Fissures Flashcards
(24 cards)
Name this Fissure and what it seperates

Longitudinal Fissure
—divides the cerebral hemisphers from one another,
creates a left and right side
Name this fissure and what it seperates

Transverse Fissure
—Divides the cerebral hemisphers from the cerebellum
Name this sulcus and what it seperates
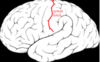
Central Sulcus
—Divides each cerebral hemispher into a front and back
***runs opposite of longitudinal fissure
What does the central sulcus divide? (3)
Divides:
- ) Frontal Lobe from Parietal Lobe
- ) Pre-Central Gyrus from Post-Central Gyrus
- ) Primary motor corticies from primary sensory cortices

Name this sulcus and what it seperates?

Lateral Sulcus
—Divides the Temporal Lobe from the Frontal & Parietal Lobe
Identify this region
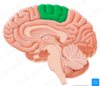
Paracentral Lobule
Identify the sulcus and what it divides

Parieto occipital sulcus
—Divides Parietal and Occiptal lobe
Identify the landmark “C” and explain its roll

Pre-occiptial Notch
—If an imaginary line is drawn from the Parieto-Occiptal sulcus to the Pre-Occiptial notch then the occiptal lobe can be seperated/distinguished from the parietal and temporal lobes
Identify the following Sulcus and what it seperates

Calcarine Sulcus/Fissure
—Located on the medial surface of the occiptial lobe
- Divides the visual cortex into two
- Seperates Cuneus and Lingual Gyrus

Identify the Sulcus

Cingulate Sulcus
—Midline Sulcus
Identify the area

Corpus Callosum
—Large bundle of neural fibers that connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres
—Facilitates interhemispheric communication
What is the Fornix and it’s purpose/location?
An arching, fibrous band of nerve fibers
It extends from the hippocampus to the mamillary body of the hypothalamus and forms an arch over the thalamus.
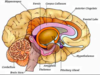
Anterior Commissure
—Connects the two temporal lobes of the cerebral hemisphers across the midline

What/where is the Lamina Terminalis
A thin plate that passes upward from the optic chiasm to form the frontmost (rostral) wall of the third ventricle

What is the Interventricular Foramen aka Foramen of Monro?
A structure that connects the paired lateral ventricles with the third ventricle at the midline of the brain.
—Allows for CSF to reach the third ventricle

The Thalmus is affiliated with what Cranial Nerve?
CN II
Name this area and it’s function

Thalmus
—Part of the diacephalon
—Surrounds the 3rd ventricle
–Main function is to relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral cortex, it also regulates sleep, alertness and wakefulness
What is the function of the Hypothalamus?
—Section of the brain responsible for hormone production.
***hormones produced by this area govern body temperature, thirst, hunger, sleep, circadian rhythm, moods, sex drive, and the release of other hormones in the body
Where is the Hypothalamus located?
—Below the thalamus and right above the brain stem
—Forms the anterior part of the diencephalon

Midbrain or mesencephalon is affiliated with what Cranial Nerve?
CN III, IV
Where is the midbrain located and what is it’s function?
—-the most rostral part of the brainstem and sits above the pons and is adjoined rostrally to the thalamus
-Functions include the eye, auditory, and visual processing

The pons are affiliated with what Cranial Nerves?
CN V, VI, VII
The medulla is affiliated with what Cranial Nerves?
CN VIII, IX, X, XI, XII


