
What foramina are present in the middle cranial fossa?
Optic foramen
Superior orbital fissure
Foramen rotundum
Foramen ovale
Foramen spinosum
Foramen lacerum
Carotid canal
What structures pass through the optic foramen?
Optic nerve
Opthalmic artery
What structures pass through the superior orbital fissure?
Superior and inferior divisions of occulomotor nerve
Abducen nerve
Trochlear nerve
Opthalmic division of trigeminal nerve
What structures pass throughj the foramen rotundum?
Maxillary division of trigeminal nerve
What structures pass through the foramen ovale?
Mandibular division of trigeminal nerve
What structures pass through the foramen spinosum?
Middle meningeal artery
What structures pass through the foramen lacerum?
Internal carotid artery
What structures pass through the carotid canal?
Internal carotid artery
What foramina is present in the posterior cranial fossa?
Internal acoustic foramen
Jugular foramen
Hypoglossal foramen
Foramen magnum
What structures pass through the internal acoustic foramen?
Vestibulotrochlear nerve
Facial nerve
What structures pass through the jugular foramen?
Internal jugular vein/sigmoid sinus
Vagus nerve
Glossopharyngeal nerve
What structures pass through the hypoglossal foramen?
Hypoglossal nerve
What structures pass through the foramen magnum?
Medulla oblongata
Vertebral arteries
Spinal accessory nerves
What is A?

Optic canal
What is B?

Foramen rotundum
What is C?

Foramen spinosum
What is D?

Jugular foramen
What is E?

Foramen magnum
What is F?

Foramen magnum
What is G?

Hypoglossal canal
What is H?

Foramen lacerum
What is R?

Internal acoustic meatus
What is I?

Foramen ovale
What is J?

Superior orbital fissure
What is K?

Foramen spinosum
What is L?

Carotid canal
What is M?

Stylomastoid foramen
What is N?

Hypoglossal canal
What is O?

Jugular foramen
What is P?

Foramen lacerum
What is Q?

Foramen ovale
Between what layers of meninges are intra-cranial venous sinuses found?
Outside of dura mater
Inner layer is the dura mater and oluter layer is the periosteum of the inside face of the skull bone
What artery is found in the groove that begins just lateral to the foramen spinosum?

Middle meningeal artery
What is a consequence of the middle meningeal artery being close to the pteryion and the skull making the groove being thin?
Artery is commonly damaged in injuries such as blow to the head, causing an extradural haemorrhage

What kind of haemorrhage is this?

Extradural haemorrhage
What is shown in the image?

The grooves that run laterally from both sides of the internal occipital protuberance contains what?
Transverse sinus
The transverse sinus groove becomes as S-shaped curve laterally, what does this contain?

Sigmoid sinus
Into which foramen does the groove for the sigmoid sinus lead?
Jugular foramen
Which major vein emerges into the neck from the jugular foramen?
Internal jugular vein
What is the sella turica?
Deep depression in the midline in the middle cranial fossa which houses the pituitary gland

What is the pituitary gland housed in?
Sella turica

In the body of which bone is the sella turica found?
Sphenoid bone
What is found on either side of the sella turica?
Anterior and posterior clinoid processes

What do the anterior and posterior clinoid processes give attachment to?
A fold of dura mater, called the tentorium cerebelli
What is the groove on either side of the sella turica for?
Cavernous sinus

What foramen lies immediately anterior to the groove for the cavernous sinus?
Optic canal
The groove running along from posterior to anterior on the internal surface of the skull cap is for what?
Sagittal sinus
What is A?

Sphenoid bone
What is B?

What is C?

Palatine process of maxilla
What is D?

Choana (palatine bone)
What is E?

Posterior nasal spine (vomer bone)
What is F?

Temporal bone
What is G?

Occipital bone
What bones are the pterygoid plates and the pterygoid hamulus apart of?
Sphenoid bone
What bone is this?

Sphenoid bone
What is A?

Superior orbital fissure
What is B?

Lesser wing of sphenoid
What is C?

Greater wing of sphenoid
What is D?

Lateral pterygoid plate
What is E?

Medial pterygoid plate
What is F?

Pterygoid hamulus
What muscles attach to the medial pterygoid plate?
What muscles attach to the lateral pterygoid plate?
Medial pterygoid muscle to medial surface
Lateral pterygoid muscle to lateral surface
Why are neonatal skulls less rigid and more flexible than adult skulls?
They are not fully ossified
What are some advantages of neonates having a flexible skull?
During childbirth allows for squeezing out
During infancy allows for brain growth
In the event of accidents and falls protects the brain
What type of ossification occurs in the:
- flat bones of the vault of the skull
- irregular bones of the base of the skull
in neonates?
Flat bones - intramembraneous
Irregular bones - intramembraneous
What are the differences in the following between children and adults:
- fontanelles
- dentition
- tympanic membrane
- styloid and mastoid processes of temporal bone?
Fontanelles - harden and close over time
Dentition - children have 20, adults have 32
Tympanic membrane - thicker in infants
Styloid/mastoid process - absent in neonatal skull
What is A?

Styloid process
What is B?

Mastoid process
At what age do the anterior fontanelles fuse?
9 to 18 months
At what age do the posterior fontanelles fuse?
First few months
What is A?

What is B?

What is C?

What does this histology image show?

Tongue
What kind of epithelium lines the dorsal surface of the tongue>
Stratified squamous keratinised epithelium
What kind of muscle fibres underlies the epithelium of the tongue?
Smooth muscle
Each salivary gland is responsible for different kinds of secretions, what are the different types?
Predominantly serous
Predominantly mucous
Mixed
How does each salivary gland differ histologically?
By the present and amount of serous or mucous acini (secretory component)
How do serous acini and mucous acini differ?
Serous secretes proteins so stain strongly with H&E stain
Mucous secretes the glucoprotein mucous which stains poorly with H&E
Which kind of acinis is A and which is B?

A - serous acinis
B - mucous acinis
Cell labled D is a myoepithelial cell, what is the function of this cell?

Contractile function, helps to expel secretions
What cell helps expel secretions of salivary glands?
Myoepithelial cell
In terms of mucous/serous acini, sublingual glands are?
Mainly mucous acini
In terms of mucous/serous acini, parotid glands are?
Mainly serous acini
In terms of mucous/serous acini, submandibular glands are?
A mixture of serous and mucous acini
What is image A, B and C?

A - parotid gland (serous glands)
B - sublingual gland (mucous glands)
C - submandibular glands (mixed serous and mucous)


