forces Flashcards
(62 cards)
When forces are applied to materials, the…. can change
the size and shape
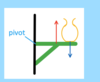
draw apparatum hook’s law
and describe experiment
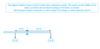
Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram.
A single mass (0.1 kg, 100g) is attached to the spring, with a pointer attached to the bottom, and the position of the spring is measured against the ruler.
The mass (in kg) and position (in cm) are recorded in a table.
A further mass is added and the new position measured.
The above process continues until a total of 7 masses have been added.
The masses are then removed and the entire process repeated again, until it has been carried out a total of 3 times, and averages can then be taken.
Once measurements have been taken:
The force on the spring can be found by multiplying the mass on the spring (in kg) by 10 N/kg (the gravitational field strength).
The extension of the spring can be found by subtracting the original position of the spring from each of the subsequent positions.
Finally, a graph of extension (on the y-axis) against force (on the x-axis) should be plotted.

A graph of extension against force for a metal spring



Hooke’s law states that:
The extension of a spring is proportional to the applied force.
force hooke’s law equation

Hooke’s law is associated with the … of a force-extension graph.
initial linear (straight)
Objects that obey Hooke’s law will
return to their original length after being stretched.
If an object continues to be stretched it can be taken past the
at this point will no longer
limit of proportionality (sometimes called the elastic limit).
At this point the object will no longer obey Hooke’s law and will not return to its original length.


A relationship is said to be proportional if the graph is a
straight line going through the origin.
the relationship is linear if
a graph is a straight line but does not go through the origin
forces can
change the spped of an object
change the direction of movement of an object
change the shape of an object
change the size of an object
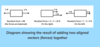
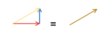
When several forces act on a body, the resultant (overall) force on the body can be found by
adding together forces which act in the same direction and subtracting forces which act in opposite directions:


When the forces acting on a body are balanced (i.e. there is no resultant force), the body will
ither remain at rest or continue to move in a straight line at a constant speed.


Friction is
a force that opposes the motion of an object caused by the contact (rubbing) of two surfaces. It always acts in the opposite direction to the direction in which the object is moving.
Air resistance (sometimes called drag) is a form of friction caused by
Friction (including air resistance) results in
a body moving through the air.
energy loss due to the transfer of energy from kinetic to internal (heat).
The resultant force is sometimes also known as the
net force or the unbalanced force.
Force, mass and acceleration are related by the following equation:
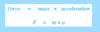
The greater the force, the the acceleration (for a given mass).
For a given force, the smaller the mass the the acceleration.
greater
greater


If you are trying to find the acceleration, check that you know both the
unbalanced (resultant) force and the mass of the object.
If you don’t, you might need to calculate the acceleration using a different equation.