Final - Spring Flashcards
capitulum –>
radial head
true joint of the elbow
humeroulnar joint
what ligament stab the radial head
radial anular lig
ROM of elbow and what it is limited by
flex: 145 - lim by muscles
ext: 5-10 - lim by olecranon fossa and tension of anterior lig
main m of elbow flexion
brachialis
main M of elbow extension
triceps
and anconeus
carrying angle
>15: cubitus valgus –>
- ULNAR deviation of wrist
<5: cubitus varus: aka gunstock deformity
supinators
biceps
supinator
pronators
pronator quad
pronator teres
pronation and supination: coupled motion
pronation: radial head –> posterior
* b/w distal radius crosses over ulna
supinator: radial head –> anterior

the prox ulna has accessory motions of ____ with supination and _____ with pronation
adduction
abduction
interosseous membrane
- tightens with supination
- transmits E from wrist to elbow to decrease strain
nursemaids elbow
sublux of radial head –> flex and pronated
- tears anular ligament
tx:
- traction
- supination
- flex elbow to 90
ulnar n compression
by FCU: arcuate ligament
- weakness of 4 and 5
- claw of 4 and 5
- hypothenar atrophy
radial n compression
supinator –> pain @ lateral epicondyle
- WORSE with pronation
median n compression
- struthers
- pronator teres: can pass b/w 2 heads of pronator
- FDS
- carpal tunnel
lateral epicondylosis
degen and tearing of extensor tendons
- not inflammation so not -itis
MOA:
- neuro-M dysfx
- inability of antag M to relax with contraction of agonist
- results of breakdown of tendon as it attaches to periosteum
- lower c-spine dysfx
tx:
- ME
- traction of c-spine
- corticosteroid injection
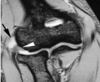
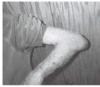
olecranon bursitis: P leaning on elbow
- gout
- RA
medial adduction of the ulna–>
wrist ABduction –> superior radius –> lateral olecranon
- decreased carrying angle
falling forward on outstretched hand
hand in pronation –> anterior distal radius –> ANTERIOR “disloc” of hand
- results in radial HEAD to be POSTERIOR
- b/c pronation –> posterior SD
falling backwards on “backwards” hand
hand is SUPINATED –> posterior distal radius –> ANTERIOR slide of radial head
true wrist joint =
radiocarpal
fx joints of wrist
radiocarpal: F, E, ulnar and radial deviation
midcarpal: sliding b/w bones, radial deviation
ulnomeniscotriquetral: pesudojoint - ulnar deviation
wrist range of motion
F: 80
E: 70
Ab: 20
Ad: 30
accessory motions of slide, rotation, traction are GREATEST @
radioscaphoid
radiolunate
muscles acting on wrist
FCU: flex, adduct
FCR, palmaris longus: flex, abduct
ECU: extend, adduct
ECRL/B: extend, abduct