Genetic Expression Flashcards
(9 cards)
Explain what genetic expression by a summary of its stages

Genes are rewritten (transcribed) into a usable matter which then can be translated (interpreted) into a functional protein
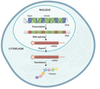
List the stages of genetic expression (in order) and where they occur (as well their location in the cell)

Transcription - DNA in the nucleus of the cell
↓ Gets exported by mRNA to outside the nucleus ↓
Translation - mRNA in the cytoplasm of the cell
In terms of sugars, bases, and shape, what are the differences in RNA compared to DNA?
DNA - deoxyribose sugar, ATCG base, and double-helix shape
RNA - ribose sugar, AUGC base, single-strand shape
What’s the big deal with transcription and how does it get to the translation stage?
DNA’s genetic code is transcripted into material that will be used as instructions for making proteins that will make up traits. The material, that holds rewritten code, is then carried and exported by mRNA to the next stage of genetic expression.
What does it mean for a gene to be “expressed”?
It’s just another word for it being turned on bruh
Fill in the blanks in the image below.

A - U
C - G
T - A
G - C
How and where does mRNA code turn into proteins?
In the cytoplasm of the cell, mRNA code is translated by ribosomes into a sequence of amino acids that will make up a specific protein
What are codons and what role do they play in genetic expression?
Codons are the organized units of mRNA that will code for one specific type of amino acid
Why is genetic code universal, unambiguous, and redundant?
Genetic code is universal because all organisms use the template of genetic code.
Genetic code is unambiguous because each codon can only code one specific type of amino acid while…
genetic code is redundant because most amino acids can be coded by multiple amino acids


