Gravitiational Fields Flashcards
(24 cards)
What is a gravitational force
A force of attraction that acts between objects with mass
Define Newton’s Law of Gravitation
The gravitational force between 2 masses is directly proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
What is a uniform gravitational field
A field that exerts the same gravitational force on a mass anywhere in the field
What is a radial field
A field in which the force exerted depends on an objects position in the field. Decreases as the distance from the centre increases
Define Gravitational Field Strength
The force per unit mass exerted by a gravitational field on an object.
How does Gravitational field strength vary in a uniform and radial field
Uniform - Always the same Radial - Varies with distance
Define Gravitational potential at a point
The work done per unit mass when moving an object from infinity to that point.
Why is Gravitational potential always negative
Gravitational potential at infinity is zero, and as an object moves from infinity to a point, energy is released as the gravitational potential energy is reduced
Define Gravitational Potential Difference
The energy needed to move a unit mass between to points
What is an equipotential surface
Surfaces which are created through joining points of equal potential together, therefore the potential on an equipotential surface is constant everywhere.
What is the relationship between gravitational potential and distance between the centre of masses
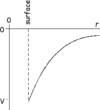
What is the gradient of a V-r graph
Gravitational field strength x -1
What is the area under a g-r graph
Gravitational potential difference
What is Keplers 3rd Law and the equation
T<strong>2</strong> is proportional to r3
T2 = r3 x 4π2/GM
Describe the context that Keplers 3rd law should be used
An object orbiting a body
M = Mass of the body being orbited
r = Dist. between the object and the centre of the body being orbitted
What is the derivation for Keplers 3rd Law
When an object orbits a mass in circular motion, the gravitational force acts as the centripetal (resultant) force
mv2/r = GMm/r2 , mv2 = GMm/r , v2=GM/r
Since v=d/t, let d be the circumference = 2πr
v=2πr/T , v2=4π2r2/T2
Equate the 2 equations
4π2r2/T2=GM/r
T2=4π2r3/GM
What is the total energy of a satellite in orbit
Sum of Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
How do the energy stores in an orbiting satellite change
Total energy is constant
i.e If it orbits at a lower height, Potential energy falls, so Kinetic energy increases to keep total energy constant
What is escape velocity
The minimum velocity an object must travel at in order to escape the gravitational field at the surface of a mass, when it is projected vertically from the surface
When Ek=Ep
As Ep is the energy required for an object to leave a field, so when its Ek is high enough, it has enough energy to transfer.
How to calculate escape velocity
When Ek=Ep
v = (2GM/r)½
M= Mass of larger mass
What is a synchronous orbit
Where the orbital period is equal to the rotational period of the object it’s orbitting
What is a geostationary Satellite
What can they be used for
A satellite that follows a geosynchronous orbit
Always stays above the same point as they orbit directly above the equator
Used in TV/telephone signals as its position never changes
What is a low orbit satellite, what are they used for
A satellite with a much lower and faster orbit
Can orbit the entire earth
Used for military, weather, scientific purposes
What is the relationship between Gravitational Field Strength and Potential Gradient
Gravitational Field Strength = -Potential Gradient
As potential gradient is how much energy a 1kg mass would transfer to move 1m further. This is the work done against the attractive gravitational force, which is facing the opposite direction.
That attractive gravitational force for the 1kg mass is just the gravitational field strength


