General Chemistry Flashcards
What are the properties of Ionic Compounds?
They are usually crystalline solids They have high melting and boiling points They conduct electricity when molten Many of therm are soluble in water
What are the properties of Covalent Compounds?
They have a low melting or boiling point They are poor electrical conductors They are not soluble in water
What effect does an increase in Carbon atoms have on the boiling point of a compound?
More carbon atoms increases the frequency of inter-molecular forces and usually raises the boiling point of a compound
What is the functional group?

Amide
What is the functional group?
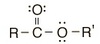
Ester CO2-R
What is the functional group?

Aldehyde
What is the functional group?

Keytone
What is the functional group?

Amine
C=C bonds are most likely to undergo what type of reaction?
An addition reaction.
What is a polar protic solvent? Give an example
A solvent that has H+ protons to give away.
Water
Alcohols
Reactions of an Alkane
Addition to Halokane
Cracking to an Alkene
Reactions of Haloalkane
Substitution
NaOH to make Alcohols
KCN, ethanoic acid to make Nitrile
Conc NH3 heat in sealed tube to make an Amine
Reactions of an Amine

Non Reactive
Reactions of a Nitrile functional group
Reduction - Produces an Amine
Hydrolosis - Produces an Amide or Carboxylic Acid
What are the Reactions of an Amide functional group?

Elimination Reaction to produce a Nitrile
Hydrolisis produces Carboxylic Acid
Reactions of a Carboxylic Acid Group

Reduction to an Alcohol
Substitution to an Acyl Chloride
Elimination to an Acid Anhydride
Addition to an Ester

Reactions of an Ester functional group

Hydrolisis to a Carboxylic acid

Reactions of a Keytone functional group

Reduction to an Alcohol

Reaction of an Ether functional group
Non Reactive
Reactions of an Aldehyde functional group

Oxidation to a Carboxylic Acid
Reduction to an Alcohol
Reactions of an Alcohol Functional Group

Oxidation to form a Keytone or Carboxylic Acid
Elimination to form an Alkene or Ether

What is a Carbocation?
A positively charged Carbon aton.
One that may have lost an electron in a oxidation reaction
Markovnicov’s rule
The carbon that has the most hydrogens is more stable. Reactions favour the less stable bond
When groups are on the same side the molecule is refered to as what?
Cis Isomer
The planar is always along the double bond


