GI Pathology: Stomach Flashcards
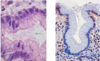
What is shown in the provided image?

normal gastric mucosa
What is the names of these types of mucosa?
Where are these types of mucosa found in the stomach?
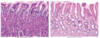
- Oxyntic types mucosa
- body and fundus
- Parietal cells
- HCl
- intrinsic factor
- Chief cells
- pepsinogen
- lipase
- Parietal cells
- neutralize acid
- body and fundus
- Antral type mucosa
- antrum
- gastrin secreting cells
- bicarb to neutralize acid

What is shown in the provided image?
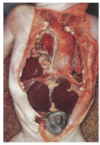
congenital diaphragmatic hernia
- small intestien has herniated into right thoracic cavity with partial collapse of right lung and deviation of trachea to the left
- acquired forms in adults
- abdominal trauma
What is the difference between omphalocele and gastroschisis?
Causes?
- Herniation of abdominal contents through an abdominal wall defect
- Omphalocele
- defect of abdominal wall (abdominla contents get soved into umbilical chord)
- herniation of viscera into base of umbilical cord
- viscera covered by membranous sac of amnion, Wharton jelly, and peritoneum
- due to incomplete closure of abdominal musculature
- Cause:
- Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and other developmental abnormalities
- maternal smoking
- defect of abdominal wall (abdominla contents get soved into umbilical chord)
- Gastroschisis
- defect of abdominal wall
- no involvement of umbilical cord
- herniation of viscera with no surrounding membranous sac
- Causes
- possibly due to vascular injury to abdominla wall
- less association with other developmental abnormalities
- defect of abdominal wall

What is congeintal hypertrophic pyloric stenosis?
Symptoms?
Causes?
- Pyloric stenosis (anatomic cause of obstruction)
- Symptoms
- 3-5:1 M/F
- Presents in first 3-12 weeks of life
- new onset regurgitation
- persistent, projectile, nonbilious vomiting
- Firm, ovoid abdominal mass
- Causes (can occur on its own)
- Turner Syndrome, Trisomy 18
- Erythro/Azithrmycen from mom
- Acquired form in adults usually is due to tumors or scarring

What is shown in the provided images?

Pyloric Stenosis
What are the intrinsic and extrinsic mechanism of gastric injury and protection. Continual injury will eventually lead to what problem?
gastritis – sever injury is ulcer

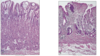
What is shown in the provided image?

Acute hemorrhage gastritis
pinpoint superficial erosion (can’t tell what caused it)
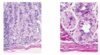
What is shown in the provided image?
Acute gastritis
PMNs on surface
Diffuse mucosal erosion
Residual glands are seen at the base of the mucosa (white open arrow)
What types of ulcers can develop under conditions of severe physiologic stress?
- All the little black dot are full thickness mucosal defects; usually found at autopsy
- Cushing Ulcer- head trauma (vagal stiumlation)
- Curling Ulcer - (stress related to splanchnic vasoconstriction)

What is the most common cause of chronic gastriris?
- H. Pylori
- spiral or curved bacilli
- fecal-oral transmission
- virulence:
- flagella, urease, adhesins, CagA
- predominantly anral, but can progress to cause patchy proximal disease with oxyntic atrophy
- initially results in increased acid production (risk of ulcers), but with body/fundus involvement, decreased acid production, and IM (risk gastric carcinoma)
- CagA expressing strains increase risk of proximal migration and cancer development
What is shown in the provided image?


What is shown in the provided image?

Chronic gastritis is too many plasma cells in the lamina propria
In H. pylori, there is a tendency for that infiltrate to be more superficial

What is shown in the provided image?
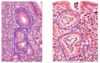
PMN infiltration of epithelium and gastric glands
acute inflammation on top of chronic gastritis
more common with H. pylori

What is shown in the provided images?

What diseases are associated with H. pylori?
- Chronic (active) gastritis
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Antrophic gastritis (preneoplastic)
- intestinal metaplasia
- glandular dysplasia
- Gastric adenocarcinoma
- Gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma
Describe the endoscopic appearance of peptic ulcer disease?
Major causes?
- sharply defined ulcer with gray fibrinopurulent exudate and a surrounding rim of fibrous tissue (black curved arrow). Slight erythema (white curved arrow) is seen in the surrounding mucosa
- Cause
- H. pylori
- NSAIDs
- Because H. pylori infection initially increases acid production, you can get ulcers in the duodenum

What is shown in the provided image?

notice the abrupt loss of gastric mucosa

What is the difference between the two endoscopies?
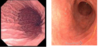

What is the difference between the to images of autoimmune gastritis?
In the severe autoimmune gastritis, there is a bunch of space between glands and there are very few glands
additional goblet cells

you What are the indicated signs of autoimmune gastritis with atrophy?

you usualy don’t have an active phase with PMNs like in helicobacter

What freatures of autoimmune gastritis with atrophy are shown in the provided images?


Table

What is reactive/chemical gastropathy?
- Foveolar hyperplasia with mucin depletion and serrated gastric pits
- mucosal edema with dilated capillaries
- Splaying of muscularis mucos (not shown)
- NSAIDS an EtOH common causes

What are hypertrophic gstropathies?
- Giant rugal folds (“cerebriform”)
- uncommon
- linked ot excessive growth factor release
- Menetrier disease (TGF-alpha)
- Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (Gastrin)
What condition is shown in the provided image?


What is the name of the syndrome that produces gastrin-secreting tumors (gastrinomas) of the small intestine or pancreas?
Associated symptoms?
Zollinger-Ellision Syndrome
- gastrinomas asre malignant, but slow-growing
- 25% of patients have MEN I
- duodenal ulces and/or chronic diarrhea

What is shown in the provided images?

What is shown in the provided images?
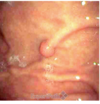
Describe the provided image
Fundic Gland Polyp
bic cystically liked clanned (chief and parietal cells)
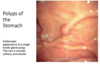
What is shown in the provided image?

Gastric hyperplastic polyp
lining of glands is mucin type cells
typically see in backdrop of chronic gastritis
What is shown in the provided image?

Gastric Adenoma
What are the major gastric malignancy types?
- Adenocarcinoma >90%
- intestinal type
- diffuse type
- Also
- lymphoma ~5%
- Neuroendocrine (carcinoid) tumor ~3%
- gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) ~2%
- Symptoms of gastric adenocarcinoma?
- prognosis?
- Where are incidence most common?
- Symptoms
- often mimic chronic gastriris and PUD
- often not discovered unil advanced
- weight loss
- anorexia
- early satiety
- bleeding
- mets
- Prognosis
- early gastric ca: ~90% 5 year survival
- Avoid gastric va: <20% 5 year survival
- Incidence
- very common in Japan
- incidence is steadily falling in US since ’30s
- intestinal adenocarcinoma is decreasing
- Risk factors
- dietary: nitrates & cmoked, salty, or pickled foods, lack of fresh fruits/vegetables
- gastric atrophy and intestinal metaplasia
- H. pylori
- produce urease
- gastritis –> mucosal atrophy –>intestinal metaplasia –> dysplasia
- autoimmune gastritis
- FAP (germline APC mutations)
- H. pylori
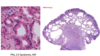
What is shown in the provided image?

Sharing gland walls & invading into muscle
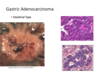
Important features of gastric adenocarcinoma, diffuse type
- ~50% us gastric adenocarcinomas
- world-wide incidence stable and uniform across countries
- environmental/dietary risk factors not well established
- relationship to H. Pylori not well established
- Familial gastric cancer is strongly associated with this type of carcinoma
- Mutations in CDH1(encodes E-cadherins- responsible for holding glands together) or silencing (methylation) of the CDH1 promoter present in almost all cases (familial or sporadic)

What is shown in the provided photo?

Linitis plastica = leather bottle
spread diffulsely & make whole stomach wall hard

What is shown in the provided image?
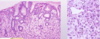
not making good glands b/c E-cadherin expression is inappropriate

What is a MALT lympona?
Describe the pathogenesis.
- B-Cell lymphoma
- most common type to occur in stomach (DLBL also occur)
- Pathogenesis
- Tend to arise at sites of chronic inflammation
- gastric MALTs often coexist with H. pylori gastritis
- symptoms similar to H. pylori gastritis
- H. pylori infection induces a polyclonal lymphoid inflammatory response
- Monoclonal B cell clone emerges, still dependent on antigen-stimulated T helper cells for growth
- at this stage, antibiotic prescription for H. pyori leads to tumor regression
- with time, tumor may acquire 1 of 3 known chromoslmal translocations. At this point, elimination of H. pylori wiht antiotic is inneffective.
-
*t(11;18)/API2-MALT1 fusion protein
- Fusion of apoptosis inhibitor gene with MLT gene
- May be ptorective against high grade transformation
- T(14;18)
- increased expression of MALT1 protein
- T(1;14)
- increased expression of BCL-10
-
*t(11;18)/API2-MALT1 fusion protein
- Tend to arise at sites of chronic inflammation
Describe the provided image

glands are gone
lymphomas in general are cohesive cells
tumors of hematopietic cells tend not to stick together

Features of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor?
Where do they arise?
Common features of the tumor?
- most common primary non-epithelial neoplasm of the stomach
- stomach the most common site for this rare mesenchmal tumor
- aveage age at diagnosis is 60 (<40 is uncommon)
- tumors arise from interstitial cells of Cajal
- “pacemaker cells” in muscularis propria
- control GI peristalsis
- “pacemaker cells” in muscularis propria
- Varying micro patterns:spindled/epithelioid
- ~95% have one of two mutually exclusive Tyrosine kinase receptor family mutations
- marjority oncogenic gain-of-function mutations of gene encoding tyrosine kinase, c-KIT, the receptor for stem cell factor
- minority, mutations in PDGFRA, however:
- more common in the stomach than elsewhere
What is the Carney’s triad?
Other associations with gastrointestinal stromal tumors?
treatments?
Prognosis?
- Carney’s triad- YOUNG females
- gastric GIST
- extra-adrenal paraganglioma
- also seen in association with
- NF1, with paragangliomas, familial syndrome with germline KIT mutations
- Treatment
- primary - complete surgical resection
- In patients with unresectable or metastatic disease, effective therapy for tumors with KIT/PDGFRA mutations
- tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib mesylate (Gleevec)
- Prognosis linked to tumor size/mitotic rate/location
- stomach generally behave better than elsewhere
- mets can occur 30 years after removal of the primary tumor
- liver, lung, peritoneum
What is shown in the provided images?
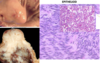
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor


