Haemostasis Flashcards
What is the vessel wall lined with and what are it’s characteristics?
- Epithelium
- “Non-stick surface teflon”
Which substances do we have to encourage flow?
- heparans, anticoagulants – TFPI, prostacyclin, nitric oxide
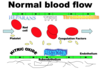
What happens when you are cut? What systems are at play?
- You bleed at the site of the injury
- For how long? 3-4 mins
- Stops – you form a clot Platelets, vWF, Coagulation Factors
- The clot remains confined to the site of injury Natural Anticoagulants
- 1 week later the clot has vanished Fibrinolytic System
What states are platelets and coagulation factors generally in the blood?
- Platelets and coag factors remain in resting state until activated – localised signals, production at area of damage of physiological activators cause activation
What causes platelets to adhere to site of damage?
- Platelets are seeing something not used to – subendothelial collagen, as soon as they see this they stick to it and become sitcky/activated.
- Vwfactor binds and allows us to start clotting. Just at area of damage there is physiological activator (tissue factor)

What exist on the surface of platelets and their roles?
- Receptors – normally for things created in context of trauma
- Glycoprotein receptors – capable of binding to ligands, relevant to blood coagulation
How do platelets work?
- Bind to collagen
- Bind to von willebrand factor
- Bind to fibrinogen
What are platelets role in haemostatis?
- Adhere
- Activate
- Aggregrate
- Provide phospholipid surface for coagulation
Which parts of the platelet are responsible for adherence?
- GP 1b
- GP1a (x2)
How do platelets activate?
- ADP pathway (P2Y12)
- Activation of cyclooxygenase pathway
What allows the aggregration of platelets?
- Thromboxane allows platelets to stick to each other
What allows proteins to attach to platelets?
Externalised phospholipids
What is the PRIMARY platelet plug?
- Platelets have adhered, activated and bound fibrinogen = PRIMARY haemostatic plug
What stabilises the primary platelet plug?
- Fibrin clot formation
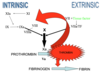
How can we make a fibrin clot?
- Primary aim is to cleave fibrinogen..
So:
- There is a clotting cascade of proteins, much like a row of dominoes, they must all ‘fall over’ to finally cleave fibrinogen creating the fibrin clot