Gastro Flashcards
definition of diarrhoea?
increased stool water
-> increased freq
definition of steatorrhoea?
increased stool fat
-> pale, float, smelly
Causes of bloody diarrhoea?
vascular: ischaemic colitis
infective: campylobacter, shigella, salmonella, e coli, c diff
Inflammatory: UC, crohns
Neoplastic: polyps, colorectal ca
differential for pus w diarrhoea?
IBD
diverticulitis
abscess
differential for mucus w diarrhoea?
IBD
colorectal ca
polyps
diarrhoea due to systemic disease?
hyperthyroid
autonomic neuropathy
carcinoid
diarrhoea assoc w drugs?
Abx
PPI, cimetidine
NSAIDs
digoxin
Ix of Diarrhoea?
Bloods: anaemia, WCC, U+Es
ESR/CRP
coeliac serology: anti-TTG or anti-endomysial Abs
Stool culture: MCS and c diff toxin
Mx of diarrhoea?
tx cause
oral or IV rehydration
codeine phosphate or loperamide after each loose stool
anti emetic if assoc w n+V: e.g. prochlorperazine
abx e.g. cipor in infective diarrhoea -> systemic illness
risk factors for c diff pseudomembranous colitis?
abx use e.g. clindamycin, cephalosporins, augmentin, quinolones
increased age
in hospital: contact, length of stay
PPIs
complications of pseudomembranous colitis?
paralytic ileus
toxic dilatation -> perforation
multi organ failure
features of pseudomembranous colitis?
severe systemic features: fever, dehydration
Abdo pain, bloody diarrhoea, mucus PR
pseudomembranes (yellow plaques) seen on flexi sig
Mx of C diff Pseudomembranous colitis?
General:
stop causative abx
avoid antidiarrhoeals and opiates
1st line: Metronidazole 400mg TDS Po 10-14d
2nd: Vanc 125 mg PO 10-14d
Urgent colectomy may be needed if toxic megacolon, deteriorating condition, raised LDH
Mx of recurrence of C diff pseudomembranous colitis?
repeat course of metro 10-14d
if further relapses -> vanc
Mx if extremely severe C dff colitis?
Vancomycin 1st line PO may add metro IV
What determines severe pseudomembranous colitis?
WCC >15
Cr >50% above baseline
Temp >38.5
Clinical / radiological evidence of severe colitis
1 or more of the following
definition of IBS?
disorders of enhanced visceral perception -> bowel symptoms for which no organic cause can be found
Diagnosis of IBS?
ROME criteria
Abdo discomfort/ pain for ≥12 wks which has 2 of:
- relieved by defecation
- diarrhoea/ constipation
- change in stool form: pellets, mucus
+2 of:
- urgency
- incomplete evacuation
- abdo blating/ distension
- mucous PR
- worsening symptoms after food
Exclusion criteria:
>40yo, bloody stool, anorexia, weight loss, diarrhoea at night
Ix of IBS?
Bloods: FBC, ESR, LFT, coeliac serology, TSH
Colonoscopy: if > 60 yo or any features of organic disease
Mx of IBS?
Exclusion diets can be tried
Bulking agents for constipation and diarrhoea (e.g. fybogel)
antispasmodics for colic/ bloating e.g. mebeverine
Amitriptyline may be helpful
CBT
definition of constipation?
Infrequent Bowel movements (≤ 3/wk) or passing BMs less often than normal or w difficulty, straining or pain.
Causes of constipation?
Mechanical obstruction: adhesions, hernia, cancer, inflamm strictures
non-mechanical: post op ileus
pain: anal fissure
endocrine: hypothyroid, hypoCa/K, uraemia
Neuro: MS, myelopathy, cauda equina
elderly
diet/ dehydration
IBS
toxin: opioids, anti muscarinics
Mx of constipation?
General: drink more, increase dietary fibre
Bulking agents to increase faecal mass -> increase peristalsis
e.g. bran, ispaghula husk (fybogel), methylcellulose
Osmotic agents to retain fluid in bowel
e.g. lactulose
Stimulant: increase intestinal motility and secretion
e.g. senna
Softeners e.g. liquid paraffin
enemas: e.g. phosphate enema (osmotic)
Suppositories: Glycerol (stimulant)
When are bulking agents for constipation contraindicated?
fybogel (Ispaghula husk), bran, methylcellulose
obstruction, faecal impaction
when are stimulant laxatives contraindicated?
Obstruction
acute colitis
e.g. Senna, Bisacodyl, Docusate sodium
Glycerol suppositories
definition of dysphagia?
difficulty swallowing
Inflammatory causes of Dysphagia?
tonsillitis, pharyngitis
Oesophagitis: GORD, candida
Apthous ulcers
Mechanical causes of dysphagia?
Luminal:
large food bolus
Mural:
Benign stricture (plummer vinsoons, oesophagitis, trauma eg. OGD)
Malignant Stricture
Pharyngeal pouch
Extra mural:
Lung Ca, rolling hiatus hernia, mediastinal LNs, retrosternal goitre, thoracic aortic aneurysm
Causes of dysphagia?
inflammatory: inc infection
Mechanical block: luminal, mural, extramural
Motility: local, systemic
Motility disorders causing dysphagia?
local:
achalasia
diffuse oesophageal spasm
nutcracker oesophagus
bulbar/ pseudobulbar palsy (CVA/ MND)
systemic:
systemic sclerosis/ CREST
Myasthenia gravis
dysphagia for liquids and solids at start?
motility disorder
dysphagia for solids first then liquids?
stricture/ expanding mass
intermittent dysphagia for liquids and solids?
oesophageal spasm
dysphagia
neck bulges or gurgles on drinking?
pharyngeal pouch
odonophagia (pain) + dysphagia?
Ca, oesophageal ulcer, spasm
signs of dysphagia?
Cachexia
Anaemia
Virchows node
Neurology
Signs of systemic disease e.g. scleroderma
Ix of Dysphagia?
Bloods: FBC, U+E
CXR
OGD
Barium swallow
oesophageal manometry

Achalasia
birds beak sign on barium swallow
- dilated tapering oesophagus

Diffuse oesophageal spasm
Ba swallow shows corkscrew oesophagus
definition of dyspepsia?
non specific group of symptoms:
epigsatric pain, bloating, heartburn
ALARM symptoms of dyspepsia?
Anaemia
Loss of weight
Anorexia
Recent onset progressive symptoms
Melaena or haematemesis
Swallowing difficulty
Causes of dyspepsia?
Inflammation: GORD, gastritis, Peptic ulcer disease
Ca: oesophageal, gastric
Functional: non-ulcer dyspepsia
initial mx of new onset dyspepsia?
OGD if >55 or ALARMS
try conservative measures for 4 wks:
stop drugs NSAIDs, CCBs (relax LOS)
Lose weight, stop smoking, less alcohol
avoid hot drinks, spicy food
OTC antacids, alginates (gaviscon)
mx of new onset dyspepsia if conservative measures dont work after 4 wks?
Test for H pylori if no improvement: breath or serology
+ve -> eradication therapy
-ve -> PPI trial for 4 wks
consider OGD if no improvement
Mx of proven GORD?
Full dose PPI e.g. omeprazole/ lansoprazole
(inhibits acid secretion) for 1-2 mo
then low dose PPI PRN
Mx of proven peptic ulcer disease?
Full dose PPI e.g. lansoprazole for 1-2mo
H pylori eradication if positive: Omeprazole, clari, amoxicillin
Endoscopy to check for resolution if gastric ulcer
then low dose PPI PRN
What is H Pylori eradication therapy?
note: PPIs and cimetidine -> false -ve C13 breath tests -> stop 2 wks before
7 days tx
PAC 500:
PPI lansoprazole 30mg BD, Amoxicillin 1g BD, Clarithromycin 500mg BD
or
PMC 250:
PPI lansoprazole 30mg BD, Metronidazole 400mg BD, Clarithromycin 250mg BD
95% success, failure due to poor compliance -> add bismuth
what medications may cause False -ve C13 breath and antigen tests for H pylori?
PPI
cimetidine
Differentials for Haematemesis?
Vascular: Oesophageal varices, Angiodysplasia, Dieulafoy lesion (rupture of large arteriole in stomach)
Inflammation: PUD (DU most common cause), oesophago/ gastro/ duodenitis
Trauma: mallory-weiss tear, Boerhaave’s Syndrome, Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu)
General bleeding diasthesis: Warfarin, thrombolytics, liver failure
Differential for Rectal Bleeding?
Vascular: Haemorrhoids, lower GI bleed, ischaemic colitis, HHT (osler weber rendu), angiodysplasia
Diverticulae
Infection: Campylobacter, Shigella, Salmonella, C diff, E col
Inflammation: UC, Crohns
Neoplasia
Polyps
When is jaundice visible?
at 3x Upper normal limit
50 uM
How is Hb converted to unconjugated Br?
by splenic macrophages
How is unconj Br converted to conj Br?
by BR-UDP-glucuronyl transferase in liver
what makes stools dark?
stercobilinogen (brown)
which was converted from urobilinogen
Causes of post hepatic jaundice?
Obstruction:
stones, ca of pancreas
drugs
PBC, PSC
biliary atresia
cholangioca
choledochal cyst
hepatic causes of jaundice?
decreased Br uptake:
drugs- contrast, rifampicin
CCF
decreased Br conjugation:
Gilberts (AD), Hypothyroidism, Crigler-Najjar (AR)
hepatocellular dysfunction:
- congenital: HH, Wilsons, a1ATD
- infection: Hep A/B/C, CMV, EBV
- toxin: alcohol, drugs
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Neoplasia: mets, HCC
- Vasc: budd-chiari
decreased hepatic br excretion:
Dubin-Johnson
Rotors
Hepatic causes of jaundice?
due to hepatocellular dysfunction
- congenital: HH, Wilsons, a1ATD
- infection: Hep A/B/C, CMV, EBV
- toxin: alcohol, drugs
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Neoplasia: mets, HCC
- Vasc: budd-chiari
What causes hepatic jaundice due to decrease br conjugation?
Gilberts (AD), Hypothyroidism, Crigler-Najjar (AR)
causes of pre-hepatic jaundice?
increased Br production
Haemolytic anaemia
ineffective erythropoiesis e.g. thalassaemia
What causes hepatic jaundice due to decreased br uptake?
drugs: contrast, rifampicin
CCF
What is Gilberts syndrome?
auto dom
partial UDP-GT deficiency
jaundice occurs during intercurrent illness
diagnosis of Gilberts?
increased unconj Br on fasting
normal LFTs
What is Crigler Najjar syndrome?
rare auto recessive
total UDP-GT deficiency
cant conjugate Br
- > severe neonatal jaundice and kernicterus
tx: liver transplant
Mx of Crigler Najjar?
liver transplant
Drug induced jaundice
what drug causes haemolysis?
antimalarials e.g. dapsone
drug induced jaundice
what drugs cause hepatitis?
Paracetamol OD
Rifamp, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide
Valproate
Statins
Halothane
drug induced hepatitis
what drugs cause cholestasis?
fluclox
co-amoxiclav
OCP
sulfonylureas
chlorpromazine, prochlorperazine
Ix of Jaundice
Post hepatic obstruction?
Pale stools, dark urine
Urine: high bilirubin, no urobilinogen
LFTs: high conj Br, high ALP (higher than raise in ALT/AST), high GGT
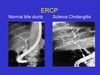
Abdo US: ducts > 6mm, ERCP/ MRCP
Abs: anti-mitochondrial, ANCA, ANA
Ix of jaundice?
hepatic cause
Urine: high Br, high urobilinogen
LFTs: usually high conj Br,
high AST and ALT (if AST VV high -> alcohol, if ALT vv high -> viral)
GGT high
Function: low albumin, prolonged PT
FBC: anaemia
Abs: Anti-SMA, LKM, SLA, ANA
a1AT, ferritin, caeruloplasmin
Liver biopsy
Ix of jaundice?
pre hepatic cause
Urine: no Br, high urobilinogen, high Hb
LFTs: high unconj Br, LDH, AST
FBC and blood film
Coombs test
Hb electrophoresis
Causes of Liver Failure?
Cirrhosis
Acute:
infection- Hep A/B, CMV, EBV, leptospirosis
Toxin- alcohol, paracteamol, isoniazid, halothane
Vasc: budd chiari
Other- wilsons, autoimmune hepatitis
Obs- eclampsia, acute fatty liver of pregnancy
Signs of liver failure?
jaundice
oedema + ascites
bruising
encephalopathy - asterixis
fetor hepaticus
signs of cirrhosis/ chronic liver disease
Ix of Liver Failure?
FBC
U+Es: hepatorenal syndrome
LFTs: low albumin
Clotting: raised INR
Glucose
ABG: metabolic acidosis
Cause: ferritin, a1AT, caeruloplasmin, Abs, paracetamol levels
Hepatitis viral serology
Blood and urine culture
ascites tap for MCS + clinical chemistry
Imaging: CXR, Abdo US + portal vein duplex
what is hepatorenal syndrome?
renal failure in pts w advanced chronic liver failure
diagnosis of exclusion
cirrhosis -> splanchnic arterial vasodilation -> effective circulatory vol -> RAS activation -> renal arterial vasoconstriction
persistent underfilling of renal circ -> failure
Classification of Hepatorenal syndrome?
Type 1: rapidly progressive deterioration (survival <2 wks)
Type 2: steady deterioration (survival 6 mo)
Mx of Hepatorenal syndrome?
IV albumin + splanchnic vasoconstrictors (terlipressin)
Haemodialysis as supportive mx
Liver transplant
Mx of Liver Failure?
Manage in ITU
tx underlying cause
good nutrition - via NGT w high carbs
thiamine supplements
prophylactic PPIs vs stress ulcers
Monitoring in Liver Failure?
Fluids: urinary and central venous catheters
Bloods: daily FBC, U+E, LFT, INR
Glucose: 1-4 hrly + 10% dextrose IV 1L /12h
Complications of liver failure?
Bleeding: Vit K, platelets, FFP, blood
Sepsis: tazocin
Ascites: fluid+salt restrict, spiro, fruse, tap, daily weight
Hypoglycaemia: regular BMs, IV glucose if <2 mM
Encephalopathy: avoid sedatives, lactulose
Seizures: lorazepam
Cerebral oedema: mannitol
prescribing in liver failure?
what to avoid
avoid: opiates, oral hypoglycaemics, Na-containing IVI
warfarin effects increase
hepatotoxic drugs: paracetamol, methotrexate, isoniazid, salicylates, tetracycline
Poor prognostic factors in liver failure?
grade 3/4 hepatic encephalopathy
age >40
albumin<30g/L
raised INR
drug induced liver failure
Criteria for Liver Transplant in Paracetamol induced liver failure?
pH< 7.3 24h after ingestion
or all of:
PT>100s
Cr >300
Grade 3/4 encephalopathy
Kings College Hospital Criteria for liver transplant in non-paracetamol induced liver failure?
PT> 100s
or 3 out of 5 of:
- drug induced
- age <10 or >40
- >1 wk from jaundice to encephalopathy
PT> 50s
BR>300
causes of cirrhosis?
Common:
chronic Alcohol
chronic Hep C and hep B
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/ NASH
Other:
genetic: wilsons, a1ATD, HH, CF
AI: AIH, PBC, PSC
Drugs: methotrexate, amiodarone
neoplasm: HCC, mets
Vasc: budd chiari, RHF, constrictive pericarditis
signs of cirrhosis in hands?
clubbing
leuconychia (hypoalbumin)
Terry’s nails (white proximally, red distally)
Palmar erythema
Dupuytrens contracture
Signs of cirrhosis in the face?
Pallor: ACD
Xanthelasma: PBC
Parotid enlargement: alcohol excess
signs of cirrhosis in the trunk?
spider naevi (>5, fill from the centre)
gynaecomastia
loss of secondary sexual hair
signs of cirrhosis in the abdomen?
striae
hepatomegaly (may be small in late disease)
splenomegaly (portal HTN)
dilated superficial veins (caput medusae)
testicular atrophy
signs of chronic liver disease?
palmar erythema
dupuytrens contracture
gynaecomastia
spider naevi
clubbing
signs of decompensation -> liver failure?
jaundice
encephalopathy: asterixis
hypoalbuminaemia -> oedema + ascites
coagulopathy -> bruising
signs of portal HTN?
splenomegaly
ascites
varices: oesophageal varices, caput medusa
complications of cirrhosis?
decompensation -> liver failure
(jaundice, encephalopathy, oedema, bruising)
Portal HTN: splenomegaly, ascites, varices
spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
increased risk of HCC
Ix of cirrhosis?
Bloods:
FBC: low WCC, low Pl indicate hypersplenism
LFTs
Prolonged INR
low Albumin
find cause:
alcohol: high MCV, GGT
NASH: hyperlipidaemia, high glucose
infection: hepatitis, EBV, CMV serology
Genetic: ferritin, a1AT, caeruloplasmin (low in wilsons)
Autoimmune: Abs
Ca: alpha-fetoprotein
Abdo US + Portal Vein Duplex
Ascitic Tap + MCS
Liver Biopsy
what tumour marker is assoc w HCC?
Alpha fetoprotein
what may you see on abdo US + portal vein duplex in cirrhosis?
small/ large liver
focal lesions
reversed portal vein flow
ascites
Ascitic tap + MCS in cirrhosis?
PMN > 250 mm3 indicated SBP
general mx of cirrhosis?
good nutrition
alcohol abstinence: baclofen can help reduce cravings
colestyramine for pruritus
screening for HCC: US and AFP & oesophageal varices: endoscopy
tx of wilsons?
penicillamine
tx of PBC?
ursodeoxycholic acid
tx of Hep C virus -> Cirrhosis?
IFNa
Monitoring for varices in cirrhosis?
OGD screening + banding
Monitoring for HCC in cirrhosis?
US + AFP every 3-6 mo
Mx of ascites in cirrhosis?
fluid and salt restrict
spironolactone
frusemide
ascitic tap
daily weights
Mx of coagulopathy in cirrhosis?
Vit K
platelets
FFP
blood
Mx of encephalopathy in cirrhosis?
avoid sedatives, lactulose+/- enemas, rifaximin
Mx of hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis?
IV albumin + terlipressin
Mx of Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis?
Tazocin
What is Child-Pugh Grading of cirrhosis?
predicts risk of bleeding, mortality and need for tx
Graded A-C using severity of 5 factors
Albumin
Bilirubin
Clotting
Distension: ascites
Encephalopathy
Score >8 = significant risk of variceal banding
Causes of Portal HTN?
Pre-hepatic:
portal vein thrombosis e.g. pancreatitis
Hepatic:
cirrhosis (most common), schisto (most common worldwide), sarcoidosis
Post Hepatic: Budd Chiari, constrictive pericarditis, congestive HF -> congestive splenomegaly
Where are the likely locations for porto-systemic anastamoses?
Oesophageal varices:
left and short gastric veins + inf oesophageal veins
Caput Medusae:
Peri umbilical veins + superficial abdo wall veins
rectal (haemorrhoids):
Superior rectal veins + inf and mid rectal veins
difference between caput medusae and prominent abdo veins?
blood flow down below the umbilicus: portal HTN
blood flows up below the umbilicus: IVC obstruction

Caput Medusae
pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy?
decreased hepatic metabolic function -> diversion of toxins from liver directly into systemic system
ammonia accumulates and pass to brain where astrocytes clear it causing glutamate -> glutamine
high glutamine -> osmotic imbalance -> cerebral oedema
classification of hepatic encephalopathy?
- Confused - irritable, mild confusion, sleep inversion
- Drowsy - disoriented, slurred speech, asterixis
- Stupor - rousable, incoherent
- Coma - unrousable, upgoing plantars
presentation of hepatic encephalopathy?
Asterixis, ataxia
confusion
dysarthria
constructional apraxia
seizures

precipitants of hepatic encephalopathy?
Haemorrhage: varices
Electrolytes: low K/Na
Poisons: diuretics, sedatives, anaesthetics
Alcohol
Tumour: HCC
Infection: SBP, pneumonia, UTI
Constipation (commonest cause)
Sugar (glucose) e.g. low calorie diet
Ix of hepatic encephalopathy?
raised plasma NH4
Mx of hepatic encephalopathy?
Nurse 20o head up
correct any precipitants
avoid sedatives
Lactulose +/- PO4 enemas to decrease Nitrogen-forming bowel bacteria
Consider rifaximin PO to kill intestinal microflora
pathophysiology of ascites?
back pressure -> fluid exudation
decrease in effective circulating vol -> RAS activation
In cirrhosis: low albumin -> low plasma oncotic pressure
all lead to fluid within abdominal space
symptoms of ascites?
distension -> abdo discomfort and nausea
dyspnoea
decreased venous return