General Math Cards Flashcards
What are the outcomes when Adding and Subtracting Even and Odd numbers?
Even ± Even = Even
Even ± Odd = Odd
Odd ± Odd = Even

Outcomes when Multiplying Odd and Even numbers?

How can you figure out if something is divisible by 3?
If the sum of the digits in a number add up to a value that is divisible by 3, then the number itself is divisible by 3.
What is a trick to figure out if a number is divisible by 4?
That the last two digits of a number, and if this value is divisible by 4 then you know the whole number itself is divisible by 4.
How do you know if a number is divisible by 5?
Just needs to have a 5 or 0 at the end…
How do you figure out if a numebr is divisible by 6?
If a number is divisible by 2 (even) and 3 (the sum of all digits is divisible by 3) then you know that the number is divisible by 6.
How do you figure out if a number is divisible by 8?
If the last three digits form a number that is divisible by 8.
How do you figure out if a number is divisible by 9?
If the sum of the digits is divisible by 9 then the number itself is divisible by 9.
729 / 9
(7+2+9) / 9
18/9
Which is 2 so 729 is divisible by 9.
How do you figure out if a number is divisible by 11?
If, when writing the signs -+-+ alternatively between the digits, the sum result is value divisible by 11.

What are all the prime factors up to 50?
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47
Two is the smallest prime number and its the only that’s even, the rest are odd.
What is something to remeber about the odd even relationship of prime numbers?
Two is the smallest prime number and its the only that’s even, all the rest are odd.
If they were even they would be divisible by 2.
Is 1 a prime number?
It isn’t because it cannot be divided by two different factors.
Are 51 and 91 prime numbers?
No.
51 is 3 * 17
and
91 is 7 * 13
Prime Numbers: An integer can only be divided by?
1
itself
its prime factors
and integers created by multiplying some of its prime factors with other prime factors.
When figuring out if a number is divisible by a set of numbers given, what do you need to remember?
That you can use the prime numbers to multiply into different multiples as many times as they appear when factoring down.
For example, if there are three 2s from factoring 120 down you can use 2 three times to create new factors.
What technique can we use to figure out whether a number is prime?
Technique: if a number is not divisible by any prime number smaller than its root then its a prime number. If it is divisible, it is not prime.
Once you know the root, and figured out out all the prime numbers below it, divide the original number (i.e. before the root) by the primes and if they don’t divide the number itself is prime.
How do we calculate the root of a number without a calculator? For example, the square root of 71.
By memorizing the mutliplication table we can estimate the root between the common values we do know.
With 71 we know that 8*8 is 64 and 9*9 is 81, so we know the root of 71 lies in between 8 and 9.
What is the best technique to find the GCF between two numbers?
- List out all the prime factors of both numbers
- What prime factors are in common? In what number do the appear least? Get all prime factors and list the prime number in the quantity where it appears least.
- Now multiply the prime factors by eachother to get the GCF.
The Greatest Common Factor is the largest factor that divides evenly into all numbers in a set.
What is the fact technique to find the Least Common Multiple (LCM) between two numbers?
For example for 33 and 36
- List out all the prime factors of both numbers
- Add all the prime factors to one list but importantly list the common prime factors in the quantity where they appear most, do not add them double. Any prime factors that are not common are just listed as is.
- Now multiple all the factors together to get the LCM
The prime factors of 33 are 3,11 and the prime factors of 36 are 2,2,3,3. The resulting list is 2,2,3,3,11. Multiplying this out gives: 396
Data Sufficiency: General Answer Choices Structure
- A - picking statement A
- B - picking statment B
- C - Combined, combining information would be enough to answer the question.
- D - Divided / or, each one on their own is enough to answer the question.
- E - E…impossible, even both combined together not enough information.
What is the purpose of Data Suffiency questions?
The purpose is of data suffiency questions is not to solve the question but rather you have to figure out if the question can be solved.
You DO NOT have to answer the question, just whether or not you can come up with a answer.
Can you trust sizes and proportions (such as apparent right angles) if theyre not explicility stated?
No, you can’t trust what you see.
An angle can be much larger or smaller than what it looks. Same goes for lines, areas or any other measurement.
Is zero divisible any number?
Zero is divisible by any number, except itself.
What is an acute angle? What is an obtuse angle? What is a reflex angle?
Acute = angle less than 90º
Obtuse = angle greater than 90º
Reflex Angle= angle larger than 180º but less than 360º
What is a bisector?
A bisector is a line, line segment or ray that passes through the middle of a line segment or through the middle of an angle, and divides them into two equal parts.
What is a neat way of remembering how the angles relate when parallel lines are crossed by another line?
F U N
Where the angles in F and N are equal, large and small angles, while you can imagine angles in more squared U to be different but the sum of them both is 180º.
Geometry: can straight lines be trusted when doing angle calculations?
Yes they can, but always double check.
What is something you should really do when you first see a question?
Read it carefully, make sure you don’t glaze over any important words and make sure you truly understand what they are asking.
Is 0 rational?
Yes, because it can be written as a fraction. For example, 0/7.
What are proper and improper fractions?
Proper fractions are fractions where the numerator is smaller than the denominator.
Improper fractions are frations where the numerator is greater than the denominator. Improper frations can be equal to integers, i.e. the numerator can be divided without remainder by the denominator.
What is a better way of adding fractions when both denominators produce a large number when multiplied?
You find the Least Common Multiple of both numbers. You do this by finding all prime factors, adding them to one list where the quantity of a factor is determined by where it occurs most, and finally taking the product of this list.
Once found, you multiply the fractions, numerator and denominator, by the neccessary values to get them to the LCM.
What are the decimals and percents of 1/8 and 1/6
1/8: 0.125 12 1/2 %
1/6: 0.1666… 16 2/3 %
What’s an important condition for this relation?
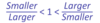
The values need to be positive.
-ve vlaues would satisfy the greater than signs, but not be following the larger and smaller relation.
Buying and Selling Products: What is the Cost price and what is the Expense?
What is the selling price and revenue?
Cost price is the basic price demanded by the person who produced the good.
The total cost of all the items bought by a seller is called the expenses.
The selling price is the price for which the goods are sold to the customers.
Revenue is the total sum recieved from selling items to customers.
What is simple interest?
Simple interest doesn’t take into account compounding and thus every year you receive or pay the same amount determined by the principal amount.
With Data Sufficiency questions, what approach should you take?
You need to take the Logical approach
What are the variables we need to know to solve simple interest problems?
How many of those variables are needed in simple interest data sufficiency questions?
In simple interest questions we need to know 3 of the following 4: interest, principal, rate or time periods.
With data sufficiency problems, knowing 3 of the 4 means there is enough data to answer the question at hand.
What is the external angle of a triangle equal to?
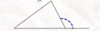
An external angle to a triangle is equal to the sum of the other two internal angles, the ones that it is not adjacent to.
What do we know about the size of a triangles side and the associated opposite angle?
A larger side is always found opposite a larger angle.
Triangles: the sum of any two sides is always greater than…
The opposite?
The sum of any two sides is always greater than the length of the third side.
A side of a triangle is always larger than the difference of the other two sides.
What is a acute triangle?
An acute triangle has three angles, each measuring less than 90º.
What is a isosceles triangle?
An isosceles triangle has atleast two equal sides (called legs) with two equal angles opposite of them.
What is the height of a triangle defined as?
The height is the shortest vertical line from the vertex to the base. The height is also referred to as the distance between the vertex and the base.
What is the formula for the area of a triangle?
What do you need to remember about obtuse triangles when it comes to this formula?
Base*Height / 2
For obtuse triangles the height line is outisde the actual triangle.
What is the ratio between the sides of a isosceles right angle triangles?
1:1:√2
What is the Golden Triangle?
Also known as the 30-60-90 triangle is defined as the right angle triangle with one leg that measures 1/2 the hypotenuse. This leg is also the smaller of the two legs and therefore opposite the 30º angle.
The ratio of the sides is 1:√3:2

What do we know about two triangles with they have all the same sides (S-S-S)?
If all three sides are the same, they are identical.
What do we know about a triangle with two of the same side and the same exact angle between this sides?
They are indentical

If two triangles have the same two angles and the same exact side between these angles, what do we know?
What about if two triangles have two sides that are the same and the exact same angle opposite the largest side?
In both cases the triangles are the same.
Why do we only need two angles to determine of triangles are similar?
Because we can determine the last angle knowing that all angles add up to 180º.
If you know the areas of two triangles, how do you figure out the proportion of the perimeter of both triangles?
√a:√b
where a and b are the respective areas.
When multiplying numbers in your head, what is something you cannot do?
i.e. 24*24
you can’t just break up the number into parts in one line of products and break it up, e.g. 20*20*4*4. This is wrong, do not do it.
Instead if you’re multiplying mentally, multiply each of the digits by each other, in other words, the ones digit with the tens, the tens with the tens and the ones with the ones.
What is the equation for the area of a equilateral triangle?

What do you have to remember about -32?
The power of two is on the three and does not include the -ve, so the value is -9. If there power was applied to a -3 brackted, then it would be 9.
x0 is?
What is √0?
1
√0 = 0
What are the main squares you need to memorise for the GMAT?
The hidden one at the bottom is 252

What are the merging rules for a to the root of c and b to the root of c, i.e. the same root?

What is a quadrilateral?
A quadrilateral is a shape with four sides and four angles.
Quadrilaterals: what is a diagonal defined as?
A segment that connects two vertices is a diagonal.
What is a trapezoid?
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with just one pair of parallel sides.

Quadrilaterals: How do you calculate the area of a kite?
Area = Product of diagonals / 2
What are the important things you need to know about parallelograms?
Opposite angles are equal.
The sum of the two sides that are adjacent, at the ends of the two sides, is 180º.
The equation to calculate the area is => Base*Height
How do you calculate the area of a trapezoid?
If you know one angle in trapezoid corner, how do you calculate the one above or below it?
What do we know about opposite angles in a isoceles trapezoid?
The area is the average of the two parallel bases times the height.
(sum_of_bases/2)* height
Since the bases are parallel, the other angle is simply 180 minus the angle you know.
Opposite angles in a isoceles trapezoid add up to 180
Other than side2 what’s another way of calculating the area of a square?
Diagonal2/2
What do the KiDS quadrilaterals all have in common?
KiDS
Kite Diamond Square
Area = Product of diagonals / 2
What do we know about two inscribed angles that face the same arc?
They are the same angle.

What is the angle of an inscribed angle that faces the same arc as a central angle?
The inscribed angle is half the measurement of the central angle.
How do arc angles relate to the amount of the circumference they take?
The bottom value is 30º => 1/12

How do you calculate the area of a sector?
Area of a sector = x/360 *πr2
What is a sequence?
A sequence is a group of numbers (called terms) in a certain order with some sort of relationship between them.
How many sides do pentagons and hexagons have?
Penta = 5
Hexa = 6
What is the equation for the sum of the internal angles of a polygon?
How would you find the internal angle of a regular polygon?
180(n-2)
where n is the number of sides.
An internal angle of a regular polygon is 180(n-2)/n
What is the sum of the external angles of a polygon?
The sum of the external angles of any polygon is 360º.
What is a regular polygon?
A regular polygon is a polygon whos sides are all equal and whose angles are all equal.
Like a traingle, square, regular pentagon, regular hexagon and regular octagon.
What does it mean when a polygon circumscribes a circle?
What about when a polygon is inscribed in a circle?
It means that the circumference of the circle touches all the sides of the polygon (all sides are tangent to the circles circumference).
An inscribed polygon has all its vertices on the circumference of the circle.
What is something we know about the angle of a quadrilateral if it’s inscribed in a circle?
If a quadrilateral is inscribed in a circle, the sum of each two opposite angles is 180º, and also the other way around, if the sum of two opposite angles in a quadrilateral is 180º it can be inscribed in a circle.
Counting Methods: When we have to count the possible combinations between two different groups without any limitations what can we do it to solve it?
You can just multiply the options., e.g. 4 of one group and 5 of another means 20 different combinations.
Counting Methods: How many different ways can 5 people stand in a row?
You multiply the possible people you can choose for the 1st place, then from the remaining people how many you can choose for the 2nd place, etc.
5*4*3*2*1 = 120
Counting Methods: What should we know if order doesn’t matter?
When order doesn’t matter, we divide the number results by k! (where k is the number of possible inner arrangments of any given selection).
What are the two main values you need to remember to divide by when dealing with combination problems where order doesn’t matter?
2 objects: We divide the number of options by 2! which is 2.
3 objects: We divide the number of options by 3! which is 6.
When you’re dealing with probabilities stemming from more than one object, what is a key thing you need to remember?
If there is overlap between the items, don’t count the overlapped possibility twice.
For example if you’re trying to figure out the probability that you get a 1 on the first or second die (or both) you need to mindful of the fact that (1,1) occurs in both sets, and thus you need to remove 1/(6*6) from the basic probability calculation you make.
What is the equation for the surface area of a cylinder?
2πr2 + 2πrh
What is the median?
What is the mode?
The median is the number that is in the middle of a list, half the numbers are larger, half are smaller.
The mode is the value that occurs the most in a list.
How do we calculate the standard deviation for a set of numbers in the GMAT?
- Find the average
- Find the difference between each of the items and the average
- Apply the power of two to each of the differences individually
- Now calculate the average of these differences, you now have the variance.
- The standard deviation is the square root of the variance.
What do ∩ and U mean?
∩ = means the intersection between two sets, so P(A ∩ B) is the equivalent of A and B happening.
U = the set made by combining the elements of two sets.
What are general things you need to be doing when solving Data Sufficiency problems?
Get used to cancelling out answers that are not possible.
Write down the equations when possible. This will help you visualise whether you can solve it using one statment alone, need both or neither are sufficient.
No need to solve the equations, you just need to get to the point where you realise that it can be solved or not.
What’s the difference between Combination and Permutation?
Combinations are used when the order in which the task is done does not matter.
Permutations, in contrast, are used when the order does matter.
If there is m ways to perform task 1 and n ways to perform task 2 and the tasks are independent, how do you calculate the amount of ways both these tasks can be performed together?
You multiply m by n, m*n.
This is only the case if they’re independent.
What should we think of when we see a question that looks at choosing multiple items from multiple groups using the word ‘or’?
That the events are mutually exclusive.
There are x ways to accomplish event A and y ways to accomplish event B, and if A and B are mutually exclusive, then there are x + y ways to accomplish A or B.
Combinations and Permutations: What do you have to do when a question states that some items must be chosen?
What about when some items are not to be chosen?
When some items need to be chosen, you subtract that amount from the objects in the set as well as the potential number of objects to be selected (since these places are already taken).
When some items are not to be chosen, you remove this value from the amount of objects/people in the set but the number of objects that can be selected for combination stays the same.
What is an easier way to solve permutation problems without using the full equation?
The box and fill method
Figure out how many objects can be selected, this forms the number of boxes. Then successively fill the boxes from the number of objects in the set subtracting down one by one.
In other words, each box represents a choice to be made and you multiply the values to get the final number of permutations.
When an object is x times as fast as a second object, how do you relate both rates?
Similarly percentages of another objects rate?
given that the second object has a rate r, the other object would have a rate of x*r.
With percentages the rate would be (x/100)*r.
What is the best way of splitting up the Data Sufficiency answer choices?
A/D and then B/C/E
If A doesn’t work you can automatically cross out D as well.
How many equilaterial triangles fit inside of a regular hexagon?
A regular hexagon can be divided into 6 equilateral triangles.
What happens when a regular polygon is inscribed in a circle?
When a regular polygon is inscribed in a circle, the polygon divides the circle in arcs of equal length.


