Glycolysis Flashcards
Preparatory Phase
2 ATP spent to activate glucose yield 2 glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Payoff Phase
yield 4 ATP, net gain 2 ATP, 2 NADH result in 2 pyruvate
Pyruvate fates
TCA cycle (aerobic) LDH (muscle) Fermentation (yeast) BIosynthesis (alanine, PEP)
Glucose fates
Structural polymer synthesis Storage (glycogen, starch, sucrose) Oxidation via PPP (ribose 5-phosphate Oxidation via glycolysis (pyruvate)
Step 1
Phosphorylation Glucose–>glucose 6-phosphate enzyme=hexokinase dG=-16.7 ATP is phosphoryl group donor KEY REGULATORY POINT
Step 2
Isomerization glucose 6-phosphate–>fructose 6-phosphate enzyme=phosphoglucose isomerase dG=+1
Step 3
Phosphorylation fructose 6-phosphate–>fructose 1,6 bisphosphate enzyme: phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) PFK-1 catalyzes transfer of phosphoryl group from ATP to fructose 6-phosphate KEY REGULATORY POINT
Step 4
Cleavage fructose 1,6 bisphosphate–>dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate enzyme: aldolase readily reversible reaction
Step 5
Isomerization DHAP–>glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate enzyme: triose phosphate isomerase
Step 6
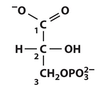
Oxidation/Phosphorylation glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate–>1,3 bisphosphoglycerate enzyme: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) First of 2 energy conserving reactions of glycolysis that eventually lead to formation of ATP NAD+ oxidizes enzyme substrate intermediate endergonic
Step 7
Phosphorylation 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate–>3-phosphoglycerate enzyme: phosphoglycerate kinase Transfer of phosphoryl group from 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate to ADP Second of 2 energy conserving reactions very exergonic
Step 8
Isomerization 3 phosphoglycerate–>2 phosphoglycerate enzyme: phosphoglycerate mutase
Step 9
Dehydration 2-phosphoglycerate–>phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) enzyme: enolase
Step 10
Phosphorylation phosphoenolpyruvate–>pyruvate enzyme: pyruvate kinase KEY REGULATORY POINT
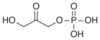
glucose